McKinsey 7S Model
A tool that assesses organizational design by examining seven key elements for achieving performance.
What Is The McKinsey 7s Model?
The McKinsey 7-S Model is a tool that evaluates a company's "organizational design." Its purpose is to portray how an organization's performance may be accomplished through the interplay of seven main elements:
- Structure
- Strategy
- Skill
- System
- Shared Values
- Style
- Staff.
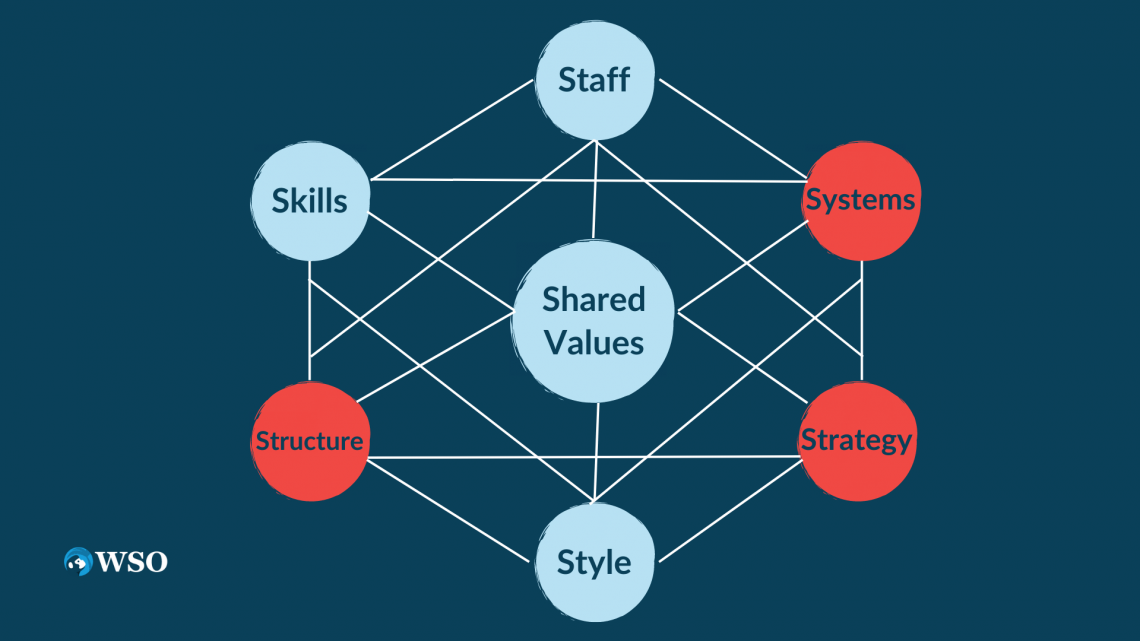
The concept is based on the premise that these seven factors must be aligned and mutually reinforcing for an organization to operate successfully.
As a result, the model may be used to determine what needs to be realigned to increase performance and keep alignment (and performance) during other sorts of change.
Regardless of the type of change such as:
- Restructuring
- New procedures
- Organizational mergers
- New systems
- Leadership changes, and so on
the model may be used to understand how organizational parts are interconnected and to ensure that the wider impact of changes made in one area is considered.
The interconnection of the aspects described by "Soft Ss" and "Hard Ss" is the emphasis of the McKinsey 7-s Model, suggesting that altering one element has a cascade effect when maintaining an effective balance.
The importance of the influence of changes in founding values on the other parts is shown by placing "Shared Values" as the "center."
The 7-S model may be applied to a number of circumstances in which it is beneficial to study how various components of your business interact.
It can, for example, assist you in improving your organization's performance or determining the best method to implement a particular plan.
Key Takeaways
- The McKinsey 7-S Model evaluates organizational design by considering seven key elements: Structure, Strategy, Skill, System, Shared Values, Style, and Staff.
- Alignment and mutual reinforcement of these elements are crucial for successful organizational performance.
- The model helps identify areas for realignment and improve performance during various types of organizational changes.
- The interconnection between "Soft Ss" (Shared Values, Style, and Staff) and "Hard Ss" (Structure, Strategy, Systems, and Skills) emphasizes the importance of maintaining an effective balance.
- The model can be applied to various situations, such as improving performance, implementing plans, or studying the interactions between different components of a business.
Structure of the McKinsey 7-S Model
McKinsey's model has seven components that are separated into two groups: hard S elements and soft S elements.
1. Hard S elements
-
Strategy
-
Structure
-
Systems
2. Soft S elements
-
Style
-
Staff
-
Skills
-
Shared values

Soft S elements are often more difficult to edit than hard S components, which is why you should work on both groups at the same time.
You will not only be able to identify possible problems before they occur, but you will also be prepared to respond to them if you create an organizational change management strategy that includes all seven components.
It will be easier to build a strategy for implementation that does not derail if your organization understands how each of these Ss influences the whole structure and system of the firm.
1. Structure
Structure describes how company divisions and units are organized and provides information about who is responsible for what. In other terms, structure refers to the company's organizational hierarchy. It's also one of the framework's most visible and changeable aspects.
2. Strategy
A strategy is a plan devised by a company to get a competitive edge and compete effectively in the market. In the 7-s McKinsey model, what does a well-aligned strategy imply?
Generally, a solid strategy is well-articulated, long-term, contributes to competitive advantage, and is backed up by a strong vision, purpose, and values.
Note
When studied alone, it's difficult to establish if such a technique is well-aligned with other factors.
So, under the 7-s model, the idea is to look at your organization to see whether it has a fantastic strategy, structure, processes, and so on, rather than to see if it is aligned with other parts.
For example, a short-term plan is often a bad choice for a business, but if it is linked with the other six aspects, it may provide excellent outcomes.
3. Systems
Systems are the company's processes, and procedures that disclose how decisions are made and everyday tasks are carried out.
The section of the company that dictates how business is done is called systems, and it should be the primary focus of managers throughout the organizational transformation.
4. Skills
The talents that a company's personnel excel in are referred to as skills. Capabilities and skills are also included. During organizational transformation, the question of what capabilities the firm will require to support its new strategy or structure emerges frequently.
5. Style
The way top-level managers run the organization, how they communicate, what actions they do, and their symbolic worth are all represented by style. In other words, it refers to the leadership style of the company's executives.
6. Staff
The staff element addresses the type and number of people a business will require and how they will be recruited, trained, motivated, and rewarded.
7. Shared Values
The McKinsey 7s approach is built around shared values. They are the norms and standards that influence employee conduct and corporate operations and are thus the bedrock of every firm.
Application of the McKinsey 7-S Model
Because of the subjectivity surrounding the idea of alignment in relation to the seven main factors, this approach appears to have a difficult implementation.

However, a top-down approach is recommended, including everything from broad strategy and common values to style and personnel.
Step 1: Identify the areas that are not effectively aligned
The goal of the first stage is to examine the 7-S elements and determine if they are successfully aligned with one another.
Normally, you should be aware of how your company's seven aspects are aligned, but if you aren't, you may utilize WhittBlog's checklist to find out. After you've answered those questions, check for any gaps, inconsistencies, or flaws in the links between the pieces.
For example, you may have devised a strategy that relies on rapid product introduction, but the matrix structure's competing linkages obstruct this, resulting in a conflict that necessitates a shift in strategy or structure.
The following checklist questions will help you explore your situation.
Strategy
-
What is the goal of your business strategy?
-
How are you going to do this with your current resources and capabilities?
-
What distinguishes you from your competitors?
-
What strategies do you use to compete in the market?
-
How do you intend to adjust to changing market conditions?
Structure
-
What is your company's organizational structure?
-
Who is in control of the decision-making process? Who is in charge of whom?
-
Do you make decisions in a centralized or decentralized manner?
-
How do you get your employees on board with the strategy?
-
How is information shared throughout the organization?
Systems
-
What are the organization's main procedures and systems?
-
Where are the system controls, and what do they do?
-
How do you keep track of your progress?
-
What are the procedures and guidelines that the team follows to stay on track?
Skills
-
What are the organization's fundamental competencies? Are these abilities widely available?
-
Do you have any skill gaps?
-
How do you evaluate and enhance your skills?
-
What is it that the firm is well-known for?
Staff
-
How many staff do you have?
-
What are your current staffing needs?
-
Are there any resources that are missing?
-
What should be done to deal with them?
Style
-
How would you describe the managerial style?
-
How do employees react to this management style?
-
Do your staff work in a competitive, collaborative, or cooperative environment?
-
What duties, habits, and deliverables do the leadership encourage?
-
What kind of teams does the company have? Is it true that there are genuine teams, or are they merely fictitious groups?
Shared Values
-
What are the organization's mission and vision?
-
What do you consider to be your ideal and true values?
-
What are the foundational principles of the organization?
-
What are the company's plans for incorporating these principles into everyday operations?
Step 2: Determine the optimal organization design
The second phase, with the support of senior management, is to figure out what kind of successful organizational design you want to attain.
You can define your objectives and develop action plans much easier if you know what alignment you want.
Note
For several reasons, this phase is more difficult than establishing how your organization's seven areas are now linked.
First, you must determine the optimum ideal alignment, which you do not yet know, which necessitates more than simply answering the questions or gathering data.
Second, you won't be able to utilize any templates or established organizational designs, so you'll have to perform a lot of research or benchmark to find out how other comparable firms dealt with organizational change or what organizational designs they employ.
Step 3: Decide where and what changes should be made
This is essentially your action plan, outlining the areas you wish to realign and how you intend to do it.
If you discover that your company's structure and management style are not in line with its values, you must decide how to reorganize reporting relationships and which top managers the company should let go or persuade to change their management style so that the company can function more effectively.
Step 4: Make the necessary changes
Implementation is the most crucial stage of any process, change, or analysis, and only well-implemented changes yield positive results.
As a result, you should employ consultants or discover personnel inside your firm who are most equipped to make the adjustments.
Step 5: Continuously review the 7-s
Strategy, structure, processes, skills, staff, style, and values are all dynamic and change on a regular basis.
Changes in one aspect always have an impact on the others, necessitating the implementation of new organizational design. As a result, it is critical to check each region on a regular basis.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the McKinsey 7-S Model
The advantages of the model are:
-
When the firm's fundamental components are aligned with its vision, the business will be able to achieve its goals more effectively.
-
The strategy aids in bringing disparate divisions and procedures into alignment, particularly during mergers and acquisitions.
-
The management can examine the effects of changing corporate culture, policies, strategies, structure, and technology over the company, as well as the systematic execution of the rules, regulations, and strategies established by top management.
-
Using the 7-S model is a comprehensive approach since it looks at each and every one of the seven aspects and how they relate to one another.
-
This model has not only been theoretically established but it has also been tested and utilized in the field of company management.

The disadvantages of the model are:
-
The 7-S model is a strategy used for the long term. It would not provide much result if it is aimed at achieving a short-term goal.
-
It is not clear how the approach of the 7-S model will adapt to the dynamic nature of an enterprise.
-
It appears to be dependent on internal aspects and procedures, which might be problematic in cases when external influences have an impact on an organization.
Example of McKinsey's 7-S model
Here's how McDonald's employs McKinsey's 7-S model to drive organizational change:

1. Strategy
McDonald's was able to achieve a large market share by following a cost-cutting strategy. It also establishes SMART objectives to fulfill the long- and short-term visions.
2. Structure
McDonald's, unlike other multinational corporations (MNCs) with complicated hierarchical systems, has a flat organization where employees are managed by a shop manager. Employees operate as a close-knit group and have quick access to top management.
3. Systems
McDonald's is noted for always innovating to cut wait times and improve the efficiency of its whole production and supply chain, such as its new Mcdonald's app and self-ordering kiosks.
4. Shared Values
With its core principles of:
- Serve
- Inclusion
- Integrity
- Community
- Family
McDonald's seeks to have a high degree of integrity, serve a diverse variety of customers, hire people from all backgrounds, foster collaboration, and lastly, donate some profits back to the community.
5. Style
McDonald's employs a participatory leadership style in which senior executives solicit feedback from employees at all levels in order to improve operations and manage issues.
6. Staff
McDonald's is one of the world's largest employers, with approximately 210,000 employees. It is committed to employee happiness and believes in the notion of diversity.
7. Skills
McDonald's personnel are routinely trained to deliver an exceptional customer experience and address disputes.
Conclusion
The McKinsey 7-S Model may be used in a number of circumstances when it's important to understand how different sections of an organization interact. It may be utilized to help determine future company strategy decisions.

The framework may also be used to assess the potential consequences of future organizational changes, as well as to align departments and procedures after a merger or acquisition. Individual teams or projects can benefit from elements of the McKinsey Model.
The model is most commonly used as a tool for organizational analysis to examine and track changes in an organization's internal condition.
This is because the 7-s tool firmly thinks that organizational principles are important in growing a business and that all other factors are framed around this issue.
To successfully execute any form of change inside a company requires a lot of effort. At the same time, don't anticipate too much to change in a short period of time.
To avoid overwhelming your staff with too many changes at once, continue with caution and make sure you're going at a sensible pace.
Remember, the more work you put into understanding your organization's current situation, the easier it will be to make improvements in the future.
Researched and authored by Tanay Gehi | Linkedin
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:



or Want to Sign up with your social account?