Foreign Exchange Risk
The chance that the value of an investment may decline due to shifts in the relative prices of affiliated currencies.
What is Foreign Exchange Risk?
The decentralized worldwide market where currencies are traded is referred to as the foreign exchange market, commonly known as forex or FX. Market dynamics relating to commerce, investment, tourism, and geopolitical risk determine the value of any given currency.

Banks, large organizations, hedge funds, and small-time traders are the main participants in the FX market. These parties participate in currency exchange transactions to ease international commerce, hedge against currency risk, or benefit from exchange rate swings.
The development of the global economy and the facilitation of commerce depends on the foreign exchange market. Therefore, fundamental knowledge of foreign currency is essential for everyone involved in global activities or interested in global financial markets.
Other pitfalls come with excellent openings. This word is true in currency trading, where pitfalls outweigh the possibility of substantial earnings.
Foreign Exchange Risk, also known as currency threat, FX threat, or exchange rate threat, is the chance that the value of an investment may decline due to shifts in the relative prices of affiliated currencies.
Investors and all businesses engaged in transnational commerce are impacted. The threat exists when a contract between two parties defines precise costs and deadlines for the force of products or services.
However, any party might lose plutocrats if the exchange rate changes between when the contract was inked and the delivery date.
NOTE
These pitfalls significantly influence profitability, competitiveness, and investment returns. To reduce their impact, it's pivotal to understand and manage foreign exchange pitfalls.
This threat is brought on by exchange rate oscillations, which significantly affect the sales value. However, the business will suffer a loss if the changed currency's value declines. Hence, the sale will be profitable if the currency's value increases.
Currency threat is a major concern for businesses and individuals engaged in transnational trade and investment.
A European supplier agrees to sell 1,000 widget components to a US widget-maker for 10,000 Euros, with payment due when the widgets are delivered (which will be three months in the future).
$1.10 is currently being exchanged for one Euro. However, the currency rate has deteriorated to $1.20 for one Euro by the time the widget producer receives the widget's parts. This implies that the firm owes its supplier $12,000 instead of $11,000 under the original agreement.
Key Takeaways
- Foreign Exchange Risk, also known as currency threat, FX threat, or exchange rate threat, is the chance that the value of an investment may decline due to shifts in the relative prices of affiliated currencies.
- However, any party might lose plutocrats if the exchange rate changes between when the contract was inked and the delivery date.
- This threat is brought on by exchange rate oscillations, significantly affecting sales value.
- Currency threat is a major concern for businesses and individuals engaged in transnational trade and investment.
- Transactions Risk is the threat arising from exchange rate oscillations from the opening of a sale to its agreement.
- Sovereign Risks refer to the threat of financial loss performing to political or profitable developments in another country that affect the value of its currency.
- Changes in exchange rates can affect the cost of goods and profit perimeters of companies that import and export goods and services.
- Foreign exchange pitfalls can also impact transnational investment overflows.
Understanding Foreign Exchange Risk
A corporation runs the risk of foreign exchange when it transacts in financial transactions that are valued in a currency other than the one in which it is headquartered. The transaction's cash flows will be impacted by any increases or decreases in the value of the base currency or the denominated currency.
When a business transacts in money and keeps its financial records in a currency other than its home currency, there is a risk.
Foreign exchange risk arises, for instance, when an Australian corporation conducts business in Japan and declares its financial statements in Australian Dollars while receiving financial transactions in Japanese Yen.
For the financial transactions to be included in the company's financial statements, they need to be converted from Japanese Yen to Australian Dollars. Foreign exchange risk refers to variations in the exchange rate between the Japanese Yen, which is considered a foreign currency, and the Australian Dollar, which is considered a local currency.
Businesses that import and export goods and services to numerous nations, as well as investors who deal in global markets, may be impacted by foreign exchange risk.
Upon closing a trade, the investor's gains or losses will be expressed in the foreign currency and will require conversion back to their home currency. Exchange rate fluctuations may have a negative impact on this conversion, causing the amount to be less than anticipated.
Types of Foreign Exchange Risks
Businesses and individuals face various FX risks when engaging in international transactions. Here are the most common ones:
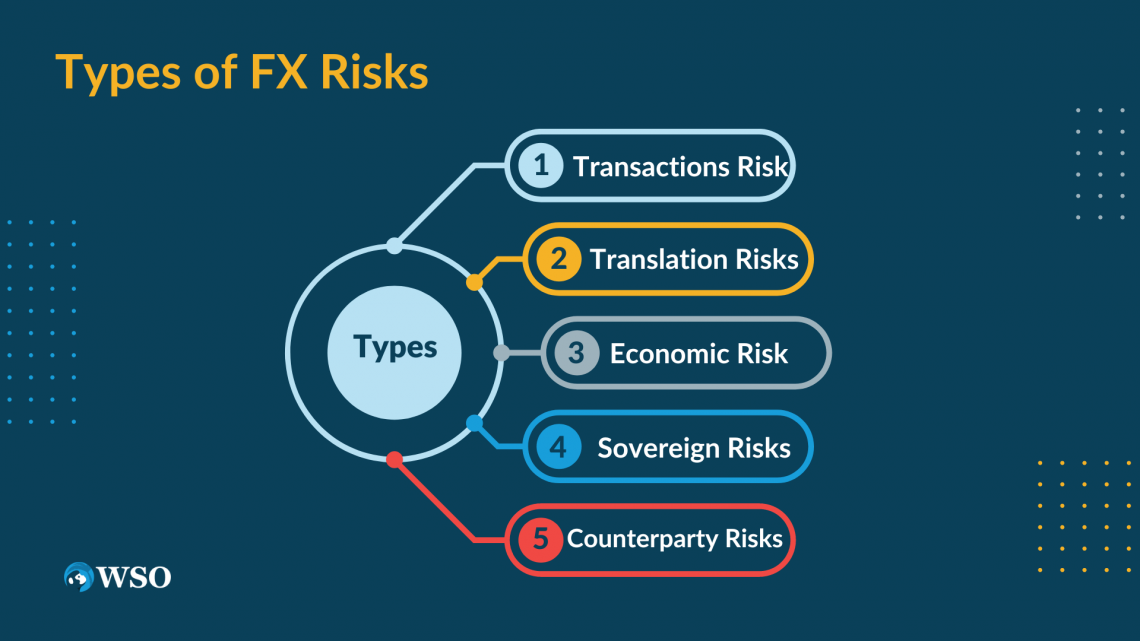
1. Transactions Risk
Transactions Risk is the threat arising from exchange rate oscillations from the opening of a sale to its agreement.
For example, if a business in the United States has a contract to buy goods from a supplier in Japan for 100,000 yen, the transactional threat arises if the exchange rate changes before the agreed date.
The US business may gain from the sale if the exchange rate changes in favor of the US Company.
2. Translation Risks
Translation Risks are the threat arising from the restatement of financial statements from one currency to another. This is the threat faced by transnational companies that operate in multiple countries and need to report financial results in their home currency.
The translational threat appears, for example, when earnings reported in Yen by a Japanese attachment of a US company are converted into a US firm for financial reporting purposes.
The US establishment may profit from the restatement if the exchange rate changes in favor of the US firm, but the US business may lose plutocrats if the exchange rate changes against the US firm.
3. Economic Risk
Economic Risk is the threat caused by macroeconomic variables similar to political unpredictability, interest rates, and affectation. These factors can affect exchange rates, affecting your investment and business success.

For example, suppose a US company sells particulars to Japan. In that case, there's a profitable threat if the Yen appreciates and drives up the price of the goods for Japanese consumers.
The US company's products may become less popular, resulting in a loss of request share. Analogous to this, if someone invests in a foreign currency, there's an economic threat that the exchange rate would move negatively and reduce their return on investment.
4. Sovereign Risks
Sovereign Risks refer to the threat of financial loss from political or profitable developments in another country that affect the value of its currency.
For illustration, political or profitable insecurity might beget a significant deprecation of a foreign currency, affecting a company's investments or marketable conditioning in that nation.
5. Counterparty Risks
It is the threat of losing plutocrats when a counterparty in a foreign exchange sale is unfit to uphold their end of the bargain.
An association has the threat that the counterparty will not be suitable to deliver the currency when the contract matures, for case, if it enters into a forward contract to acquire foreign currency at a forward date.
Impacts of Foreign Exchange Risks
FX risks are real to everyone involved in international trading. Whether you're an entrepreneur, an investor, or a rubberneck, exchange rate oscillations can significantly impact your fiscal operation.

The profitability of a company is one of the most direct goods. Therefore, changes in exchange rates can affect the cost of goods and profit perimeters of companies that import and export goods and services.
For illustration, a business importing goods from a nation where the original currency has lost value in comparison to its currency may have advanced costs, which might reduce profit perimeters.
Oscillations in exchange rates can affect unanticipated earnings or losses on foreign currency deals and affect a company's capability to pay bills or make investments. Exchange issues can also affect a company's cash inflow.
NOTE
Cash flow is the net amount that flows into and out of your business during a period.
For illustration, if a corporation has cash reserves in a foreign currency, a quick depreciation might erode its value and vitiate the company's cash overflows. Foreign exchange pitfalls can also impact transnational investment overflows.
Investors may be reluctant to invest in a country if they perceive a high position of foreign exchange threat, which can lead to a drop in foreign investment and profitable growth.
How do Foreign Exchange Risks Affect Financial Operations?
Here are some examples of how FX risks can affect your financial operations:

1. Increased Costs
You'll have to pay much further for your significance if you're an importer and the currency of the country you're importing from is downgraded. This will lead to increased costs and eventually affect your profitability. There's a possibility.
2. Decreased Revenues
Your profit will fall if you export and the currency of the philanthropist nation weakens. However, this might be an issue if you have fixed charges and are unfit to modernize your rates to reflect exchange rate variations.
For businesses and investors, currency rate changes can lead to large losses, especially if they've not hedged their effects or successfully managed their exposure to foreign exchange pitfalls.
For example, if a corporation purchases items from abroad and the value of the originating currency declines, the cost of importing those goods rises, resulting in lower profit margins.
3. Reduced Competitiveness
Foreign exchange concerns can also affect a firm's competitiveness in foreign markets. For example, a company's exports will cost more to buy in international markets if its native currency increases, which would decrease demand for its goods.
In contrast, if the domestic currency declines, the company's goods will become more competitive in overseas markets. Therefore, organizations must carefully manage their foreign exchange risks to maintain competitiveness in international markets.
NOTE
Competitors based in nations with declining currencies might be able to provide the same goods or services at a cheaper cost. Competing may be challenging, particularly if prices cannot be dropped because of high production costs.
4. Increased Volatility
Currency markets are volatile, and future exchange rates can be difficult to predict. This can create uncertainty for companies and investors and affect their decision-making process.
5. Macroeconomic Impacts
The macroeconomic effects of foreign exchange risks on economies can be more extensive. For example, consumer pricing, wage growth, and total economic growth may all be impacted by this.
Like how trade balances and foreign capital flows may be affected, exchange rate variations can also affect an economy's balance of payments and general health.
For example, if a country's currency weakens, the rising cost of imports may result in inflationary pressures.
Managing Foreign Exchange Risks
Managing FX risks is essential for companies, investors, and people conducting foreign business. Effective risk management techniques can assist in reducing the impact of exchange rate swings on financial operations.

While it is impossible to eliminate foreign exchange risks, there are several ways to manage them:-
1. Hedging
It involves using financial products to hedge against unfavorable changes in currency rates, such as options, futures, and futures.
For example, a company can eliminate trading risk by using futures contracts to lock in exchange rates for future transactions. Similarly, companies can use futures or options to hedge against adverse exchange rate fluctuations, reducing their economic risk.
2. Diversification
It involves distributing the risk among several currencies, markets, and goods. Risks can be reduced via diversification by lowering the exposure to any currency, market, or product.
For instance, a company can reduce the risk of unfavorable currency rate swings by diversifying its product range by selling items in other countries. Similarly, one might invest in a portfolio of stocks and bonds from other nations to lower the risk of unfavorable exchange rate fluctuations.
Diversification includes spreading your investments across many markets and currencies to reduce risk exposure. Investments in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or foreign equities can be made to achieve this.
3. Pricing Strategy
If you export, you can modify your pricing to reflect changes in currency rates. If the currency of the nation you are exporting to weakens, this might help you keep your profit margins stable.
Besides traditional risk management strategies, technological improvements make new ways to manage foreign exchange risk possible.
For example, real-time monitoring of currency rates and trends can help businesses and individuals quickly adapt their risk management plans to changing market conditions.
NOTE
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technology can be used to predict exchange rate changes and identify invisible patterns and trends to the naked eye. Blockchain technology offers secure and open transactions.
In conclusion, businesses, investors, and people doing overseas business face foreign exchange risks. The management of these risks through hedging, diversification, and pricing methods can have a substantial influence on financial operations.
You may lessen the impact of exchange rate variations on your financial operations by comprehending the various FX risks and implementing appropriate risk management measures.
For companies and investors that can handle them properly, they can provide difficulties and uncertainty but also possibilities.
Businesses and investors may confidently navigate currency markets and attain their financial objectives by knowing the various foreign exchange risks and implementing the necessary measures.









or Want to Sign up with your social account?