Merger
The willful combination of two organizations based on comprehensively equivalent conditions into one new legitimate element
What Is A Merger?
The expression "merger" alludes to the conjoining of two elements to frame another substance. It is basically the blend of two separate elements into a solitary, legitimate substance. In the corporate world, a few kinds have various goals, such as:
-
Expanding into new markets
- Growing the organization's goals
- Acquiring more of the current market share
Some examples are as follows.
Congeneric
The consolidation of Broadcom and Mobilink Telecom Inc. in 2002 illustrates concentricity.
Both substances were from the hardware business. Thus, it is permitted for them to consolidate their specialized skill.
Market Extension
The consolidation of RBC Centura and Eagle Bancshares Inc. in 2002 illustrates market expansion.
It permitted RBC to extend its tasks in the North American market.
Conglomerate
The consolidation of ABC Inc. and Walt Disney Co. in 1995 illustrates a combination.
ABC Inc. took part in the transmission broadcasting company, while Walt Disney had a place with media outlets.
Horizontal
The consolidation of Hewlett-Packard (HP) and Compaq in 2001 illustrates a flat consolidation.
The consolidation brought about the making of a worldwide innovation pioneer that was esteemed at more than $87 billion.
Vertical
The consolidation of Time Warner and AOL in 2000 illustrates an upward consolidation.
Time Warner was in the data business through CNN and Time Magazine, while AOL appropriated data over the web.
Key Takeaways
- Mergers refer to the combination of entities to create a stronger new company.
- Mergers include Congeneric, Market Extension, Conglomerate, Horizontal, and Vertical.
- Mergers are performed by voluntary unions of similar-sized firms for growth.
- There are benefits like market share, and economies of scale, but risks of slow growth and communication issues.
- Bear hugs, brand power, and strategic alliances are takeover methods. Notable examples include Tata Motors and Jaguar Land Rover, Facebook, and WhatsApp.
How does Merger work?
It is the willful combination of two organizations based on comprehensively equivalent conditions into one new legitimate element.
The organizations that consent to combine are generally equivalent concerning:
- Measures
- Clients
- The size of the tasks
Hence, the expression "mergers of equivalents" is at times utilized. In contrast to consolidations, acquisitions are not deliberate and include one organization effectively buying another.
These are generally done to:
- Acquire a piece of the pie
- Diminish activities expenses
- Extend to new regions
- Develop incomes
- Increment benefits — all of which should help the organizations' investors.
After a consolidation, portions of the new organization are disseminated to existing investors of both unique organizations.
A shared asset was made because of an enormous number of consolidations, allowing financial backers to benefit from consolidation bargains — called The Merger.
Fund from Virtus Investment Partners. The asset catches the spread or sum left between the proposition cost and exchanging cost.
It puts resources into organizations that have freely reported a consolidation or takeover. As a result, the store has returned 5.8% every year since its origin in 1989. This is the intentional mix of two elements into one new lawful substance based on indistinguishable conditions.
Regularly, elements that choose to go into a consolidation understanding are estimated of equivalent size with regard to the size of tasks.
It is sometimes known as the "Merger of equivalents."
Most of these are done to:
- Grow new domains
- Acquire a portion of the overall industry
- Reduce working expenses
- Extend the top line
- Boost benefits
Post-consolidation, the new combined element portions are given to the current investors of both the blending substances. This is done on:
- A money premise
- A stock premise
- A mix of both
In a money consolidation, the objective substance is bought by getting the element in actual money. In contrast, in a stock consolidation, the supplies of the objective element are bought in return for loads of the securing substance.
Differences between merger and acquisition
A merger is the most common way of consolidating at least two elements to shape another substance. During this process, the monetarily more grounded substance assumes control over the portions of the monetarily more vulnerable element.
These outcomes are in a genial circumstance after the industry life cycle as the choice is taken after conversation and arrangement between the consolidating elements.
Then again, procurement frequently brings about a turbulent environment after the cycle as, by and large, the choice isn't common, which gives way to antagonism and frenzy.
Generally, the organizations that go into a consolidation understanding are of equivalent height, and consequently, they can draw the advantages of collective energy.
In a securing merger, the getting organization frequently forces its will on the gained organization bringing about an obvious power slope.
Both strategies seek expansion and are often helpful for corporate restructuring and other growth strategies.
| Aspect | Merger | Acquisition |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Creation of a new legal entity | Keeps the other company as a separate legal entity |
| Financial Arrangement | Stakeholders receive a proportional exchange of shares | Involves the payment of cash, stock, or both |
| Management | Usually shared by both companies | The acquiring company maintains control of the target company |
| Purpose | Achieve synergy | Expanding market share, decreasing competition, accessing new markets |
|
Risk |
Challenges blending two different cultures, systems, and processes | Less cultural integration required |
Both strategies are potential tools for expansion and corporate restructuring. The choice between each strategy hinges on multiple factors, from legal structuring to potential culture-blending risk.
Understanding the disparities between strategies is pivotal for anyone looking to shoot a shot on M&A.
Advantages and disadvantages of Merger
Some of the advantages are:
- If elements are contending in a similar market, the merger between them assists them with acquiring a more significant market share.
- A few organizations go for consolidation as it offers the advantage of economies of scale that decrease the expense of tasks.
- These outcomes in income development, on occasion, squeeze into the goal of a portion of the organizations that need to accomplish inorganic income development.
- For organizations that find it challenging to venture into different geologies, this assists them with extending their tasks to one more planet region without setting themselves up in another market or geology.
On the other hand, the disadvantages are:
- In a portion of the cases, it has been seen that the development pace of the recently blended element is lower than that of the consolidating substances.
- The course of correspondence and coordination among the workers of the blending organizations can be a complex undertaking.
- This frequently brings about a more significant element that might participate in imposing a business model.
Merger Takeover methods
As the name implies, takeover methods are strategies an acquiring business uses when bidding to buy another company - the target company.
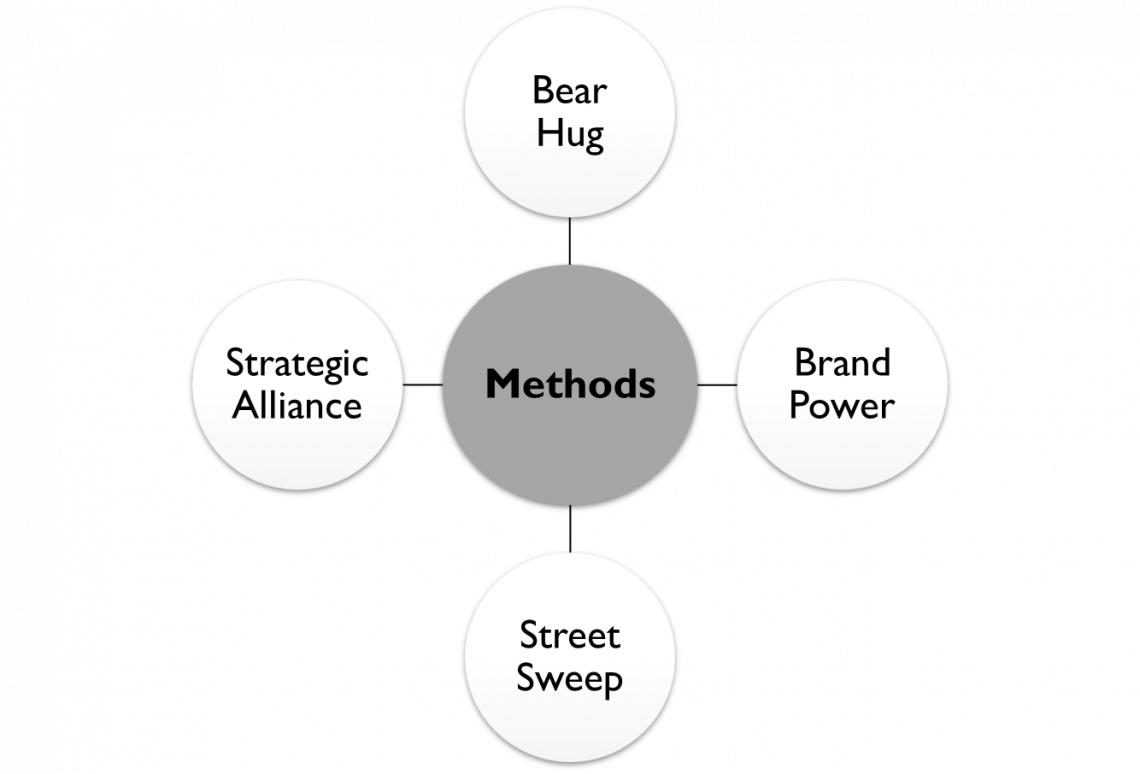
- Bear Hug: Like a bear, the acquiring corporation threatens the target by making an open bid to be acquired.
- Brand Power: Facebook's acquisition of Whatsapp represents an alliance with big brands to replace the target's brand(s) and strengthen one's position.
- Street Sweep: This brilliant approach entails infiltrating the opposing camp and compromising it from within! Before making an open offer for purchase, the purchasing corporation collects a substantial number of shares in the target company.
- Because the purchasing business already holds many shares, the target company has little alternative but to sell itself.
- Strategic Alliance: A well-planned purchase to boost one's market position – more of a joint venture – a mutually beneficial collaboration (like Air India and Star Alliance, Vistara = Tata Sons, and Singapore Airlines!) rather than a buyout. Recent vital mergers and acquisitions include:
- Jaguar Land Rover Co. was purchased from Ford by Tata Motors in 2008.
- Facebook bought Whatsapp K (a U.K. company), which generated a lot of headlines.
- Star Alliance and Air India (German Group).
- Sun Pharmaceuticals purchased Ranbaxy Laboratories.
- Now Daiichi Sankyo (a Japanese company) is selling Sun Pharma shares that it acquired when Sun acquired Ranbaxy.
- Vistara is a joint venture between Tata Sons and Singapore Airlines.
- Microsoft purchased Nokia.
- Flipkart acquired Myntra.
- Network 18 was purchased by Reliance Industries Limited, which owns the company's bulk.
Conclusion
It tends to be seen as a vital business procedure, as it is an essential strategy to grow a business, naturally and inorganically, to support the continually developing business sector.
Many small and large businesses favor this tactic to compete or survive in today's market. Enterprises that are losing money or are tiny always desire to merge with larger companies to save money and gain market share.
Mergers, on the other hand, often fail due to a lack of adequate planning and tactics. As a result, both organizations should do rigorous research and analysis to ensure their ideas succeed.
Rather than broadening their company, it allows firms to concentrate on their core competencies and review and analyze their market share. As a result, leading corporations began to restructure their operations to have a presence in the critical sectors of their operations.
These are some of the most successful corporate restructuring instruments and have become an important element of company plans.
Before commencing the process, it is recommended that attorneys be consulted when determining the target firms.



or Want to Sign up with your social account?