EOQ
Refers to the optimal level of inventory to be ordered that minimizes the overall costs related to the inventory orders.
What Is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)?
EOQ, or Economic Order Quantity, refers to the optimal level of inventory to be ordered that minimizes the overall costs related to the inventory orders.
The businesses whose primary activities revolve around buying and selling inventory/merchandise are primarily concerned with understanding the amounts of goods needed to be ordered.
Along with ordering the right amount of inventory, it's also essential to collect the quantity of stock that best fits the economic and financial needs of the organization.
Let us suppose that if the organization's orders are too large, this could mean a lot of resources are stuck in the inventory. And the firm isn't paid back until the merchandise is completely sold out.
Along with the unsold inventory, there are multiple tied costs such as acquisition costs, storage costs, warehouse expenses, and cost of unsold inventory.
On the contrary, if the organization purchases little inventory. It might have a problem filling customer orders and satisfying their needs.
It is where the Economic Order Quantity comes in. EOQ, helps you find the optimal level that keeps the business running smoothly and efficiently. It enables you to find an ideal order quantity and maximizes profitability and potential cash flows.
Economic order quantity calculates
- The ideal size of the order
- Facilitates meeting demand without overspending.
- Cut holding costs
- Excess inventory
The EOQ helps an organization with the proper quantity taking into account the different factors affecting the ordering decisions.
The factors affecting the EOQ are:
- Annual Quantity Demanded
- Volume per Order
- Ordering Cost (Fixed Cost)
- Unit Cost (Variable Cost)
- Holding Cost (Variable Cost)
- Carrying Cost (Interest Rate)
You might sell electronic appliances, furniture, cars, bikes, and bicycles. The quantity pointed out by EOQ is supposedly beneficial to the organization.
With this metric and indicator at its disposal, an organization can reap benefits from what the calculations and interpretations suggest.
Key Takeaways
- EOQ stands for Economic Order Quantity.
- It’s most beneficial for the organization whose primary business activities revolve around buying and selling merchandise.
- It helps the firm to understand and identify an optimal level of quantity of inventory.
- Primary benefits include optimization of cash flows. It aids in lowering the investments made in an inventory purchase since cash is held in a buffer between the process of selling goods and its collection of money.
- Help improve customer experience by always having inventory and returning the customer without any sale.
- It is excessively dependent on assumptions.
- It Doesn’t account for real-world factors such as the demand & taste of customers along with the changing trends.
- It is as accurate as the provided financial data.
- Helpful for organizations with a simple and stable inventory.
- It is challenging to take into account the changing economic and financial trends.
Formula For Calculating Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
It’s the critical metric that aids businesses in managing acquisitions, holding inventory, and understanding the costs related to acquiring and maintaining merchandise.
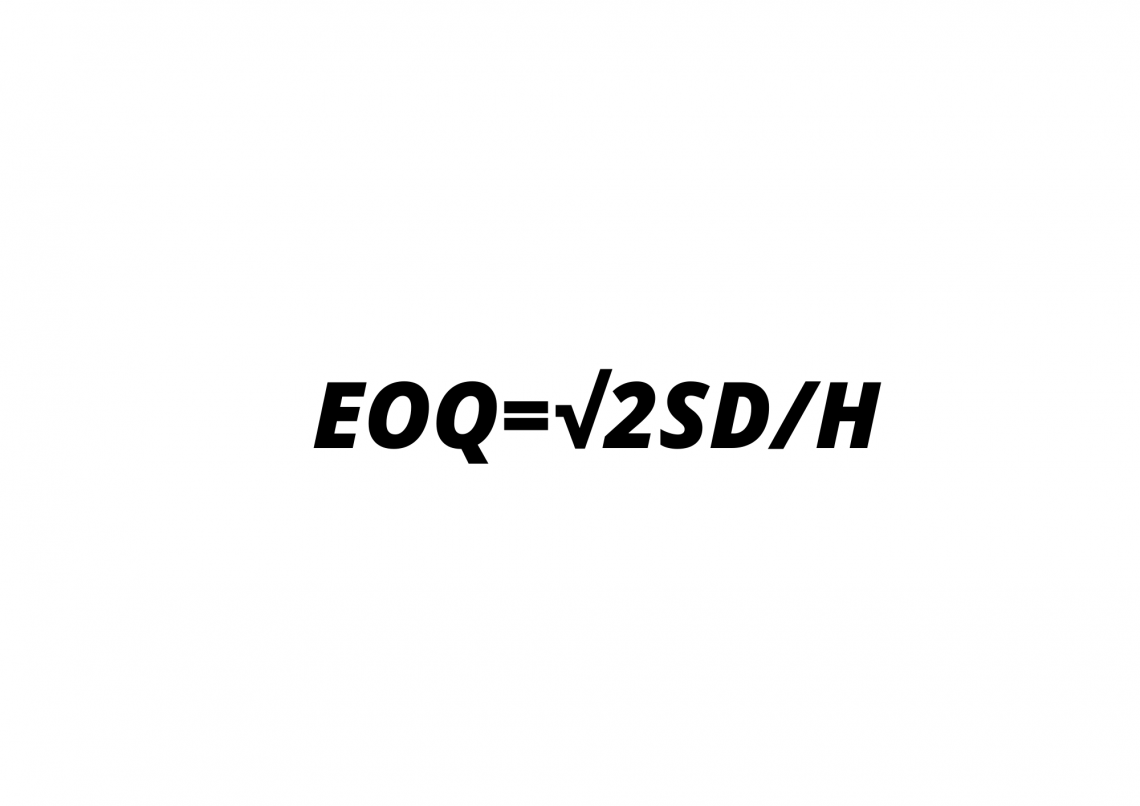
It provides a detailed view of all the costs related to an order. Thus, providing the business owners a perspective on the ideal levels of hierarchy.
Starting with the first component in the formula -
S = Ordering Cost
The ordering cost calculation starts with determining the number of orders that can occur in the period. The number of orders can be calculated by dividing the annual quantity demanded(D) by the volume per order(Q).
Number of orders = D/S
Where,
D = Annual Quantity Demanded
The annual ordering cost is a fixed cost independent of the units ordered or produced.
The annual ordering cost(S) = number of units x fixed cost
Which can also be expressed as:
Ordering Cost = D/Q x S
Next in line is the explanation of Holding Costs(H), which is the Cost of holding or storing the inventory. It also includes the opportunity cost of investing the money elsewhere.
Inventory is considered a direct cost since it includes the funds for financing the storage. It assumes that the demand is constant over a given period.
Annual holding costs are calculated by averaging the yearly quantity demand(Q) and multiplying it with the holding costs(H).
Annual Holding Cost = Q/2 x H
H = i x C
Where,
- H = The holding cost.
- i = Carrying cost
- C = Unit costs, which is a variable cost.
Uses of the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The economic order quantity model is valuable, especially in supply chain management. It helps in logistics and operations to calculate the frequency and number of orders.
The optimal order quantity is necessary to meet the customer's needs and demands. Therefore, the primary benefit of using this model is that it considers every possible factor.
Starting from order cost, carrying cost, storage cost, and other factors.
- The formula helps a great deal in supply chain management. It helps in minimizing costs. It's not only used to cut costs but also to optimize cash flows.
- Bring the inventory costs, inventory levels, and inventory management to optimal levels.
- By perfecting the flow of costs to the right areas, the funds can be allocated to the prioritized areas.
- Helps to reduce the opportunity costs of the organization. Because the organization can direct the resources where it's in need the most, deploying these methods will reduce the diversion of funds to more productive regions.
- An important factor in developing the inventory reorder point is the formula. The algorithm can be set to trigger reordering and replenishment points.
- Helping to avoid stockouts. A company would have the optimal quantity of stock on hand to meet customer demand.
- The calculation can be used to find a good balance of order size and number of orders, considering any available quantity discounts.
The formula can be adjusted depending on production costs, size lot, setup costs, and lead time. Some companies use a fixed cost approach, and some use the variable cost model in their formula to account for these changes.
The retailer can bring these costs to optimal levels. It finds the right balance of when to place orders and at what price to lower the holding cost and other expenses.
Importance & Benefits Of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Every metric and method that the organization uses will have its importance, merits, and benefits. The benefits will depend upon the management and costing techniques used.
1. EOQ can help an organization understand the optimal level of ordering. They are promoting sustainability and stability. These resources tied up in inventory could be invested elsewhere.
Marketing, research, or even financing other operations can prove more profitable to the organization.
2. Inventory is a part of current assets. Cash stuck in the inventory means money tied in working capital. Working capital is the funds that facilitate the smooth functioning of a regular firm's activities.
Excessive funds stuck in working capital can erode profits.
3. Besides optimizing inventory and cash flows, the economic order quantity can also help the firm prevent reordering the stock.
4. Since there is limited inventory at hand and optimal resources are expended in acquiring merchandise, we can say that it also promotes less wastage of resources.
5. A firm can have a storage facility of 1000 Sq yards. But, according to the inventory size, the need for 400 Sq yards of the warehouse would be enough.
It is not just about the size of the warehouse. It is also about the cash expended to store the inventory. And the carrying costs on each piece of merchandise.
6. This metric can also help improve customer experience with the firm since EOQ will ensure that the product or inventory is always there and prevent stock from going ultimately zero.
Carefully timing and placing the orders can also help the firm fetch ordering discounts.
Limitations & Challenges of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Every metric used by organizations will always have its utilities and limitations. The utilities mentioned above can be reaped when the organization is in a particular position. Limitations could arise from the inherent limitations of the metric itself or the environment the organization is in.
1. Excessive dependence upon the assumptions to manage the inventory. The assumption includes:
- Constant consumer demand
- Ordering and holding costs being held constant
2. EOQ fails to account for:
- Ever-changing demand of consumers
- Fluctuations in inventory costs
- The opportunity cost of lost sales due to inventory shortages
3. The result of EOQ is as accurate as the data provided. Therefore, the metric is heavily dependent upon the quality of furnished data.
4. This method is most suitable for organizations with stable inventory levels. However, if the firm that uses this method happens to be a growing company can end up under-ordering, hampering business growth.
5. Using the assumptions, it's complicated to account for seasonal changes and trends.
Example Of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Illustration: this is the basic calculation where every component is given. Then, the analysis is quite simple. The ingredients are substituted for shared, respected values, and the end product is the answer.
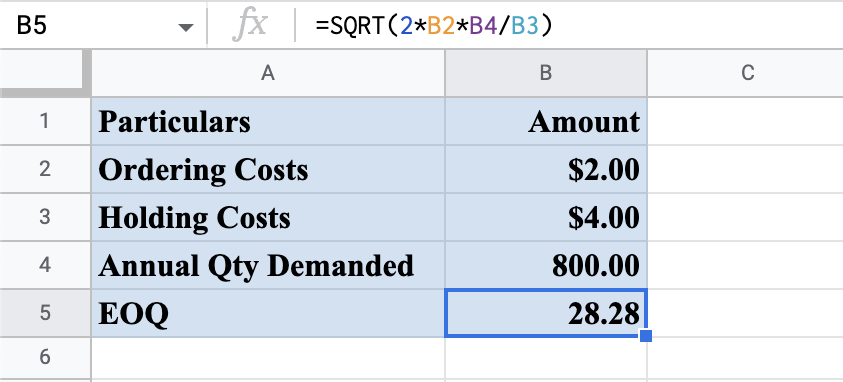
If a person wants to know the number of orders per year, they should divide the annual quantity by EOQ. In this scenario, it would be:
= 800/28.28 = 28.3
To know the annual ordering costs, the person can multiply the ordering cost by the number of orders per year.
= $2 x 28.3 = $56.6
If the person wishes to know the annual holding costs, they may average the units and multiply them by the holding costs.
= 28.28/2 x 4 = $56.56
Researched and authored by Farooq Azam Khan, CMA | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:




or Want to Sign up with your social account?