Capital Gains Yield
The price growth of a security or an asset, such as common stock or bonds, over a specific time period
What Is Capital Gains Yield (CGY)?
The price growth of a security or an asset, such as common stock or bonds, over a specific time period is referred to as capital gains yield. This, for instance, would be 25% if an investment was bought for $100 and sold for $125.
It is a gauge of the return on investment a shareholder can anticipate from a security whose value has increased. In other words, it is the price difference between the beginning and end of the ownership period.
The percentage increase in the asset price since you initially purchased it is known as the capital gains yield. A capital gain on an investment is only conceivable if the price at which the asset is sold is higher than the price at which it was originally purchased.
In the event that the current asset price is lower than the acquisition price, CGY will be negative. A loss on the investment is considered to have occurred if the purchasing price is higher than the selling price.
Selling financial assets like stocks might result in a capital gain. When a stock is sold, the cost price is deducted from the sale price to determine if there was a capital gain or loss. A capital gain can be obtained by selling physical assets such as houses, apartments, or land.
A capital gain may be earned through the sale of intangible financial assets such as bonds.
If the bond's selling price is higher than its purchase price, the investor will have realized a capital gain. On the other hand, if the bond's selling price is lower than its purchase price, the investor will have suffered a capital loss.
Key Takeaways
- Capital Gains Yield (CGY) represents the percentage increase in the price of a security or asset over a specific time period.
- CGY provides insight into the return on investment solely based on the appreciation or depreciation of the asset's value.
- Stocks with high price volatility may yield high CGYs, offering the potential for above-average returns, but they also carry higher risks.
- Combining capital gains yield with dividend yield gives the total return on investment.
Understanding Capital Gains Yield
CGY is equal to the total return if there are no cash flows from the investment. It is predicted by seeing how much the price of an asset is expected to go up or down. Its true value is the percentage change in the market price of the asset over time. If the value of a stock, for example, goes down, that is a capital loss.
The performance of an investment using CGY is determined purely by the change in its price; dividends are not taken into account in this calculation. However, depending on the company, dividends could represent a bigger percentage of overall return than capital gains.
Because it is solely reliant on the market value of the company, the rate of change yield is the metric with the highest level of volatility. The capital gains yield calculation is used to quantify the return on a stock that is exclusively based on the stock's appreciation.
This tool is very useful when attempting to estimate returns on investments that do not generate cash flows in a format that simulates cash flow returns. It is crucial for investors since it displays the return on investment associated with capital growth.
A stock with a high degree of price volatility may be a high-risk investment. The investor may be able to earn above-average returns, but there is a chance that, if the price drops, things could turn out differently.
A valuable tool for investors looking to determine the prospective return on their investment is capital gains yield, commonly referred to as the "rate of change formula." An investor can use this to determine whether securities are wise investments.
However, it is essential to keep in mind that the rate of change yield is just one of the many factors that should be taken into account whenever decisions about investments are being made.
Other aspects of security, such as its dividend yield and its price-to-earnings ratio, can also be extremely helpful in gaining important insight into the possible return that the investment may produce.
How to Calculate Capital Gains Yield
The calculation of CGY can provide useful information regarding the risk associated with an investment. The more capital gains during a given time period (indicating superior stock performance), the higher the share price for that particular time frame.
As mentioned previously, this is also known as a rate of change formula, and depending on the original and current purchase prices, it can be positive, negative, or a capital loss.
Capital gain is the portion of the total return on an investment that happens as a direct result of an increase in the market price of the securities that were originally invested in.
CGY calculation is connected to the Gordon growth model, which is used to calculate stock value based on a series of perpetuity payments that grow at a constant pace.
The asset's sale price and its acquisition price are both factors that influence the predicted return on the asset.
-
The higher the sale price, the higher the expected return.
-
The lower the purchase price, the higher the expected return.

Where,
- P0 = Original price of the security
- P1 = Current market price of the security
1. When capital gains yield is positive, and stock value is increasing
Sam purchases a share at $100 (market value). A year passes while he owns the stock, and during that time, the market price of Tesla stock rises to $150. Sam determines that the time is right to sell the shares. What would his yield be?
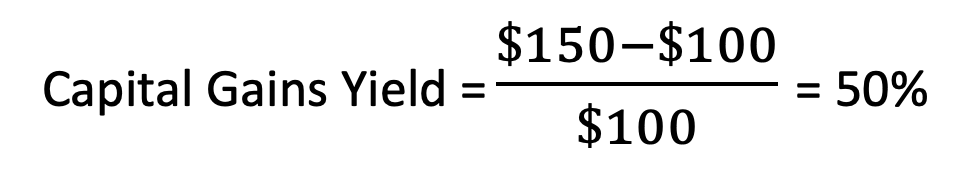
2. When it is negative, and the stock value is falling
Two years ago, John invested in shares in a retail business, paying $67 per share. Due to the shift in consumer purchasing habits brought about by internet shopping, the share's current market price has dropped to $41, and John anticipates a further reduction. What are his yields if he sells now?
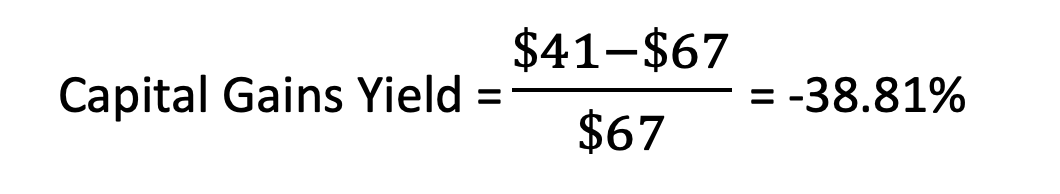
Due to the falling stock price, there is no capital gain in this instance; instead, there is a capital loss of 38.81%.
Examples of Capital Gain Yield
The yield on capital gains is the rate of price growth of an investment. It is calculated as the rise in an investment's price divided by the cost of the investment at purchase.
When we wish to determine how much return we will obtain based only on the appreciation or depreciation of stock, we use this formula.
Apple CGY 2022
The closing price of Apple shares on July 16, 2021, was $146.39 per share. The stock's closing price on July 15, 2022, was $150.17 per share. The company's CGY for the year is, therefore, ($150.17- $146.39) / $146.39 = 2.58%
IBM CGY 2022
The price per share of Google stock was $132.67 when trading was closed on July 16, 2021. The price of one share of stock was $139.92 at the market's closure on July 15, 2022. Therefore, the company's CGY for the year is 5.46% because ($139.92- $132.67) / $132.67 = 5.46%.
Ford CGY 2022
On July 28, 2021, the price of a share of Ford stock was $13.86 at the close of trading. The price per share was $13.9 at the market's close on July 28, 2022. As a result, the CGY for the year for Ford is ($13.9 - $13.86)/ $13.86, which equals 0.9%.
CVS CGY 2022
On July 16, 2021, the price of a share of CVS stock was $81.72 at the close of trading. The price per share was $95.37 at the market's close on July 15, 2022. As a result, the CGY for the year for CVS is ($95.37 - $81.72)/ $81.72, which equals 16.70%.
Capital Gains Yield vs. Dividend Yield
Investors looking to assess the performance and possible returns on their assets must comprehend the differences between dividend yield and capital gains yield.
Although they reflect different characteristics of investment income, both indicators are essential for evaluating an investment's soundness and profitability. The main distinctions between dividend yield and capital gains yield are shown in the following table.
| Aspect | Capital Gains Yield | Dividend Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage increase in the price of an asset over time | Percentage of dividends paid out relative to stock price |
| Calculation | (Current Price - Purchase Price) / Purchase Price | Dividend per share / Stock's purchase price |
| Source of Profit | Profit from selling shares or assets | Profit from regular dividend payments |
| Frequency of Income | Realized upon selling the asset | Regularly distributed by the company to shareholders |
| Tax Implications | Taxed based on holding period and applicable tax rates | Taxed at different rates depending on dividend type and tax status |
| Complementary to | Combined with dividend yield for total return assessment | Combined with capital gains yield for total gain yield assessment |
| Impact on Total Return | Contributes to the total return on investment | Contributes to the total return on investment |
| Considerations | Reflects price appreciation; doesn't consider dividends | Reflects dividend income; doesn't consider price changes |
Example
Let's look at an example to understand this better. Alex invested in Google, which had a market value of $50 per share at the beginning of the year. The company's market price at the end of the year is $60 per share.
Google also pays a $20 dividend per share to its shareholders.
As a result, Alex's capital gains yield is ($60-$50)/$50 = 20%
The dividend yield is $20/$50 = 40%
Therefore, the total profit that Alex would make from an investment in Google is (20%+40%) = 60%.
Summary
CGY can be erratic as a gauge of investment performance. Similar to this, many stocks have low CGYs but high dividend yields. This occurs because every dollar that a corporation distributes as dividends prevents it from being reinvested in further expansion.
Other stocks may generate significant capital gains but pay little or no dividends. If the corporation is reinvesting capital in the business, these may be labeled growth stocks.
As a result, capital gains yield is an important indicator that all investors must understand.
Having said that, one should constantly keep in mind the restrictions of the potential profit from capital gains.
To be more specific, considering that capital gains yield does not take into account income obtained from dividends or interest, this metric should not be used as a blind substitute for the computation of total return.
Capital gains yield shows the price appreciation of a security over a given time period. As a quick review of what capital gains yield is, it is important to keep in mind the following:
-
It doesn't apply to dividends; it only applies to stock price growth.
-
Capital gains yield can be positive, negative, or a capital loss.
-
In the calculations of the Gordon growth model, CGY serves as the constant growth rate variable g.
-
Investors may be required to pay capital gains tax, though this can sometimes be offset or carried over to the next quarter.
Capital Gains Yield FAQs
In the United States, the "realization of a capital gain" occurs when an individual sells a capital asset in order to make a profit. This action is referred to as a "realization of a capital gain," and the individual is required to pay tax on the gain.
The length of time that an asset was held and the amount of income earned by the taxpayer both have a role in determining the tax rate that applies to capital gains. Capital losses may be used to offset capital gains.
Short-term capital gains are assessed and taxed as ordinary income if an asset was held for less than a year before being sold for a profit.
Long-term capital gain is defined as the profit made from the sale of an asset that was kept for more than one year before being sold for a profit. Inflation-adjusted income criteria are used to determine long-term capital gains tax rates.
It's possible for the value of a company's shares to shift for reasons that have nothing to do with the underlying company's performance or its capacity to pay dividends. The following are examples of some of these factors:
-
Interest rates and inflation
-
Confidence in a market or economy among investors
-
Index fund purchasing and selling requirements
-
The amount of time that the security is kept in one's possession
The primary distinction between current yield and capital gains yield is that capital gains yield is solely concerned with price appreciation and does not take dividends into account. When calculating the current yield, both the dividends and the price of the investment are taken into account.
The rate at which a given investment produced returns or appreciated is measured using the rate of change yield.
A bond's current yield is a gauge of the income the bond is now generating. The current yield for a bond is calculated by dividing the investor's yearly interest dividend by the bond's current price
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:







or Want to Sign up with your social account?