Sensex
A broad market free-float market-weighted stock market index.
What Is The Sensex?
The BSE SENSEX, also known as the S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index or simply SENSEX. It originated from two words, SENsitivity and IndEX. It is a broad market free-float market-weighted stock market index.
Thirty of the most established companies are included in the Index.
These 30 companies represent the various industrial sectors of India, which are the largest and most actively traded in secondary markets.
The index uses the company's free float rather than outstanding shares, which means the number of stocks currently trading in secondary markets is taken rather than the aggregate number of shares issued by the company.
Characteristics
1. It is used to measure India's overall economic activity or performance.
2. It is also called the benchmark index of the BSE in India.
3. It is calculated both in Indian rupees and US dollars.
4. It is regarded as the pulse of the domestic stock market of India
5. It is reviewed semiannually in June and December.
How Does The Sensex Work
When the weighted average price of 30 companies that constitute the Sensex index increases, Sensex goes up.
And when the aggregate price of 30 companies that are included in the Sensex index decreases, it goes down.
Top 5 companies that constituent S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index (2022)
1. Reliance Industries Ltd. (12%)
2. HDFC Bank Ltd. (10.47%)
3. Infosys Ltd. (9.72%)
4. Housing Development Finance Corporation Ltd. (7.67%)
5. ICICI Bank Ltd. (7.49%)
To learn more about this topic, you can refer to this YouTube video:
History Of The Sensex
It was published on 1 January 1986. The base period (year) is taken as 1978-79, and the base value is taken as 100.
On 25 July 2001, BSE launched a dollar-linked version of the Sensex named DOLLEX-30.
Globalization and the opening of the Indian economy to the world have led to substantial growth in the S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index.
The worst single-day fall in history was on 18 April 1992; the S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index experienced a fall of 12.7% due to the Harshad Mehta scam, also known as the scam of 1992.
Harshad Mehta illegally transferred money from public sector banks to secondary markets to raise valuations.
The second worst single-day fall was on 9 March 2020, when the S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index was down by 1941.67 points due to fears caused by the coronavirus pandemic and the Yes Bank crisis.
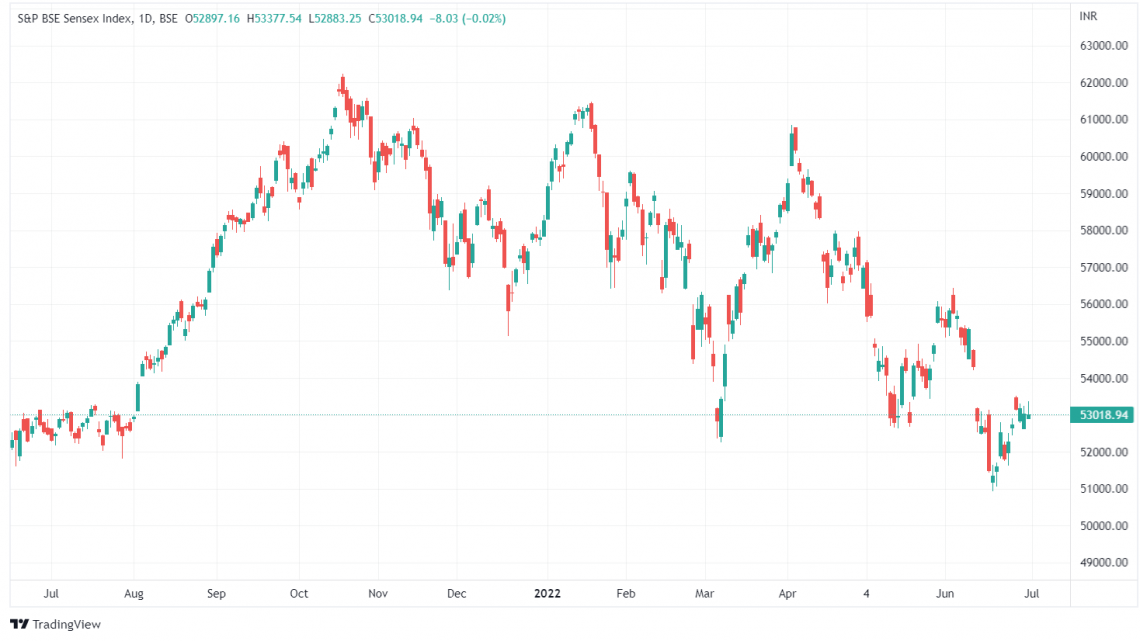
This chart represents the latest price chart (30 June 2022) of the S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index.
It has generated around 12-14% CAGR returns, meaning the investment value is 2x after every five years.
Criteria of Constituents of Sensex are:
- The company should be listed on India's Bombay stock exchange
- It should be a large to mega-cap company.
- The stocks should be relatively liquid.
- Revenue generated from core business activities should Consistently grow.
- Keeps that particular industry sector balanced and in line with the Indian equity market
- It should maintain the specific industry sector, balanced and aligned with the Indian equity market.
How Is Sensex Calculated?
Before getting into calculations, we should know specific terms, which are as follows:
1. Free Float:
It refers to the number of shares available for trading with the general public or which can be actively traded on secondary markets.
For example - If company A Ltd has issued 10,000 shares. Out of which, 4,000 shares are with promoters and government bodies, and 6,000 shares are available for trading. So , the percentage of free-floating shares are = 6,000/10,000 = 60%.
So 60% or 6,000 shares are available as free float shares for the trading of A Ltd.
It is the market value of the total outstanding shares of a company. The formula calculates it -
Market capitalization = current market price of one share * company's outstanding shares
3. Outstanding Shares:
It refers to the aggregate number of shares the company issues to its shareholders, retail and institutional investors, and shares held by promoters and insiders.
4. Calculating Sensex:
In the beginning, it was calculated by weighted average distribution based on each company's market capitalization method. But since September 1, 2003, as per new guidelines, it is now estimated by the free-float method.
It uses free float rather than outstanding shares, which means it doesn't include shares held by promoters, insiders, CEOs, etc.
Follow the specific steps which are mentioned below:
The top 30 companies are selected as per the S&P Bombay Stock Exchange Sensitivity Index criteria
Calculating the market capitalization of these 30 companies
Calculating the free-float market capitalization of these 30 companies
Aggregate or sum the free-float market capitalization of all 30 companies
After calculating all the items mentioned above, use the Sensex index formula to calculate the final value, which is given below-
Sensex index = Total free-float market capitalization/ base market capitalization * Base period (year) index value.
The base period ( year ) for calculating it is 1978-79.
And the value of the base index is 100.
SENSEX FAQs
The Bombay stock exchange (BSE) was established in 1875. Initially, it was named "the native share & stock brokers Association" in 1875. It is the oldest stock exchange in Asia and the world's 10th most prominent stock exchange, with a record order matching speed of 6 microseconds.
Sensex comprises 30 actively traded stocks on BSE.
1. Diversification - Investing in broad market index funds helps diversify funds invested, which reduces the portfolio risk to some extent.
2. Less expensive - it is a passively managed fund requiring very minimal fees. Lower expenses will increase returns earned through an investment.
3. Better returns - past performance of Indian indices, i.e., of nifty 50 and Sensex, reveals that the returns generated are slightly higher than that caused by Nifty 50.



or Want to Sign up with your social account?