Strategic Management
An organization's long-term goals and objectives to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage in the marketplace
What Is Strategic Management?
Strategic management involves planning, executing, and assessing an organization's goals and actions to achieve competitive advantage, long-term success, and alignment with its mission and environment.
It refers to an organization's long-term goals and objectives to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage in the marketplace. It provides an organization with a clear direction for conducting its operations and pursuing success.
A strategy can be modified to suit the external environment of an organization's place of conduct. It is an important component because it is not foreseen and, therefore, organizations must adapt to the business environment where changes are unprecedented.
Strategy is focused on long-term processes rather than immediate and short-term operations. It deals with employees predicting employee behavior as it is a properly defined roadmap of a company.
A strategy defines the company's growth by capitalizing on its strengths and minimizing its weaknesses. It narrows the gap between "where we are" and "where we want to be."
When identifying a company's resources and capabilities, a firm can deploy strategies to achieve sustainable competitive advantage and obtain customer loyalty where consumers purchase its goods and services instead of the organization.
It is focused on identifying the strategies managers use to enhance competitive performance and maximize profitability within the industry. It involves managers making critical decisions that impact the firm's overall choices.
A manager needs to have detailed knowledge of the organizational environment to make the correct decisions for the company's betterment. It involves preparation for contingencies in advance.
It deals with developing and formulating the right strategies as they create a competitive advantage and determine the company's direction.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic management involves planning, executing, and assessing an organization's goals to achieve competitive advantage, long-term success, and alignment with its mission and environment.
- It focuses on long-term processes, providing a clear direction for operations and predicting employee behavior.
- Strategic management continuously evolves with external influences, evaluating competitive forces and setting goals to overtake competitors.
- There are three types of Strategic Management Strategies - Corporate strategy, Business-level strategy and Functional-level strategy
- It promotes a strong focus on organizational objectives, fostering collaboration, integration, and adaptability in a changing environment.
Understanding Strategic Management
Strategic management (SM) continuously evolves as the external environment influences change according to trends. It evaluates competitive forces, sets goals to overtake competitors, and re-evaluates strategies.
Employees of an organization develop a better understanding of how their role aligns with the organizational objectives and how it is related to organizational bodies. They develop a stronger sense of trust, commitment, satisfaction, and belonging as a deeper commitment to the organizational goal is cultivated.
The key role of this strategic process is to combine several functional areas of the company and synchronize harmony while monitoring the organization's objectives constantly. To sustain a clear organizational direction, a vision and mission must be developed in alignment with the organization's long-term goals.
Creating a strategy includes large amounts of risk and assessment of resources, methods of countering those risks, and effective optimization of resources alongside trying to achieve an essential purpose. A company is often developed with a set of objectives that define the reason for its existence.
All the activities and duties carried out by the company are highlighted and focused around this specific significant goal that must align the internal resources against the external environment where the objective is obtained in a reasonable timeframe.
Without a doubt, as an organization is a large establishment with, ideally, a substantial underlying investment, developing a strategy is expected to be a key variable for successful operation internally to get safe returns on the money used for investments.
SM analyzed at a corporate level usually combines planning and preparing for long-term risks, market opportunities, and market trends. This creates a smooth path for the organization to examine, analyze, and execute strategies in a way that will ideally help achieve the destined goals.
The components of a strategy are defined as below:
- The plan should have a set of long-term goals stated clearly.
- The scope of the firm should be limited.
- A clear state of competitive advantage's aim of achievement.
- Representation of internal contests in an environment of competition.
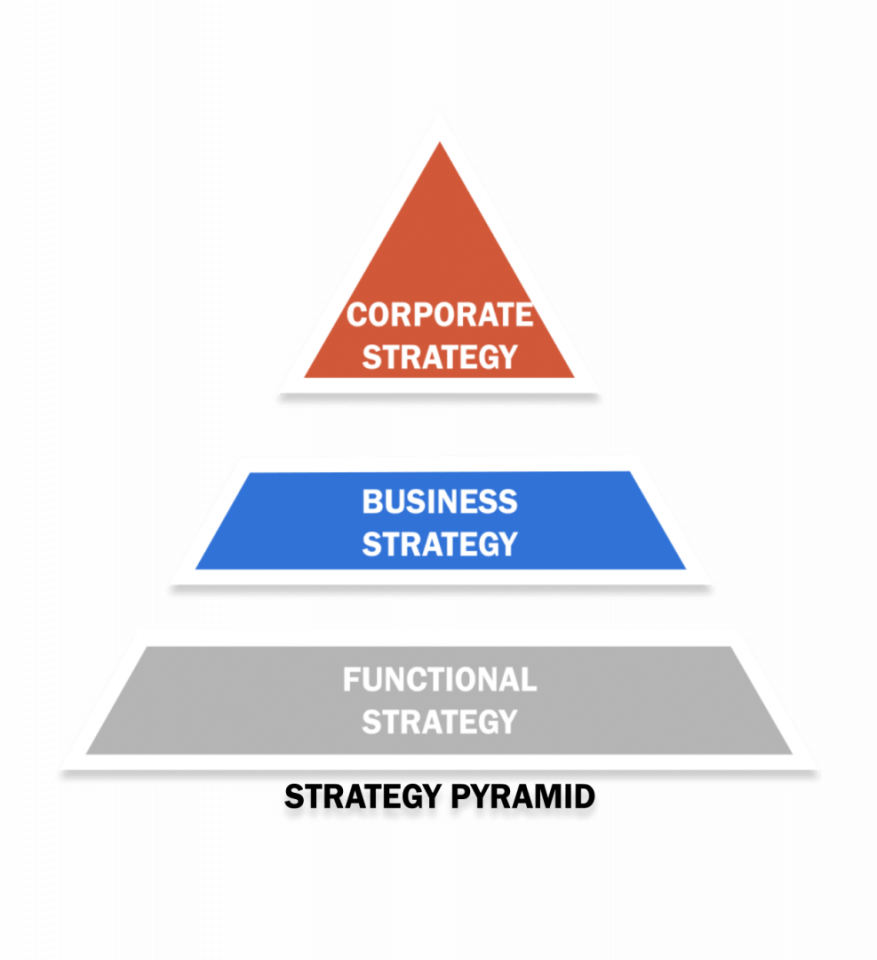
Types of strategic management strategies
There are three levels of strategy. The first strategy is a corporate strategy. Corporate strategy is at the top of the pyramid, and it is a broad level of business strategy.
It is used to define a company's primary purpose and has a direct impact on organizational decision-making. As a result, strategies are formulated around organizational policies that are either value-oriented or conceptual at the corporate level.
A corporate-level strategy is necessary for companies with several product lines.
They are less solidified than either functional or Small Business Unit level strategies. Corporate-level strategies have higher risks, costs, flexibility, and profitability potential. They are innovative, long-term-oriented, and extensive.
The highest decision-making level is done under corporate-level strategies, where examples of corporate-level methods are diversification and acquisition decisions.
The board of Directors and chief executive officers carry authority in corporate-level strategy decision-making.
The following strategy is the business unit level strategy, located in the middle of the strategy pyramid. It can be used for multiple departments, divisions, or products, and its complexity depends on the number of business operations and company structure.
This enables coordination across each business unit to identify strengths and weaknesses. Business-level strategies are created by every SBU to capitalize on the resources it is given based on its environment.
Business-level strategies are detailed plans that provide objectives for SBUs, allocate resources across various functional areas, and coordinate activities between them for achieving corporate-level goals.
SBU managers are involved in business-level strategies related to a unit in the organization. It functions within the scope of operations defined by the strategy but is limited based on the allocation of resources at the corporate level.
A business-level strategy evaluates the how of a strategy rather than the 'what.'
The functional level strategy is at the bottom of the pyramid and is the last strategy used. Each department involves daily operations to supplement corporate activities.
Functional strategies are developed by the head of departments, whereas business unit strategies focus on evaluation from leadership.
A functional level strategy is based on a functional operation and the activities that are involved in it.
The functional level is part of the operational aspect of the company.
Depending on how various organizational functions contribute to the overall strategy, tactical decisions are made in functional-level strategies.
A restricted plan provides objectives for function, resource allocation, and the coordination between both to achieve business and corporate-level strategies.
Benefits of strategic management
There are several benefits of SM. The first benefit is that it allocates resources based on identifying, prioritizing, and exploiting opportunities and allows critical decisions to have improved support for established aims.
An effective time and resource distribution helps identify opportunities efficiently to minimize wastage of time.
Moreover, with proper allocation of resources, a strategic vision clarity can be achieved due to the importance of having clear organizational goals, which provide the company with a direction and a high level of discipline to achieve its objectives.
Another advantage is that there is a strong focus on the desired objectives of the organization. This promotes a harmonious synchronization between the company members since a positive attitude is encouraged towards change.
Personnel at the company collaborate enthusiastically and cooperatively and are better integrated to achieve company goals.
A strong focus on the organization's objects also establishes a sense of belonging for employees, leading to higher levels of satisfaction, dedication, loyalty, and commitment to the organization and its objectives.
SM allows for adaptability in a rapidly changing environment since resources are allocated based on the external environment.
Therefore, as resources are matched according to the pace of environmental changes, a business can adjust quickly to cater to its target market and achieve profitability, sustaining long-term growth and thus obtaining a sustainable competitive advantage.
The 5 Phases of Strategic Management
The process has four key steps: environmental scanning, strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation.
1. Environmental Scanning
Environmental scanning refers to gathering, analyzing, and providing information for strategic reasons. It supplements analyzing the internal and external factors that impact an organization.
After the environmental analysis process is executed, the company's management must regularly evaluate the internal and external factors and strive to improve its operations to create continuous long-term growth.
2. Strategy Formulation
Strategy formulation determines the next best steps for accomplishing and achieving organizational objectives and, therefore, achieving organizational purpose.
After conducting environmental scanning and screening, managers formulate and develop corporate, business, and functional-level strategies, as discussed above.
3. Strategy Implementation
Strategy implementation focuses on making the strategy selected work as planned or putting the organization's strategy chosen into launch.
Strategy implementation involves:
- Creating the organization's structure.
- Allocating resources.
- Developing a process of sound decision-making.
- Managing human resource tools.
4. Strategy Evaluation
Strategy evaluation is the last stage of the strategy management process.
Evaluating internal and external factors involves a few critical stages. These include selecting the ground framework for current strategies, measuring organizational performance, and taking corrective actions to achieve the best results for the organization.
Evaluation ensures that the organizational strategy and implementation of the selected strategies meet the corporate aims.
The stages of the strategic management process are the steps that operate in chronological order when developing a new strategic management plan.
Contemporary organizations that have already designed a strategic management plan will convert to these steps according to the situation's requirement to make the necessary changes.
Strategic management is a constant process. The steps are organized in a cohesive manner where each component is interdependent and interlinked with the next stage to design a complete strategic process.
Value of organizational culture
There is a direct correlation between corporate culture and strategic management. This is because company management and strategic decisions are developed based on the same values, beliefs, and principles implemented across the organizational culture.
Strategy creates direction and focus and generates a unique environment for the company's employees to comprehend the organization's goals.
Organizational culture helps achieve those organizational goals by embedding them in the organization's cohesive values and beliefs shared by members interconnectedly.
A strategy within an organization can only be implemented when it is supported by the corporate culture.
Corporate culture affects how a leader expresses their company vision to other employees and members of the organization and how they gain support for implementing and designing new corporate, functional, and business-level strategies.
The strategy provides a clear direction for an organization's activities, and culture generates the shared process for reaching the destination, which can either be positive or negative.
To obtain consistency in organizational behavior, it is critical to create a disciplinary environment with rules and regulations that carry an ethical framework used when making corporate decisions that impact the organization and act as guidance regardless of the nature of the decision.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, strategic management has been defined as a continuous organizational goal-setting process that contributes to its long-term growth to achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
The various benefits of strategic management that can be achieved are a strong focus on key objectives, direction, clarity of vision, and adaptability to a rapidly changing external environment.
Strategies within an organization are categorized into three different sections:
- Corporate strategy at the top
- Business-level strategy in the middle
- Functional strategy at the bottom
The stages of the SM process include environmental screening, strategy formulation, strategy implementation, and strategy evaluation.
Lastly, there is a direct correlation between strategy and culture, as culture sets the tone for a successful strategy that enables a company to achieve a competitive advantage and maximize its profitability, market share, sales, and revenue.
It is critical for every organization that aims to be a market leader in developing a successful, strong, and thorough strategic management process that adds value to the organizational goals and leads to sustainable competitive advantage.
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:

or Want to Sign up with your social account?