10-K
A Form 10-K is a legally required report that all public companies must file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) within 60 days of a company’s fiscal year end. This report provides a comprehensive rundown of a company’s business operations, financial performance and audited financial statements. The form has much more detail and information then the annual report which a company sends to shareholders prior to annual meetings to elect directors.
The form contains pretty much everything about a company that an investor would want to know when making a decision to buy or sell shares of the stock, or for assessing the credit quality for investment in corporate bonds. These documents are free to access and can be downloaded from a company’s website and from the SEC’s EDGAR database. Here is what EDGAR looks like when you search a company:
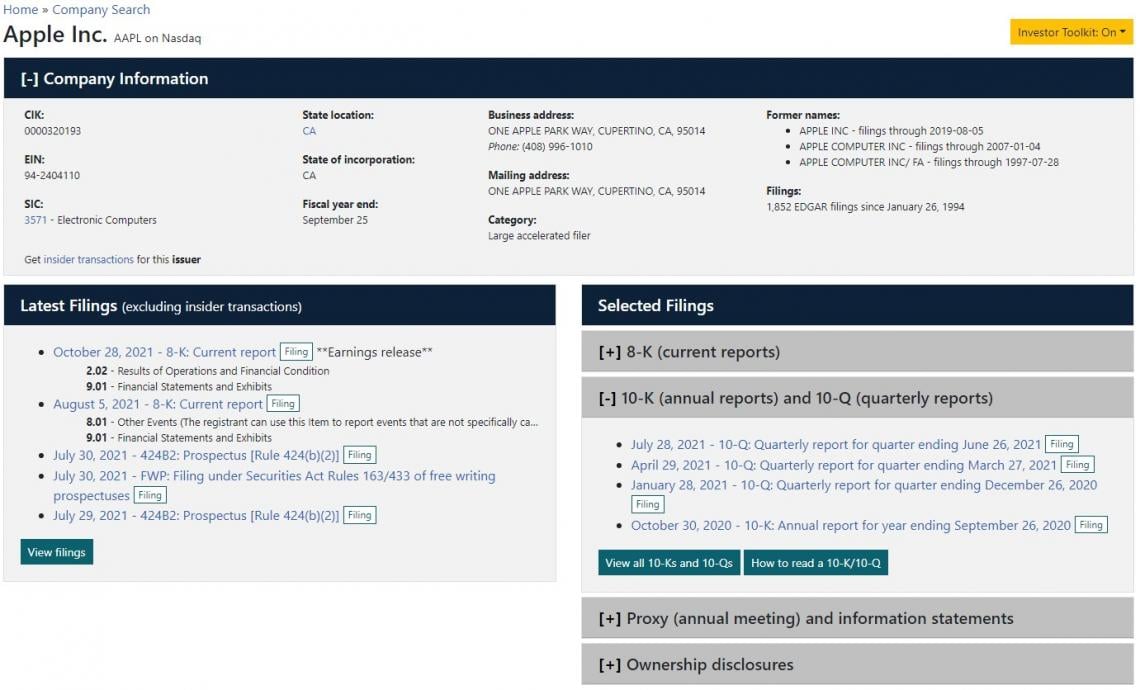
What is included in a 10-K
This report is very comprehensive and as such includes a lot of useful information. There are 5 basic sections in the report:
- Business - This section gives a high level overview of the primary operations of a company. It includes the primary source of revenue such as products and services
- Business Risk Factors - This section outlines the risks associated with the operations of the company and can be current or future risks. These are also typically ranked in the order of importance
- Selected Financial Data - This section lets the company highlight specific financial information about the company over the past 5 years. It typically presents a short-term view of financial performance.
- Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A) - This section gives company management a chance to discuss and explain its performance during the last fiscal year and go into further detail about key performance drivers and guidance on future expectations
- Audited Financial Statements - This section provides specifics on financial performance of the company in the current and prior fiscal years. A letter from the independent auditor is also included and certifies the accuracy of the information presented. The 3 core financial statements included in the report are the:
These are the 5 primary sections of the form. The more information provided by a company’s management in the report the better for investors as they can get a better understanding of the company and are able to make a more informed decision on whether or not to invest. The report also includes signed letters from the CEO and CFO of the company who’ve sworn under oath that the provided information is accurate.
10-K Examples and Annual Reports
To get a feel for what these reports look like, below is a list of recent 10Ks and annual reports from a few of the most popular publicly traded companies. Both the official link to a recent SEC filing and a link to their annual report is included:
- Tesla 10K | TSLA Annual Report
- Google's | Alphabet Annual Report
- Amazon's 10K | AMZN Annual Report
- Facebook's | FB Annual Report
- Apple's 10K | AAPL Annual Report
- Goldman Sachs | GS Annual Report
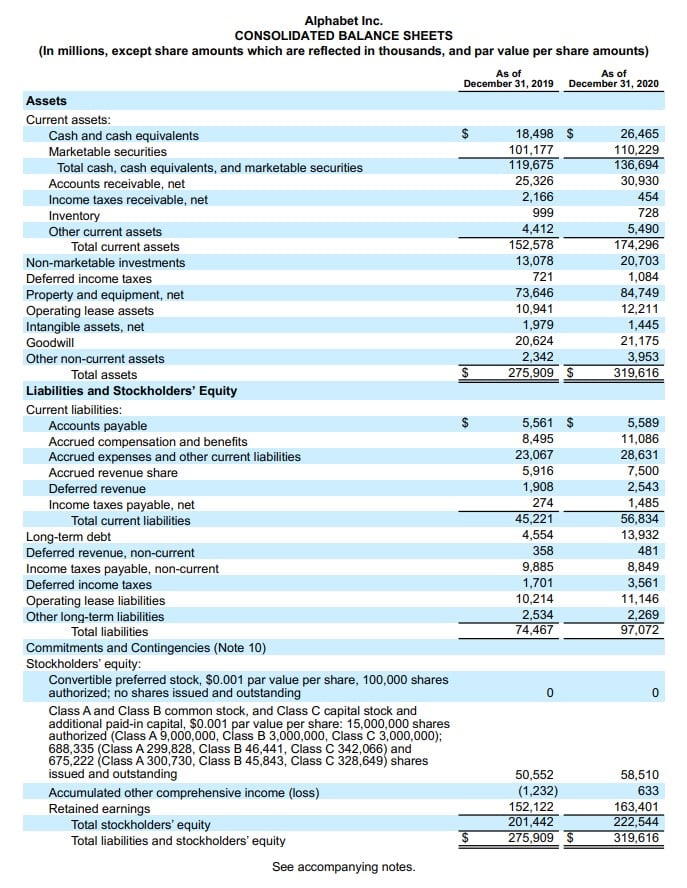
Below is what the Balance Sheet looks like in the filing for Alphabet Inc.
Annual Report Differences
Both of the documents overlap in a lot of key areas but do still have significant differences. An annual report is a much more visually appealing document and is meant to be easily digestible by shareholders. If you’ve ever looked at an annual report you’ll notice right away that it is far easier to read with plenty of pictures and graphs that visualize financial performance over time.
Annual reports typically also include:
- A letter from the CEO,
- A brief history of the company,
- Major divisions, subsidiaries, and general operations
- Detailed financial statements.
A stark difference between the 2 reports is the strict guidelines required by the SEC on how information is presented and organized, with no pictures or charts.
Here is a letter to shareholders from Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos that was included in the company's annual report

Where to Find the Reports
These reports are filed annually with the SEC and are public information. They can be found in many places with companies more often than not including a copy of their filing in the investor relations section of their website where you can also find the Annual Report.
The SEC also has a database called EDGAR where you can access the filings of any public company for free. Another option is to use API providers like Finnhub Stock API, which directly feeds data into your financial models.
Who Uses a 10K?
This form is a long and comprehensive document. As such, it provides information for a lot of stakeholders. This list includes investors to make fully informed decisions on whether to buy or sell shares in the company, and provides management an outlet to explain the results in more detail.
Investors and Analysts
These documents contain some of the most detailed information about a company an investor or analyst could use, making it the first place they often go to understand a business’s operations, its structure, and financial performance. It provides investors with current and historical information to help forecast future growth and value the company.
Management
The MD&A section of the report is useful for management as they are able to go beyond the numbers and provide explanations for their results and actions. For example, if a company issues bonds to raise capital, they can provide more insight on the proposed project and how it will provide value to the business.
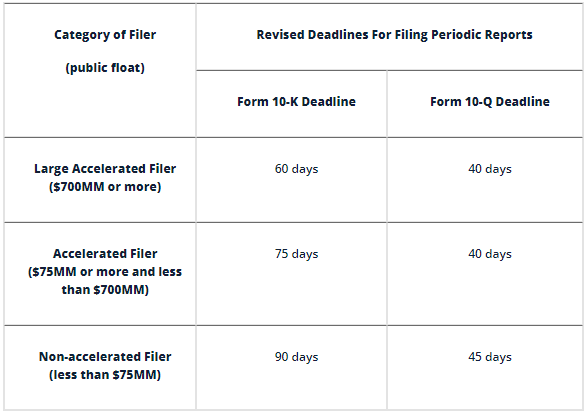
Filing Deadline
Filing deadlines are dependent on the size of the company and its public float. SEC guidelines for filing say that companies with a public float of $700m or more have 60 days from their fiscal year end date to file their report. Companies with float between $75 million and $700 million have 75 days. Companies with less than $75 million float have 90 days.
10K vs 10Q
These are both similar documents in that they are reports on the state of publicly traded companies. The main difference is the frequency of the reports, the 10-Q is filed every quarter (hence the Q). The 10-Q also does not require companies to have an auditor examine and verify the financial statements. The 10-Q form must be filed within 40 days of the fiscal quarter end. There are 3 quarterly reports filed and the results of the 4th quarter are included in the annual filing.
What is an 8-K?
The form 8-K is not a regularly filed document with the SEC. Instead the 8-K is reserved for major events for which company shareholders must be made aware. Events that require an 8-K filing include, but are not limited to:
- Election of executives
- Delistings
- Departures
- Changes in company control
- Bankruptcy
- Information about operations
- Acquisitions
The 8-K is not necessarily a bad filing, however it is filed as the information to be presented is expected to have a material effect on the operations of the business, either positive or negative. As such, investors must be aware of the events.
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:




or Want to Sign up with your social account?