Economic Justice
A set of moral principles guiding us in designing economic institutions
What Is Economic Justice?
Economic justice refers to moral principles guiding us in designing economic institutions. The goal is to create a sufficient material foundation for a dignified and productive life.
The primary focus of this ideology is ensuring everyone has equal access to resources to live a meaningful and prosperous life.
Economic justice and modern economics are two concepts that often overlap. This is because ensuring everyone has access to resources and opportunities generally also leads to economic growth.
The goal is to offer possibilities for everyone to develop and succeed, with justice following behind to drive up the economy. When citizens are not able to fulfill their needs due to low income, a strain can be put on the economy.
Capitalism is a factor that can threaten economic justice in modern society. Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit.
According to those who believe in such justice, capitalism can sometimes lead to tremendous inequality and an income gap between capitalists and laborers.
Therefore, wage disparities and other imbalances must be addressed for economic justice to prosper. Such justice can create a thriving economy that achieves sustainable growth. This means that it:
-
Enhances productivity
-
Sustains growth
-
Creates job opportunities
Some of the examples of economic injustice include:
-
Wage inequality
-
Gender pay gaps
-
Racial gaps in education
-
Racial discrimination
-
Poor jobs/employment
On the other hand, the examples of economic justice are:
-
Fair wages
-
Access to financial services and adequate housing
-
Access to education and health care
-
A fair and equal criminal justice system
-
Strong infrastructure and public services
Keep in mind that all the opinions espoused in this article are based on the ideology of economic justice.
Key Takeaways
- Economic justice aims to create a fair and equitable economic system that ensures equal access to resources and opportunities for all individuals, allowing them to lead dignified and productive lives.
- It is closely related to concepts of equality, fairness, and human rights, focusing on addressing issues such as income inequality, poverty, exploitation, and discrimination.
- Achieving economic justice requires addressing wage disparities, providing access to essential services like education and healthcare, ensuring fair and inclusive employment practices, and creating a supportive social safety net.
- Progressive taxation, inclusionary policies, increased minimum wages, and investment in public infrastructure and services are some of the strategies used to achieve economic justice.
- Economic justice is interconnected with social justice, which encompasses broader aspects of fairness and equality in areas like housing, healthcare, and human rights
Three Principles of Economic Justice
The three principles are:
1. Participative Justice (Input principle)
Participative justice, also known as the input principle, outlines how everyone contributes to the economic process to make a living. It necessitates equal access to private property and engagement in productive work.
However, participative justice does not guarantee equal outcomes. Rather, it demands that society’s institutions give everyone equal rights to contribute to the economy through labor.
2. Distributive Justice (Out-take principle)
The principle of distributive justice, also known as the out-take principle, takes into account one’s contributions to the economy in terms of exchange value.
Each individual has a right to a proportionate share of the value of the marketable goods and services they produce through their labor, capital contributions, or both. Ensuring every producer and consumer has a voice in the economy upholds human dignity.
Distributive justice breaks down when all people are not given an equal opportunity to acquire and enjoy the benefits of income-producing property.
3. Social Justice (Feedback and corrective principle)
Social justice in an economic system restores the balance between productivity and consumption. When the system fails either core premise, it rebalances participatory and distributive justice.
This limitation is a concept in social justice that discourages personal avarice and prevents monopolies and participation obstacles.
Why Economic Justice is Important
Economic injustice stems from the desire to keep the economy peaceful, balanced, and reasonable.
Everyone should have a fair share of the resources and opportunities in their respective countries. There are several ways in which such justice is significant:
-
It addresses issues of wage disparities and exploitation
-
It helps tackle the issue of poverty
-
It helps sustain and boost the economy
-
It helps avoid conflict between the poor and the state government
-
It ensures efficiency and productivity amongst workers
Achieving Economic Justice
Ways to achieve this are:
People with a higher income pay a greater share of their income in taxes. This is based on the idea that a fair tax system is one where those who benefit more pay the greatest tax. Thus, people who earn the lowest pay fewer taxes.
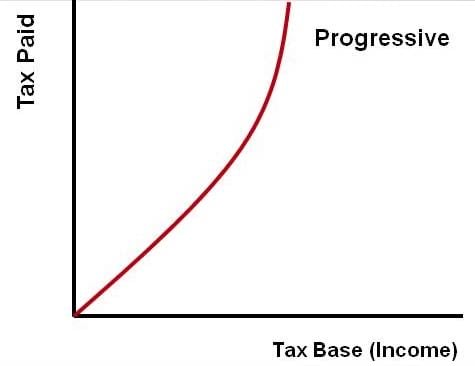
In addition, these tax funds can be used to improve the living standards of the poor through the development of education systems, health care, and job opportunities.
2. Inclusion
People from diverse backgrounds often experience underrepresentation in the workplace and other forms of discrimination in other areas.
To achieve justice, disadvantaged people (low-income families) must have more opportunities and resources to cater to their needs.
A) Increased minimum wage
In the United States and other countries worldwide, workers are often exploited and underpaid, especially those who work in factories.
According to believers in economic justice, this exploitation is due to capitalism. Therefore, workers who earn below minimum wage must increase their salaries to afford basic needs such as health care, food, and clothing to achieve justice.
B) Building shelters for the homeless
In the United States, approximately 17 people per 10,000 experience homelessness daily, and the number of homeless people is estimated at 326,126.
Social Justice vs Economic Justice
Economic justice’s central purpose is to provide people with equal opportunities and minimum needs to avoid exploitation. It is also about creating various job opportunities where everyone can use their talents and abilities.
Social justice emphasizes respecting and upholding everyone’s rights. This includes fairness and equality in housing, employment, health care, and infrastructure. In addition, it gives us a personal responsibility to work together for the common good.
Principles of Social Justice are:
-
Equity: Fairness and justice amongst individuals to experience similar outcomes.
-
Access to resources: Every citizen must have access to healthcare and housing, despite wage gaps.
However, most wealthy people can afford better healthcare and education because of the gap between the rich and the poor. -
Human rights: United Nations Human Rights Council outlines the fundamental human rights that each individual is entitled to. However, people from disadvantaged backgrounds are often neglected. Seekers of such justice believe it is the government’s responsibility to make sure that infringement of human rights does not persist.
-
Diversity: The government should acknowledge the idea that multiculturalism exists and will always exist. This means understanding that some groups may face barriers and, as a result, it is essential to offer them additional resources to meet their needs.
-
Participation in the community: Outreach, supporting minority businesses, volunteering for the greater good, protesting, and taking action against matters of economic and social injustice
| Social Justice | Economic Justice |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note
The term social justice was coined by Luigi Taparelli!
Is Economic Justice Possible?
The United Nations holds that many countries still suffer from widespread inequality, and some of the inequality is embedded in their systemic racism and discrimination against disadvantaged backgrounds.
While there have been some efforts by governments, such as a progressive tax system, and the building of educational facilities such as schools, hospitals, and public infrastructure, it is worth noting that achieving this justice is rare and somewhat impossible to achieve.
According to Denis Goulet, we live in an economy where the rich keep getting richer, and the poor do not progress. Health care is insufficient to ensure everyone has access to houses to achieve justice because the system favors the wealthy in such situations.
For instance, a private company may decide to pay workers below minimum wage, and because such workers depend on pay cheques to earn a living, they are forced to endure exploitation.
In poorer nations, people grow rich through factories with poor environments and unsanitary working conditions. Working conditions include inadequate ventilation, risky exposures to metals, and heavy machinery.
Employees risk their lives for low-income wages that barely help them through the month. In addition, the amount of hours spent is not rewarded because wealthy employers are unwilling to pay more.
Goulet also believes that economic injustice will always be an issue until the government and authorities take action against the inhumane condition that low-income families, minorities, and disadvantaged members of society are forced to experience.
A nation will not survive morally or economically when so few have so much while so many have so little.
-Bernie Sanders



or Want to Sign up with your social account?