MAXIFS Function in Excel
It is an Excel function that returns the highest value of a range of cells within a multiple of a single criterion or constraint.
What is the MAXIFS Function?
The MAXIFS function is an Excel function that returns the highest value of a range of cells within a multiple of a single criterion or constraint. The function is categorized under Excel’s Statistical functions and was added to Microsoft Excel in 2019.
When using this function, several different criteria can be applied to the range of values, such as logic operators, dates, and special wildcard characters. These wildcards only work with text, not with numbers.
- (<,>,=)
- (?,*)
It is meant as a worksheet function (WS) and is typically used as a calculation in the cell part of a sheet.
Individuals can use several functions in Excel to generate the results they need. For example, here are two functions that give similar returns to Maxif():
- MINIFS(): Returns the minimum value in a range of conditioned cells.
- SUMIF(): Returns the sum of the values in a range of selected cells.
- AGGREGATE(): Can return either the maximum or minimum value based on what the user desires from a range of conditioned cells.
A separate range and criteria for every new condition is required.
Key Takeaways
- Empty cells are ignored when the function is searching the criteria.
- The function is only available for use in Excel 2019 or later versions
- The purpose of the function is to find the maximum value based on one or multiple criteria.
- The most common error that occurs is #VALUE!
- Max_range and criteria_range must ALWAYS be the same shape and size for the function to compute correctly.
- Excel is the easiest way to find the maximum value of a range of numbers according to conditions.
- The function can be applied daily to real-world examples.
MAXIFS Function Formula
To use the Maxif Function, it's essential to understand the purpose of the function.
The general purpose is to find the greatest value among a range of values within conditioned or criterion cells.
The syntax of the Maxifs Function in Excel is represented by
Maxif(max_range, criteria_range1, criteria1, [criteria_range2, criteria2], ...)
Let's break this down into pieces to understand it better:
- Maxif(): This is the required argument you will need to type into your cell on the sheet to begin the process of calculating your return.
- max_range: The required argument is the literal range of values entered that will be used to determine the maximum.
- criteria_range1: The required argument is the (first) set of values to be evaluated with the criteria.
- criteria1: The required argument is the (first) criteria to be used in criteria_range1.
- criteria_range2: An optional argument is the (second) set of values to be evaluated with the criteria.
- criteria2: An optional argument is the (second) criteria to be used on criteria_range1.
Each part of the argument is required for the function to compute correctly. The Maxif function can take up to 126 optional function pairs.
The Maxif function is one of the trickier Excel functions since the logical expressions are split into ranges and criteria. The operators for the criteria must also be encased within quotes (“).
#VALUE! The error will be returned if the size of the max_range and criteria_range arguments isn't the same.
Note
The size of the max_range and criteria_range arguments must be the same
How to use the MAXIFS Function in Excel?
For all of our Maxif examples and explanations, we will refer to this Excel chart below that lists the range and criteria for different students in the school who were randomly placed into groups.
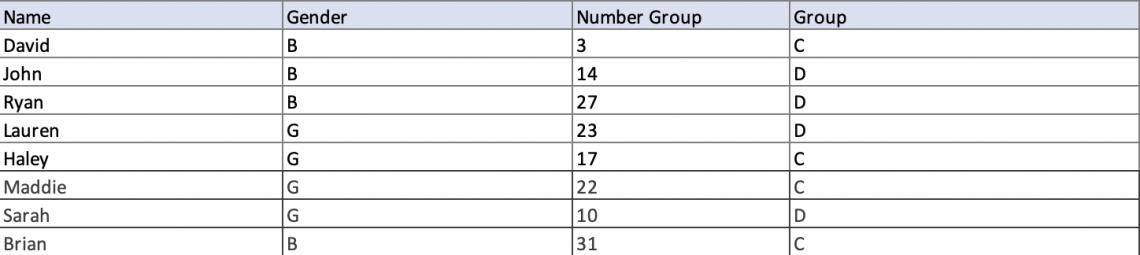
- Boys are represented by the letter B in the Gender column.
- Girls are represented by the letter G in the Gender column.
- The Number column represents the number of their class.
- The Group column represents the group each student was placed into.
Example 1: In this first example, let’s keep it basic and only use one criterion. Our objective is to find the maximum class value of boys by using the gender column and number columns.
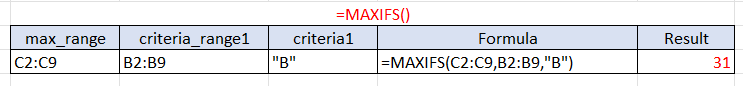
Our (max_range) in this scenario is a range of class numbers each student is in. This is where the maximum number that is returned comes from.
- 3
- 14
- 27
- 23
- 17
- 22
- 10
- 31
Our (criteria_range1) in this scenario is the range of boys and girls in the class where we want to find the maximum from.
- B
- G
Our (criteria1) is the criteria that define the first range of cells. The “B” translates to the maximum value from criteria_range1 for boys.
Our result shows that the highest class number of boys from this set of students is 31. We implemented each number in the correct arguments for our formula to find our outcome.
Example 2: We can use one more example with one criterion to ensure the syntax is fully understood. Our objective in this scenario is to find the maximum class number again based on the girls in the class instead of the guys.
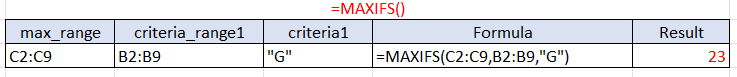
Our (max_range) in this scenario is the range of class numbers each student is in. This is where the maximum number that is returned comes from.
- 3
- 14
- 27
- 23
- 17
- 22
- 10
- 31
Our (criteria_range1) in this scenario is the range of boys and girls in the class where we want to find the maximum from.
- B
- G
Our (criteria1) is the criteria that define the first range of cells, making it so we are only choosing from the cells with a “G”. The “G” translates to the maximum value from criteria_range1 for girls.
Our result tells us that the highest class number of girls from this set of students is 23. We implemented each number in the correct arguments for our formula to find our outcome.
Example 3: For this example, since we now have a good understanding of how the arguments work, we can begin to implement two criteria. Our objective for this scenario is to find the largest classroom value of girls in group “C”.

Our (max_range) in this scenario is the range of class numbers each student is in. This is where the maximum number that is returned comes from.
- 3
- 14
- 27
- 23
- 17
- 22
- 10
- 31
Our (criteria_range1) in this scenario is the range of boys and girls in the class where we want to find the maximum from.
- B
- G
Our (criteria1) is the criteria that define the first range of cells, making it so we are only choosing from the cells with a “G”. The “G” translates to the maximum value from criteria_range1 for girls.
Our (criteria_range2) is the range of group each student was assigned to
- C
- D
Our (criteria2) is the criteria that define the second range of cells, making it so we are only choosing from the cells with a “C”. Our Results give us a return of 22. Meaning the highest class number of girls in group C was 22.
Example 4: Another way to use the Maxif function is by applying criteria that aren’t text to the argument. This includes logical operators such as (<,>,=), and And (&) operators. Our objective in this scenario is to find the maximum class number of girls same as (NOT EQUAL to “B”).
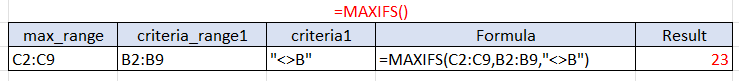
Our (max_range) in this scenario is the class number which we want to find the maximum from.
- 3
- 14
- 27
- 23
- 17
- 22
- 10
- 31
Our (criteria_range1) in this scenario is the range of boys and girls to whom we are applying the criteria to.
- B
- G
Our (criteria1) makes it so we are only choosing from the cells with a that does not equal “B”. Therefore, we are finding the maximum number group for “G”.
Our result tells us that the highest class number of girls from this set of students is 23. We implemented each number in the correct arguments for our formula to find our outcome.
This is also a different way to set up the formula in example 2 because we are looking for the same results.
Other Ways to use MAXIFS Function
It is possible to refer to different cells as criteria in Excel. For this to work, the operator must be in between quotations (“”), and the value must be attached to a concatenation. This makes sense because concatenations combine values to create a string of text.
The following two formulas will yield the same result as the MAXIF function if you are using an older version of Excel that does not include this worksheet function:
- MAX() and
- IF()
MAX() and IF() formulas can be used in the same way as MAXIF() but with a bit more work. For example, if you wanted to use MAX() and IF() to find multiple criteria, the syntax would be:
=MAX(IF((criteria_range1)*(criteria_range2), max_range))
Wildcards may also be used as criteria (?*)
- Question marks in the criteria are helpful to match any single character, no matter the order (?).
- Asterisks in the criteria are beneficial to match sequences of characters selected (*).
Note
Cell references can be included as part of the criteria argument if the operator is attached to a concatenation (&).
MAXIFS Function's Common Errors
It’s really common to get repeated errors since this Excel function requires a lot of arguments. Errors can be frustrating, but they are helpful because they help communicate a restriction in the function. This, in turn, helps us understand how to use the function.
Here are some of the most common errors and misconceptions when using the MAXIFS Function:
1. #VALUE! Error
- The #VALUE! Error can occur with any function that requires the use of numerical values.
- This can occur if the strings matched are greater than 255 characters.
- This will occur if any text is entered into the formula.
- This will occur if the max_range and criteria_range arguments are not the same size.
- The #VALUE! Error is the most common error that occurs when using the MAXIF function.
2. TRUE OR FALSE
- TRUE will return the value 1, and FALSE will return the value 0.
- It can confuse users when either TRUE or FALSE is evaluated as a different value.
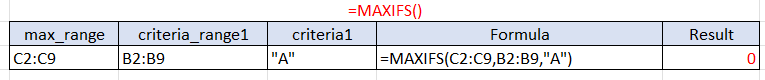
3. ZERO RETURN
- When no selected criteria matches the criteria_range, a 0 will be returned.
- Typically, it happens when a user misinputs the criteria_range with the criteria1.




or Want to Sign up with your social account?