Net Profit Margin
Used to determine how much net profit is generated as a percentage of revenue
What Is Net Profit Margin?
Net profit margin is used to determine how much net profit is generated as a percentage of revenue. It determines how much net profit an organization generates for each new dollar of total revenue.
It is known as profit margin and pressed as a percentage of sales revenue left over after operating expenditures, depreciation, amortization, interest, and income taxes have been subtracted from total revenue.
Profit margin is a significant indicator that reflects the company's financial status as it calculates the company's profits after paying taxes on each dollar of sales.
This ratio informs you how profitable your company has been throughout the past period.
It is a valuable metric for investors to evaluate a company's profitability. In addition, it is used for assessing a company's performance against the industry.
This indicator can show if a company is doing a better or worse job at managing its expenditures compared to the industry average. In other words, this ratio reflects the overall performance of a company.
A high net profit margin shows that the company can control its operating costs and set appropriate product prices. Conversely, a low profit margin indicates that the company has difficulty managing its operating expenses and doesn’t price its products correctly.
A corporation can evaluate the effectiveness of its current operations and make profit anticipations based on revenue by keeping an eye on changes in its net profit margin. Therefore, it helps to compare competitors' performance in the same industry.
It is helpful to compare the outcomes of firms operating in the same industry since they are subject to the same business environment and challenges. The raw material, overheads, and labor costs are also comparable.
Net profit margin formula
The net margin formula enables Investors to determine whether a company's management can generate a sufficient profit from the company's sales and whether the firm's operational and overhead expenditures are under control.
The profit margin is calculated by dividing net income by revenue and multiplying the answer by a hundred. Higher ratios indicate the company has greater cost control resulting in improved financial health.
Net profit margin = (Net income / Revenue) *100
Net income (NI)
Net income determines what business is left over after paying all expenses through a period. It is completely different from gross income, which only deducts the cost of goods sold from revenues.
Net income = Revenue - Cost of goods sold - Interest - Tax - Operating and other expenses.
As the formula shows, there are key metrics that you must understand since they help to calculate net income.
The key measures are as follows:
Revenue
Revenue determines the amount of money a business’s operations have generated over a specified period. A company's revenue is its whole income before any costs are deducted.
Revenue = Number of units sold * Price per unit
Cost of goods sold (COGS)
The cost of goods sold (COGS) is the total amount of direct expenses connected to a product's production.
It is listed on the manufacturing income statement and typically includes the money spent on labor and raw materials and any amortization expenses.
COGS = Beginning inventory + Purchases during the period - Ending inventory
Interest (I)
Interest is the cost of borrowing money or the fee charged to borrowing money from banks or financial institutions. It is expressed as the annual percentage rate (APR) that lenders expect to receive from borrowers.
Tax
Tax is a sum of money people are required to pay to a government according to different factors, including income level, property value, etc. The government imposes taxes to fund government spending and public expenditures.
Operating and other expenses
Selling, general, and administration expenses (SG&A) are the expenditures associated with operating a business as selling, general and administrative expenses. They also consist of expenses on marketing, computer equipment, employee benefits, rent, and utilities.
-
Selling expenses include distribution, selling, and marketing expenses.
-
General expenses include utilities, postal charges, supplies, and computer equipment.
-
Administrative expenses include salaries, benefits, and wages.
Examples of net profit margin
Example 1
Suppose company LYC reports the following numbers for one year ending December 31, 2021:
-
Revenue: 200 units.
$1000 for each unit sold.
-
Cost of goods sold = $40,000.
-
Operating expenses = $20,000
-
Tax expenses = $30,000.
-
Interest expenses = $10,000.
Calculate the NPM of the company.
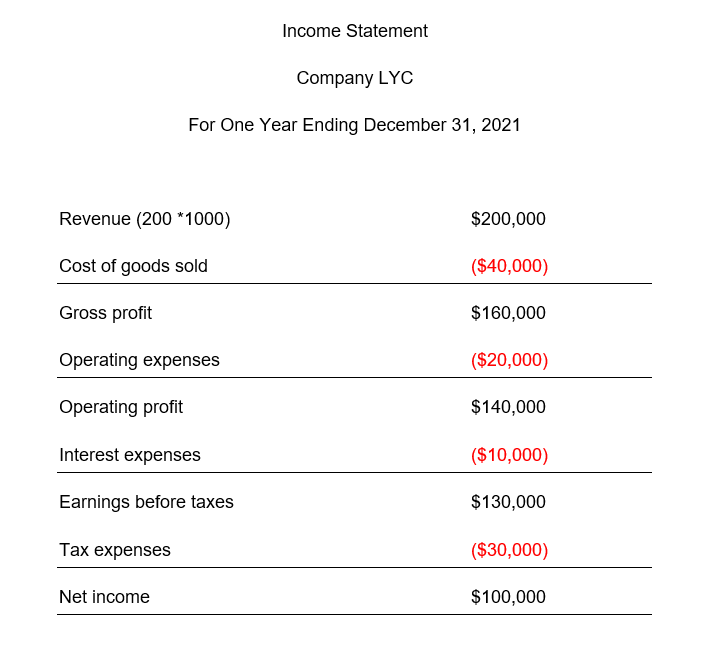
Net profit margin = (Net income / Revenue) *100
NPM = ($100,000 / $200,000) * 100
NPM = 0.5 * 100
NPM = 50%
Example 2
LYC and TYL achieved a net profit of $90.50 and $80, respectively. Both businesses have an NPM of 23%. How much revenue did each company generate?
Net profit margin = (Net income / Revenue) *100
Revenue = Net profit / Net profit margin
Revenue of LYC:
Revenue = $90.50 / 23%
Revenue = $393.48
Revenue of TYL:
Revenue = $80 / 23%
Revenue = $347.83
Hence, LYC firm makes 1.13% more revenue than TYL company.
Example 3
Suppose company TYL reports the following numbers for one year ending December 31, 2021:
- Revenue = $1,000,000
- Cost of goods sold = $300,000
- Management and office salaries = $300,000
- Marketing = $50,000
- Debts = $2,000
- Office and general supplies = $10,000
- Insurance = $7,000
- Maintenance = $5,000
- Utilities = $1,000
- Interest = $30,000
- Depreciation = $40,000
- Taxes = $10,000
Compute the NPM of TYL company.
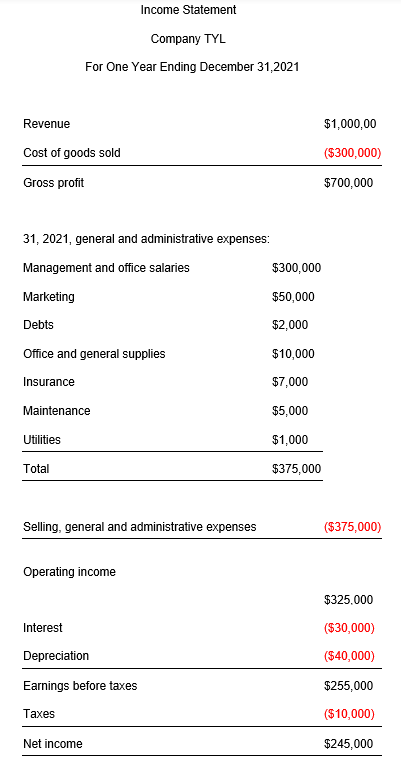
Net profit margin = (Net income / Revenue) *100
NPM = ($245,000 / $1,000,000) * 100
NPM = 0.245 * 100
NPM = 24.5%
In example 1, LYC had a profit margin of 50% compared to 24.5% of TYL. This means LYC can better control its operating costs and set appropriate product prices.
The question is how TYL company can improve its net profit margin to get stronger against its competitors in the same field. Companies can use different strategies to improve their profit margin, such as reducing expenses and enhancing sales volume.
How to improve net profit margin
The goal of all companies is to improve net margin, as it is one of the most critical evaluation measures in the market. There are different ways to increase profit margin, including but not limited to:
1. Improving inventory visibility
The capacity of a company to understand its current inventory, status, and the location at which it is stored. Inventory includes goods and raw materials for sales or used to generate new products.
Customers also rely on the visibility of your inventory to locate and purchase the products they desire at any of your locations. However, there are simple steps a company can take to improve its inventory management, including but not limited to:
-
Record accurate details upon transactions to increase data accuracy.
-
Invest in inventory management software that provides insight throughout the entire organization to ensure that it helps track things across all your stores and online marketplaces.
-
Tracking the movement of items through the warehouse and fulfillment regions requires using mobile scanners.
-
Regular inventory reviews weed out irregularities and better track demand.
2. Increase the value of your products
Find ways to increase the value that customers think your brand can offer. You can accomplish this goal by putting your attention on the psychological and lifestyle benefits that your products have to provide customers with.
To increase sales, products must meet and exceed customers'.
3. Reduce the expenses
Lowering operating costs can occur by decreasing the workforce and relocating the factory to a less expensive place by downsizing the factory space. Another way to reduce operating expenses is by expanding the production capacity.
Once you expand the production capacity means that you need more raw materials. Purchasing a high raw material rate enables you to get discounts from wholesalers, which means you get more raw materials at a lower cost.
In other words, expanding production means lower expenses and higher sales revenue that eventually help to drive profitability.
Net profit margin limitations
The net profit margin is a helpful indicator, but it does have some drawbacks that should be considered.
Profit margin drawbacks include but are not limited to:
-
It is not a valuable metric for comparing organizations operating in different businesses. Comparing companies in the online retail industry with companies in the soft beverage industry isn’t logical, as each industry has an average profit margin.
In other words, comparing profit margins for companies in different industries leads to meaningless insights. Once investors evaluate, companies in various sectors must avoid this metric as it leads to useless results.
Keep in mind that low profit margins aren’t necessarily bad for the company, as some companies sacrifice their margin and decrease their product prices to increase their market share.
Example
Suppose a tech company reports the following numbers for one year ending December 31, 2021:
-
Revenue: 200 units.
$1000 for each unit sold.
-
Cost of goods sold = $40,000.
-
Operating expenses = $20,000
-
Tax expenses = $30,000.
-
Interest expenses = $10,000.
Also, the food company reports the following numbers:
-
Revenue: 200 units.
$100 for each unit sold.
-
Cost of goods sold = $13,000.
-
Operating expenses = $3,500
-
Tax expenses = $900.
-
Interest expenses = $200.
Calculate the profit margin of the two companies and compare their profit margins.
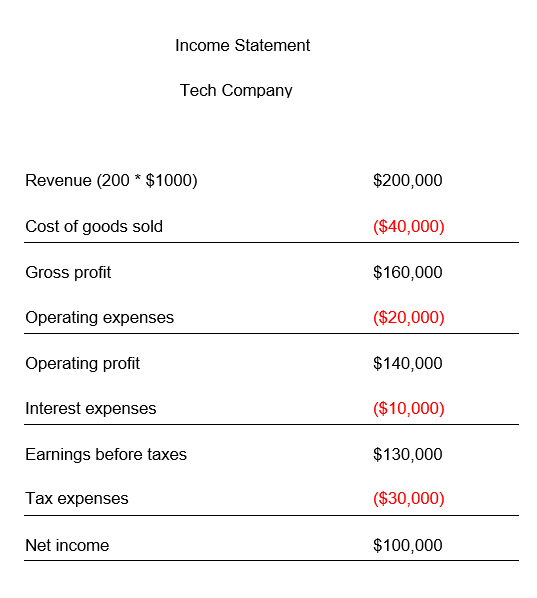
NPM = ($100,000 / $200,000) * 100
NPM = 0.5 * 100
NPM = 50%
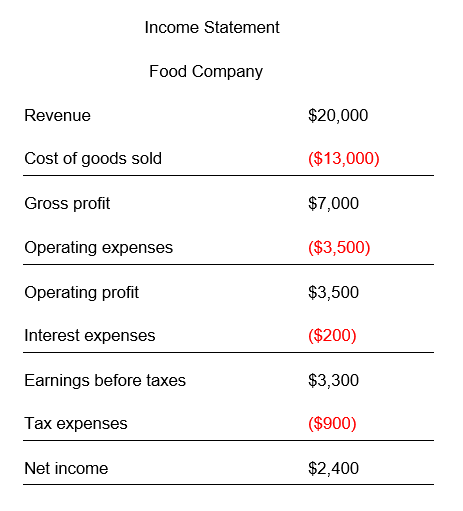
NPM = ( $2,400 / $20,000) * 100
NPM = 0.12 * 100
NPM = 12%
As shown, the tech industry's profit margin is far higher than the food company's margin. Hence, it’s not proper to compare these industries as their production and manufacturing expenses are entirely different.
-
The net margin might fluctuate substantially between reporting periods due to the market variables. Selling assets can temporarily increase income, resulting in a net margin expansion.
Net margin Vs. Gross Margin
Your company's gross margin and net margin can provide information regarding your business's profitability and its standing in the industry.
Keep in mind that considering these two metrics helps evaluate company performance and obtain more profound insights into company growth and development.
In other words, using only one metric to evaluate your business provides a partial picture of business profitability. Even though these metrics aid in evaluating business growth, they are distinct and use various methods to measure growth.
Gross margin concerns the amount of profit that remains after the COGS has been subtracted, while net margin differs from your gross margin in that it considers how much profit you retain after taxes for each dollar of revenue you earn.
Profit margin
A company's net margin, also known as the profit margin, is a metric that determines what percentage of a company's net income is created from the company's revenue.
Profit margin is a percentage of a company's revenue after deducting its operating expenses. Company profit margin is calculated by dividing net income by total revenue and multiplying by a hundred.
Net profit margin = (Net income / Revenue) *100
To better understand this metric, you can read the first section of this article, as it includes different real-world examples with deep explanations.
Gross margin
Gross margin, also known as gross profit margin, provides you with an overall picture of the effectiveness of a company's operations.
To better use, compute your gross profit margin for different periods at set intervals and look at the numbers you get over time; if the percentages of your margins do not change, your company is doing well financially.
The gross profit margins of your business can be compared to those of your competitors to determine whether or not your organization is functioning at the same levels as its competitors.
A company's margin is higher than its competitor's; it operates at a higher efficiency level.
On the other hand, if your business margin is lower than its competitors, the company needs to change in terms of sales, expenses, and pricing of products to line up with other competitors in the same industry.
Gross margin is always expressed as a percentage and calculated by getting the difference between the total revenue and cost of goods sold and then dividing that by total revenue and multiplying the result by a hundred.
Gross profit margin = {(Total revenue - Cost of goods sold) / Total revenue} * 100
Example
Suppose TYL company, during the most recent quarter, generated $10,000,000 in sales and $5,000,000 in selling costs. Compute the company's gross profits.
Gross profit = {($100,000,000 - $50,000,000) / $100,000,000} * 100
Gross profit = {$50,000,000 / $100,000,000} * 100
Gross profit = $0.5 * 100
Gross profit = 50%









or Want to Sign up with your social account?