YIELDDISC Function
It calculates the annual yield of a discounted security.
What is the YIELDDISC Function?
The YIELDDISC function stands for discounted yield. With that being said, the YIELDDISC function uses a discounted security to calculate the annual yield.

When calculating the annual yield of a discounted security, consider it useful for bills, treasuries, or commercial papers.
For the reasons stated, these would be instances where you can use the YIELDDISC function. However, if there is no dividend payment on the security, the YIELDDISC function cannot compute the annual yield.
There are a couple of other Excel functions to find similar investment returns. The first and most obvious of functions is the YIELD function which also calculates the annual yield of interest-paid security.
Second, the NOMINAL function can determine a security’s nominal yield. The nominal yield is the coupon rate of a security’s face value.
Furthermore, the article will discuss the formula, a breakdown of each component needed in calculating the annual yield, and an example to follow through on an Excel worksheet.
Key Takeaways
- The YIELDDISC function calculates the annual yield of a discounted security.
- The settlement date and maturity date must be entered as serial numbers
- The redemption component of the function is the value of the traded security
- The basis, an optional input, must be a numerical set of one to four
- Two other functions closest to the YIELDDISC function are the YIELD function and the NOMINAL function
YIELDDISC Function Formula
To begin, calculate the annual yield by following the formula in an Excel worksheet:
YIELDDISC(settlement, maturity, pr, redemption, [basis]).
Further breaking down the formula, let’s better understand what is required to properly calculate and utilize the function.
settlement: The “settlement” variable of the function considers the settlement date at which the security was traded. Typically, the settlement date noted is the date following the security purchase and is a required part of the function.

- maturity: Next, and another required aspect of the YIELDDISC function, is “maturity.” This variable is the security’s expiration date.
- pr: Following is the “pr”, a required variable that accounts for the security’s face value price.
- redemption: Lastly, one of the required variables is “redemption,” which serves as the redemption value of the traded security.
- [basis]: One optional input of the YIELDDISC function is “basis,” as noted in brackets. The basis will measure the day count of the security use.
NOTE
It calculates the annual yield of a discounted security.
Try one of our educational courses to continue practicing enhancing your Excel skills in data formatting and functions.
YIELDDISC Function example
With a new Excel sheet open, input the necessary variables (settlement, maturity, pr, redemption, and basis if needed).
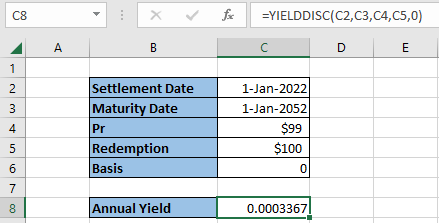
The discounted security is considered a long-term security of thirty years in the example pictured above. Therefore, with a settlement date beginning in early January 2022, the expiration date of the thirty-year security is inputted for January 2052.
In addition, the price or “pr” component is valued at $99, while the redemption value equals $100. Finally, as noted previously, the basis is optional; for this example, the basis is entered as zero.
When entering a numerical value for the basic component, remember that values of one, two, three, and four are only acceptable. Any value less than one or greater than four will return an error when utilizing the YIELDDISC function.
The annual yield returns 0.0003367 or 0.03% with all variables inputted correctly.
The highlighted cell in C8 also displays the YIELDDISC function broken down to include the necessary components.
NOTE
Remember that the settlement date and maturity date are structured as serial numbers and can be organized as so using the DATE function.
If a #NUM! Error value is returned, and one or more values may be inputted incorrectly if:
- The “settlement” value is greater than the “maturity” value
- The “pr” or “redemption” values are less than zero.
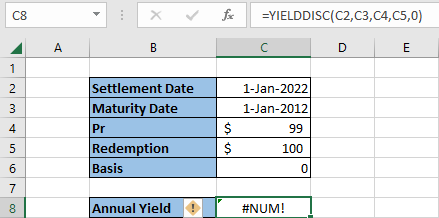
In this example, you may notice the maturity date entered occurred before the settlement date, which is impossible to calculate and, as a result, returns an error of #NUM!
Reviewed & Edited by Ankit Sinha | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:




or Want to Sign up with your social account?