Economic Inequality
It refers to the unequal distribution of economic resources among individuals within a society.
What Is Economic Inequality?
Economic inequality refers to the unequal distribution of economic resources among individuals within a society. It is an important concept that helps us understand and recognize how the economy distributes scarce resources among individuals or residents of a country.
The distribution of economic resources between the rich and poor creates an unequal gap between those who have more than enough resources to live with and those who don't.
A woman in an underdeveloped country who works as a household maid lacks education and has to settle for labor work. At the same time, a person born to a millionaire enjoys access to opportunities as money and connections open doors for people.
Key Takeaways
- Economic Inequality refers to the disparities in the distribution of economic resources within a society. The distribution of economic resources between the rich and poor creates an unequal gap between those who have more than enough resources to live with and those who don't.
- The allocation function of the government actively works toward reducing Inequality by providing assistance programs for the economically backward classes and progressively taxing the rich to fund these programs.
- There are three types of economic Inequality: Income, Wealth, and Pay Inequality. Income inequality refers to the difference in the level of income an individual earns in a society, Pay Inequality is one resulting from pay due to employment, and Wealth inequality refers to the Inequality where a group of people holds more assets than others.
- Factors that cause economic Inequality are the difference in wages due to the supply and demand in the labor market, unequal access to quality education and healthcare, gender, Race, and culture, the concentration of wealth, and globalization.
- Inequality affects economic growth and stability, dampens Investment, and leads to political instability.
- Some common ways to measure this Inequality are through Lorenz Curve, Gini Ratio, and Palma Ratio.
- Creating opportunities for disadvantaged communities, increasing public expenditure, empowering NGOs, creating better fiscal policies, and following the nordic model are some ways of reducing Inequality.
Understanding Economic Inequality
Economic inequality exists in two folds:
- Vertical inequality: refers to the disparity that is between the individuals of a different country or a region.
- Horizontal inequality: refers to the disparity between individuals within a society or cultural group. For example, between urban and rural populations.
The greater concentration of assets among a few individuals leads to the other half of the population with limited means. Inequality is present in every corner of the world, but it has been a burning topic of discussion among social scientists.
The advent of COVID-19 has further highlighted the strain on the economically backward in accessing healthcare. As a result, many policymakers have raised their voices to reduce this inequality gap.
With industrialization and globalization paving the world, economic inequality has been reduced among countries. A country that lacks one resource can import the same from another that has an abundance of it. Although, this has resulted in rising inequalities among the country's residents.
The allocation function of the government actively works toward reducing inequality by providing assistance programs for the economically backward classes and progressively taxing the rich to fund these programs.
It is crucial to understand that the living and social conditions one is born into are the external forces and are unaffected by the hard work or choices one makes in their life.
It is the responsibility of the government at all levels to pave the path to equality and provide equal access to opportunities to every individual.
Economic Inequality Types
Some of the types are:
1. Income Inequality
Income inequality is the difference in an individual's income level in society.
For example, a millionaire with his multi-million dollar business earns through multiple sources of investment. On the other hand, an average worker income employed at the grocery store earns an hourly wage.
Both have different spending and saving habits. With the rising inflation, more and more people are struggling to save. However, an average worker would also find themselves lacking the ability to have complete information on different investment avenues that will generate profit.
However, income inequality is not just restricted to pay but also includes incomes in the form of bonuses, rental income, investments, interest in savings, pensions, etc.
2. Pay inequality
Pay inequality is one resulting from pay due to employment. Pay can be monthly, weekly, or hourly payments to an individual. It ranges depending on the level of skills and qualifications of an employee. The disparity in pay is a common concern for individuals struggling to get a job.
With automation destroying most jobs and people striving their best to compete, the job market is now hazier than ever. For example, The CEO of a tech giant gets paid millions, as compared to the janitor cleaning the same warehouse floor, who is paid an hourly wage for his work.
A person with access to building unique skills has more chances of landing a well-paying job, whereas those who don't have access settle for less.
3. Wealth Inequality
Wealth inequality refers to inequality where a group holds more assets than others. Wealth equates with 'net worth,' which is the assets minus liabilities of an individual.
These assets can be properties or real estate, bonds, stocks, etc., and liabilities can be any form of debt.
This unequal distribution of wealth exists in almost all countries but is said to be highest in the United States. For example, Elon Musk is the world's highest 'net worth' individual. At the same time, people in slums earn less than $1 a day, with little to no assets.
Economic Inequality causes and effects
Some of the causes and effects are:
1. Labor Market
In a free market, supply and demand affect the wage rate. If there is more labor supply for a low-demand job, lower will be the wage rate. At the same time, higher wages exist for highly skilled jobs where fewer workers are qualified to work.
With the rising population and decreasing job market mainly due to automation, more people are willing to accept a job with a lower wage rate. For example, more and more college graduates are accepting a job that pays them less than they would be entitled to.
2. Unequal Access to Quality Education and Healthcare
The more you have access to education for learning industry-specific skills and specialization, the more employable you will be and sit higher on the income ladder.
The economically backward classes do not often have access to quality education and healthcare and end up in a job that pays little to nothing.
This creates income inequality due to reasons beyond one's control and settling for a low-paying job with no scope to grow. A healthy individual is an asset to one's economy.
3. Gender, Race, and culture
All over the world, men tend to earn more than women. As often as we see women participating in the workforce, existing social issues of the society favor the patriarch and expose them to workplace discrimination. Women are not included in important household decisions and face problems of equal inheritance.
Though gender pay has always been an issue, the feminist movement has tried to curb it. However, in an article published in 'Our World in a Data,' we can see how the gender pay gap is rooted in our culture. In a world where we as homo sapiens unite, Race and culture distinguish an individual.
A Muslim man is often perceived as dangerous due to the notion made by media and finds it difficult to either find a job or hold on to one as opposed to a white man. An African-American community, on the other hand, holds ten times less wealth than a white Christian family, according to IMF.
4. Concentration of Wealth
From the Gini Index to the Palma Ratio, the numbers always paint a picture of inequality. Not only is the wealth concentrated in the hands of a few, but the inaccessibility to grow one's wealth also gets restricted.
The rich can invest in ventures, buy stocks and acquire information that is not readily available to the poor. This helps them grow wealth while the poor use their income to meet their needs.
5. Globalization
Economic globalization all over the globe has eased the transfer of goods and services but, at the same time, created an inequality gap.
A developed country creates a wage gap by importing goods from an under-developing country that uses low-skilled labor who work for lesser wages. This reduces demand in the home country and creates possible structural unemployment.
In a way, globalization has increased the need for specialization and outsourcing as a cheaper alternative where supply is abundant. As a result, people are willing to accept reduced wages to pay their bills.
Economic Inequality Effects
Some of the effects are:
1. Affects Economic Growth
Inequality causes poor households inability to access education and health, dividing them of the opportunity to attend college and get a good job. Thus, we get lower productivity levels when people are not healthy in an unequal world.
2. Dampens Investment
The more people spend their income on consumption items, the less they save and invest. Inequality causes a large section of the society to be worse off, as they can't invest or save, nor do they have the perfect knowledge of great ROI avenues.
3. Leads to Political Instability
Major economic winners of resources reward themselves with creating and supporting political parties that benefit them. As a result, deprived people find themselves unable to voice, which leads to political instability in the country.
Measuring Economic Inequality
A few of the commons ways to measure include:
Lorenz Curve
Lorenz Curve is used to define the distribution of income and wealth graphically. In 1905, Max O Lorenz, an American economist, developed it. Below is the graphical representation of the Lorenz Curve.
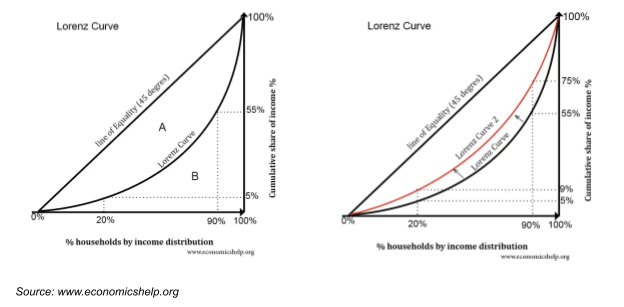
Interpreting the Lorenz Curve:
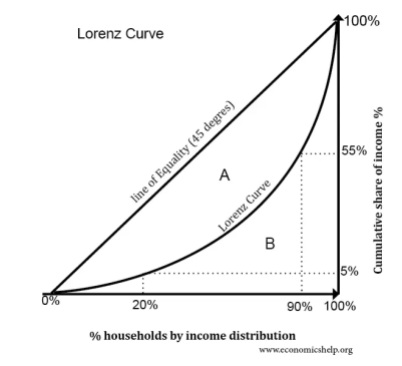
A population is said to have lesser economic inequalities if the Lorenz Curve is closer to the line of equality. For example, in the left picture of the Lorenz curve, the poorest 20% of the population holds 5% of the total income, and the wealthiest 80% owns 95% of the total income of the entire population.
In the right picture, the shift in Lorenz Curve depicts the reduction in Inequality. Now, the poorest 20% of the population hold 9% of the total income, and the wealthiest 80% hold 91% of the total income.
Gini Coefficient
Gini Coefficient or Gini Index or Gini Ratio is a statistical tool to measure the disparity of income and wealth inequality among nations. In 1912, Corrado Gini first developed the statistical tool and name.
A Gini coefficient of 0 represents perfect equality, whereas a Gini coefficient of 1 represents maximum Inequality. Hence, the more significant the inequality gap between the rich and poor, the higher the Gini Index. Check out the Gini Coefficient of the countries in 2022 by clicking here.
We calculate the Gini Coefficient of a population using the Lorenz Curve.
Gini Coefficient = Area of A / Area of (A + B)
Interpreting the Lorenz Curve effect on Gini Coefficient:
The closer the Lorenz Curve is to the line of equality, we get the small Area of A, making the Gini Ratio low.
If a high degree of Inequality exists within a population, the greater will be the area of A, and the higher will increase the Gini Ratio. Therefore, a rise in Gini Ratio indicates a rise in Inequality.
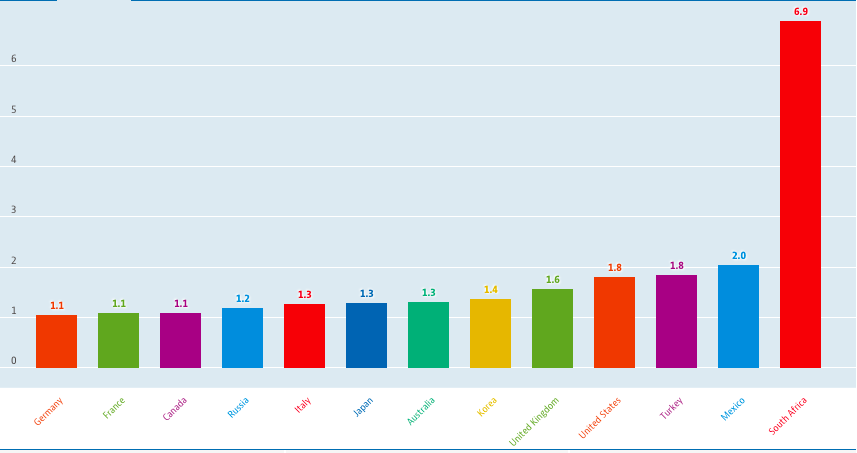
Palma ratio
The Palma ratio divides the share of the income of the top 10% of the population with the share of the income of the lowest 40%.
Developed by José Gabriel Palma, it paints a more transparent picture of the Inequality existing in a society as it represents the difference between the rich and poor without considering the middle.
Palma Ratio = Top 10% income's share / Bottom 40% income's share
Below is the data of top G7 countries and their highlighted Palma Ratio. You can access the data for other countries by clicking here.
Ways to Reduce Economic Inequality
A few of the ways to reduce are:
1. Creating opportunities for disadvantaged communities
Disadvantaged communities always find themselves in the back of the wagon when seeking economic opportunities. For example, a person with a disability may find it tough to apply for a job. Many organizations are now offering assistance programs to promote inclusivity.
Scope of employment, reservations for the economically backward, talent scholarships, and grant assistance for the poor can help solve a lot of issues for a family with a low income.
A platform to grab equal opportunity helps in opting for careers more suitable to one's talents and helps one feel part of the community.
2. Increase expenditure in the public sector
Public expenditure on health and education is a way to improve the standard of living. A healthy individual can contribute more to an economy than a bed-ridden individual. In addition, education can help equip the workforce with advanced skills that can help them get high-paying jobs.
Expenditure on other areas, such as free parks or gyms where benefits are non-economic, plays a role in shaping society.
3. Empowering NGOs
Many Non-governmental organizations are working toward raising their voice against the injustices against the poor. While some rally and protest on the streets, some provide free meals and clothes to those who can't afford them.
In a way, it empowers people to pursue other opportunities when their basic needs are met. It also draws the attention of policymakers to adopt changes in the policies. For example, workplaces offer better diversity and inclusion. In addition, they are granting assistance to the farmers to sell their produce at better prices.
4. Creating better fiscal policies
The government adopts various policies to foster social change that can reduce the economic gap. For example, the minimum wage, and unemployment benefits for those who have been unfairly dismissed, can help people sustain themselves when there is a lack of resources.
The progressive taxation policy and taxing the import of luxury goods can also help transfer the resource from the rich to the poor.
5. Following the Nordic Model
Scandinavian countries such as Sweden, Finland, and Denmark follow a well-tested economic model called the Nordic Model. As a result, the countries have achieved high living standards for their people and low-income disparities.
They focus on investing extensively in human capital and social welfare programs, such as providing the country with free education and healthcare and guaranteed pension schemes using tax funds.
The people work collectively with the government to address their problem through a democratic process and follow a mixed economy system. To understand how it has been a success, click here.
Researched and authored by Samridhi Singh | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:










or Want to Sign up with your social account?