Top Banks in the Czech Republic
It has 10,7 million inhabitants, and its size is 78,871 km sq.
Czech Republic is a country situated in the center of Europe, bordering Germany, Poland, Austria, and Slovakia. It has 10,7 million inhabitants, and its size is 78,871 km sq.

It belongs to the group of Central and Eastern European Countries and, specifically, Visegrad Group countries. The capital is Prague, one of the most beautiful historical sites in central Europe.
As part of Czechoslovakia, the Czech Republic had a form of a communist economic system and a one-party government of the Communist Party until 1989. Following the Velvet revolution in 1993, the Czech Republic became independent.
After becoming independent, it underwent extreme decentralization and economic transformation from central planning to a market-based economy. The process of privatization also affected the banking system in the country.

The “Dancing House” symbolizes the Czech Republic’s awakening after totalitarian rigidity.
The Czech Republic is an active member of the international community. It became a member of NATO in 1999, together with Poland and Hungary.
It joined the European Union in 2004. However, it has not accepted the Euro as its currency yet. The currency is the Czech Crown (CZK).
Currently, the Czech Republic is a medium-sized, export-driven, open economy. In 2016, Czechia became a new short-form name for the country.
Almost 90% of the export goes to the other countries of the European Union. There are several companies founded in the Czech Republic that are well-known worldwide.
One of them is Bata, a shoe producer with current headquarters in Switzerland. Also, the car maker Skoda, owned since 1991 by German Volkswagen, is a vital car manufacturer in Europe.
There are other critical Czech companies well-known internationally, such as Ceska Zabrojovka (firearms), Avast (IT), and Fermat (industrial equipment).
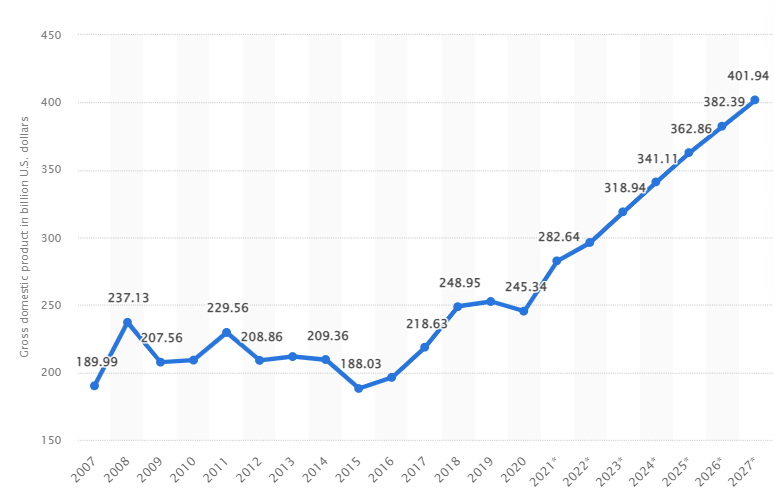
The GDP of the Czech Republic between 2007 and 2015 had a decreasing trend. However, since 2016, the country's total output has been growing, with estimated doubled values between 2020 and 2027. The chart below illustrates the GDP developments from 2007 to 2027 in billions of US dollars.
GDP of the Czech Republic (2007-2027*estimated) in billion US dollars
What is the banking system in the Czech Republic
Czech Republic has a banking system consisting of one central bank and several commercial banks. However, this was not always the case, and the system was highly centralized in the past.
The process of centralization started after the Second World War when the central bank took over the rights and obligations of all the existing commercial banks at that time.
The monopoly kind of banking system did not work and lasted only a few years. In the 1950s and 1960s, the more rational Czecho-slovakian financial system started to be formed.
The system underwent a de-monopolization process, transforming into a two-tier banking system. After the Czech Republic and Slovakia's separation, the Czech National Bank (CNB) was established in 1993.
The two-tier banking system represents a structure where the central bank is responsible for issuing licenses to the commercial and overlooking the banking system.
On the day of the separation of Czechoslovakia on January 1, 1993, the Czech National Bank and the Slovak National Bank replaced the State Bank of Czechoslovakia.

The Czech National Bank acts according to the national law (Act No. 6/1993), which gives it a mandate and responsibilities to
- maintain price stability,
- maintain the financial stability and the soundness of the Czech financial system,
- issue banknotes and coins of the Czech Crown, that is the national currency, and
- supervise all the institutions (banks and other related entities) that have operations on the financial market.
Types of banks in the Czech Republic
The table below shows the number of banks and branches of foreign banks in the Czech Republic in June 2022.
| Type of banks | Number (in June 2022) |
|---|---|
| Central bank | 1 |
| All the banks and branches of foreign banks | 51 |
| Out of which | |
| Domestic banks | 27 |
| Out of which, Specialized banks | 2 |
| Domestic home savings banks | 6 |
| Savings cooperatives | 5 |
| Credit cooperatives | 1 |
| Branch of foreign banks | 24 |
In the middle of 2022, 51 licensed banks were operating in the Czech Republic, including retail and wholesale banks. Savings and credit cooperatives are popular in the country, as they developed from a local traditional banking form called “kampelicky.”
Kampelicky was a folk name used for the local credit unions or credit cooperatives operating in the country since the 19th century.
The father of the credit union's idea was a Czech national thinker Mr. Kampelik. However, his idea was not taken by the local people, who held on to their savings at home.
After the death of Mr. Kampelik, a German economist Mr. Raiffeisen started to establish credit unions all over Germany and Europe. In the Czech Republic, they were called “raiffeisenky.”
Currently, these institutions operate as savings or credit cooperatives in the Czech market. In June 2022, there were six such institutions:
- Artesa
- Citfin
- Ceske Sporitelni Druzstvo
- NEY Sporitelni Druzstvo
- Penezni Dum
- Podnikatelsky Druzstevni Zalozna

The law from 2018 requesting all the traditional loan offices with total assets above 5 million CZK to apply for a banking license contributed to the recent growth of the banking system in the Czech Republic. Therefore, several of those offices transformed into a bank in 2019.
The newest additions to the Czech banking system are the two new banks that joined in the first half of 2022.
- AS Inbank, the digital bank with Estonian roots entered the market in June 2022.
- FCM BANK Prague specializes in corporate clients and joined the country's list of banks in April 2022.
As the output of the country has a growth outlook, the Czech banking market is expected to grow. Also, the growth of High-net-worth individuals from 78,450 in 2021 to a forecasted doubled number in 2026 can contribute to the sector's expansion.
What size are the banks in the Czech Republic?

Based on the size of the total assets, the CNB (n.d.) has divided banks since 2016 into three categories:
- Large banks (banks with total assets higher than 10 % of the total assets of the whole banking system).
- Medium-size banks (banks with total assets between 2 and 10 % of the total assets of the whole banking system).
- Small banks (banks with less than 2 % of the total assets of the whole banking system).
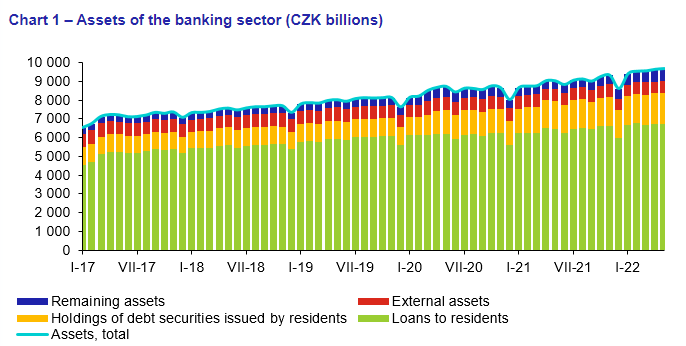
The total assets of the banking sector in 2020 were 8 139 billion CZK. The structure of the banking sector consists of
- 3 large banks,
- 7 medium-sized banks,
- 17 small banks, and
- 24 branches of foreign banks.
Also, the total assets of the banks in the Czech Republic have a growing trend. The chart below illustrates the assets’ growth between 2017 and 2022 in billions of CZK.
The list of the ten biggest banks (large and medium-sized banks) in the Czech Republic by total assets and the number of clients in 2020 is in the table below:
| # | Name of Bank | Owned (primarily) by | Total Assets in 2020 (in billion CZK) | Number of clients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large banks | ||||
| 1 | Ceskoslovenska Obchodni Banka (CSOB) | KBC Bank | 1756 | 2,06 million |
| 2 | Ceska Sporitelna | Erste Bank | 1538 | 2,8 million |
| 3 | Komercni Banka | Societe Generale | 1167 | 1,641 million |
| Medium-size banks | ||||
| 4 | UniCredit Bank Czech Republic and Slovakia | UniCredit | 664 | 450 000 |
| 5 | Raiffeisenbank | Raiffeisen CEE Holding | 411 | 680 000 |
| 6 | Hypotecni Banka | CSOB | 346 | Not known |
| 7 | Moneta money bank | JPMorgan Chase | 301 | 1,4 million |
| 8 | PPF Bank | PPF Financial Holdings | 273 | Not known |
| 9 | Fio Banka | P. Marsa and R. Kopun | 183 | 1,072 million |
| 10 | J&T Banka | J&T Finance Group | 175 | 50,000 |
What is the ownership of banks in the Czech market?
Like other post-communist countries, the Czech Republic went through a privatization process. Therefore, most banks are owned or co-owned by foreign financial groups. Twelve banks are owned by domestic owners, of which the state owns two.

Some of the domestically owned banks are in the table below, together with the owner's name:
| Name of the Bank | Owned by |
|---|---|
| Banka Creditas | P. Hubacek |
| Fio Banka | P. Marsa and R. Kopun |
| J&T Bank | P. Tkac and I. Jakabovic |
| Trinity Bank | R. Lapcik |
| Artesa (savings cooperative) | Artesa Capital (B. Koutnik) |
| Modra pyramida stavebni sporitelna | Komercni Banka |
| Citfin Banka | G. Kovacs |
| Ceska Exportni Banka | Ministry and agency of Czech Republic |
| Narodni Rozvojova Banka | Ministries of Czech Republic |
The two government-owned banks are specialized banks that focus on wholesale and support of the Czech economy. NRB (Narodni Rozvojova Banka) focuses on supporting entrepreneurs and the public sector. The Czech export bank helps Czech exporters to succeed in the international markets.
An interesting fact about the ownership of the Czech banks is that PPF financial holding is owned by the most wealthy person in the Czech Republic, Mr. Peter Kellner.
However, it is registered in the Netherlands. The group also owns several banks in the Czech Republic, such as Moneta money bank, Air bank, and Home Credit.
Furthermore, 468 foreign banks obtained a banking license in another country in the EU, offering their cross-border services to Czech clients. Those banks are operating on the single internal EU market.
Which are the top three banks in the Czech Republic?
The three biggest banks in the Czech banking market are
- Ceskoslovenska Obchodni Banka (CSOB)
- Ceska Sporitelna
- Komercni Banka
Ceskoslovenska Obchodni Banka (CSOB) is the biggest bank referring to total assets. It was established in 1964 to provide foreign currency and transaction operations. In 2020 its total assets were 1,756 billion CZK. It had 2,06 million clients and more than 200 branches.

CSOB belongs to the CSOB financial group, comprising more than 15 other financial institutions, such as domestic home saving cooperatives, insurance companies, and a small bank Hypotecni Banka.
It uses the branches of the Czech Post Office to distribute its products under the name of Postova Sporitelna.
CSOB financial group is a part of a bank-insurance integrated financial group KBC from Belgium. The core markets of KBC are
- Belgium
- the Czech Republic
- Slovakia
- Hungary
- Bulgaria,
- Ireland.
Considering the number of clients, Ceska Sporitelna would be the biggest bank in the Czech Republic. It had 2,8 million clients in 2020, with 1,538 billion CZK and more than 400 branches.

Ceska Sporitelna goes back to 1819, when it was established as a loan officer and later as a savings cooperative.
Currently, it belongs to the financial group of Ceska Sporitelna. The group comprises 14 other institutions, such as savings cooperatives or real estate companies.
Ceska Sporitelna group further belongs to the Erste Group. Erste Group was established in 1819 as the first Austrian savings cooperative. Currently, it covers markets of
- Austria
- the Czech Republic
- Slovakia
- Romania
- Hungary
- Croatia,
- Serbia.
The last large bank in the Czech banking market is Komercni Banka. It was established in 1990 with three other new banks and absorbed 50 % of the previous monobank, the State Bank of Czechoslovakia (Statni Banka Ceskoslovenska).
The primary role of these four new banks was to transform swiftly into universal commercial banks.
Komercni Banka also inherited all the State Bank of Czechoslovakia branches, which made the transformation easier. In 2001, the bank was bought by the French financial group Societe Generale. The Societe Generale group currently covers markets in 66 countries worldwide.
Komercni Banka offers services in retail, wholesale, and investment banking. In 2020 the bank’s total assets were 1,167 billion CZK, with 1,6 million clients. As a group, Komercni Banka also offers services in insurance or home saving.
The latest credit rating for the three biggest banks in the Czech Republic is in the table below (in July 2022):
| Bank | S&P | Moody's | Fitch |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSOB | A+ | A1 | n/a |
| Ceska Sporitelna | A | A1 | A |
| Komercni Banka | A | A1 | A |
Which are the three online-based banks in the Czech Republic
Even though people in the Czech Republic prefer the traditional way of banking, the self-service model of online banks is becoming increasingly popular.

It offers money savings, as most current accounts are provided without fees. Also, it saves time and is used mainly by younger customers.
There are three banks in the Czech market, either online-based or leaning toward being online-based. Those banks are
The first online bank in the Czech market was mBank. This Polish bank brought the model of self-service banking through internet application to the Czech Republic in 2007. The branches exist primarily as advisory centers.
Even though Fio banka does not claim to be an online-based bank, its services are online-based principally. The bank offers minimal personal contact with a few branches, allowing them to provide essential banking services free of charge to its clients.

Fio Banka is well known for being the first to offer Slovak and Czech clients online trading on international financial markets through a web-based application in 1997.
Air Banka was established in 2011 by the financial group PPF. It aims to provide innovations in online banking to become a friendly bank and offer its clients services conveniently.
The bank achieved 1 million clients in 2022. It provided the first voice-controlled application in the Czech language and the first mortgage request via mobile.















or Want to Sign up with your social account?