Calendarization
It helps to spread the recognition of a company's expenses over more than one period.
Comparing two companies' financial data reports during the same period is important. This ensures consistency for the data. However, comparing company reports for different periods may produce meaningless interpretations.

Many companies have their financial year, starting and ending on different dates. For instance, some might have a financial year that starts in March or April. In this case, comparing them will be improper, inadequate, and misleading.
It is the standard period report process for companies' financial statements. This method is helpful in horizontal analysis. In other words, it is the accounting process of systematizing the full financial statements of different companies. This procedure aims to ease the comparison of these companies' financial statements.
Thus, it is right that it is the operation of the following companies' financial statements for the same period.
Calendarization
Definition
Incomparable companies, the financial statements are compared in the same period. However, some companies have different financial year-end dates. Therefore, this comparison will be unfair to some companies. Hence, calendarization spreads the recognition of a company's expenses over more than one period. This is done over a fixed period.
Budget
A financial examination is usually used in the creation of a budget. Income and expenses are distributed during all the periods used within a budget. In real life, these allocations will vary from the actual income and expenses, but expectations are that they will match the budget.

Calendar year and Fiscal year
The difference between a fiscal and a calendar year helps one understand calendarization better. Unlike some, some companies base their fiscal year according to the normal calendar year in the respective country.
A fiscal year is a period when the company readies its financial statements. Every firm prepares three main financial statements for their budgetary or calendar year. They are the balance sheet, the cash flow statement, and the profit & loss account.

Companies usually follow the common fiscal years (Jan. to Dec. - April to March - July to June - Oct. to Sep.). However, companies are free to choose their fiscal year in many places.
For example, most firms have an FY from Jan to Dec in the United States. The US Federal Gov. is from Oct to Sep, while the state gov can follow different FY. India has an FY from April to March; hence almost all companies there have the same calendar.
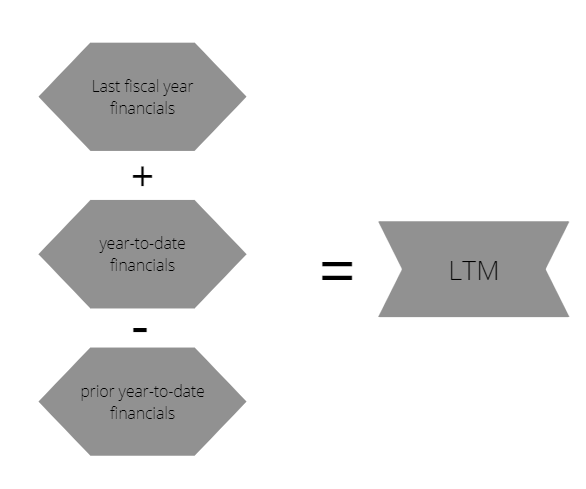
LTM
The last Twelve Months and calendarization are both used in analyzing comparisons. Comparable company analysis compares the functioning measurements of public firms in an industry's peer group.
Size, leverage, industry, and growth attributes categorize the companies in a peer group. Therefore, company assessments need a comparable analysis to accompany the overall analysis.
Calendarization analyzes financial statement data for a fiscal year. However, LTM analyzes the last twelve months precisely when calculating financial metrics (profits, revenue, EBITDA...)
Even though one year might be a short time to test a company's performance, it is a worthy element to know its latest performance and production.
LTM figures are more "up-to-date" than annual financial reports, hence considered a helping tool. In addition, LTM eliminates small, potentially misleading measurements, such as quarterly reports.
Investors must differentiate LTM figures coexisting with the company's latest fiscal year reports. Calendarization adjusts the fiscal year to the company or the parent, providing a fair and clear basis for the comparison.
LTM shows the preceding twelve months from the issued date of the financial statement. For example, if the financial statement date is September 2021, the LTM shows the period from October 1, 2021, to September 30, 2022.
Calculations
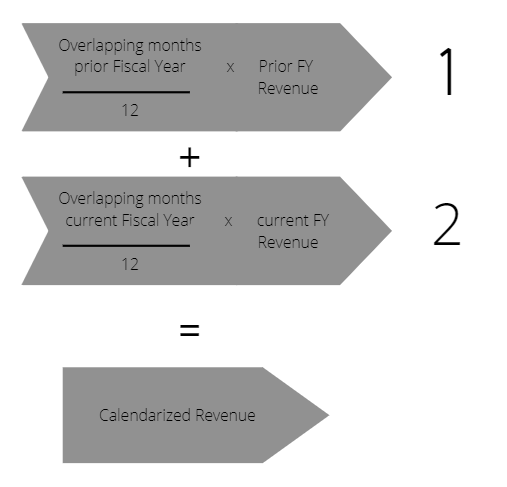
There are two steps to calculate calendarization:
1) Find Percentage Overlap from Prior FY and Multiply by Prior FY Revenue:
First, you find the number of months where the previous FY(Fiscal Year) overlaps with aligned year-end and divide by twelve.
Then, you find the company's PFS(Previous Fiscal Year) revenue. This can be found in the company's public financial filings.
With Numbers provided by the accounting department or the client, divide the number of months by 12 and multiply the percentage overlap by the prior Fiscal Year's Revenue.

2) Find Percentage Overlap from Current FY and Multiply by Current FY Revenue:
Find the overlapped number of months of the current FY and aligned year-end. Then, find the current FY's revenue where you will use the same data sources for the numbers as in step 1. Then, divide the months by 12 and multiply the percentage overlap by the current FYR.
Example
Let's assume your company's fiscal year ending date is March 31, and it's your task to calendarize its profits.

Your company generated $60 million in revenue. This revenue is expected to reach $70 million by the following year.
- 2022A Revenue: $60 million
- 2023E Revenue: $80 million
Year 1 Calendarized Revenue is calculated such that 75% of the data is provided by 2022A, and the remaining arises from 2023E.
- 2022A (%): 9 ÷ 12 = 75%
- 2023E (%): (12 – 9) ÷ 12 = 25%
According to these change factors(%), we multiply the percentage by the respective revenue amount.
- FYA: $60m × 75% = $45 million
- NFY: $80m × 25% = $20 million
The calendarized revenue for FYA (first adjusted year) equals the sum of the two numbers above, $65 million.
Financial Statement and FY Consolidation
What is financial consolidation?
The process of merging the financial data of a company's subsidiaries and segments, such as the entity controls, into one set of financial statements is called financial consolidation.
Logically, the assets, income, expenses, and all financial data of the controlling company and its subsidiaries are presented in a single financial statement as if they are a single entity.
Consolidated financial statements give a company's stakeholders a general view of the overall performance through several factors.
- Regulators and auditing entities depend on it to ensure the company follows the rules and regulations.
- It gives investors access to a compcompany'sancial situation, its profit or losses in the marketplace, and how it is operated and managed.

Financial Statement and FY Consolidation
Financial statements calendarization happens when a parent company presents combined financial statements to its collaborators.
This company has to merge all financial statements, including those of its subordinate companies. These companies must follow the same fiscal year as one of the parent companies; if they follow their own FY, they will be adjusted to the pareparent's
In the case of different FY, these consolidating financial statements won'won'te sense and will lead to false and inaccurate financial statistics.

Example:
Suppose that WSO owns two subsidiaries, A and B. WSO'WSO's(fiscal year) starts September 1 to August 31, A has a fiscal year that begins on March 1, and B has one on May 1.
When consolidating the financial statements of WSO, A, and B, the first thing to do is to adjust the reports of A and B to the fiscal year running from September 1 to August 31.
Also, WSO will have to note that A and B prepared their financial statements for the fiscal year for merging.
FAQs
Some companies don't report based on the same fiscal year-end, hence we calendarize their finances. It allows companies to become fairly comparable based on the same FY comparisons.
It is a one-year time span that relates to a company's financial reporting periods. It can differ from a calendar year and they are essential to accounting.
Companies usually pick periods different from the calendar year when they have huge intra-year jumps in their business.
As an example, retailers profit significantly during the holiday season. Hence, they usually set their FYE (fiscal year end) to the end of February. This provides them with enough time to ready their numbers after the huge mess of the holiday season.










or Want to Sign up with your social account?