Types of Due Diligence
Refers to an indispensable process that plays a critical role in any business deal or investment
What is Due Diligence?
Due diligence (DD) is an indispensable process that plays a critical role in any business deal or investment. Due diligence involves a meticulous and comprehensive investigation and verifying information about a particular matter to evaluate potential risks and benefits accurately.

The legal segment of DD requires a close and thorough examination of contracts, licenses, and any legal disputes to ensure that the company is operating lawfully and to avoid any future legal liabilities that could potentially arise.
In addition, evaluating the company's financial standing and growth potential is crucial, and investors must undertake a comprehensive financial evaluation.
By evaluating the company's financial statements and financial records, we can assess the risks and future investment opportunities to gain wide insight into the company's production.
Many types of due diligence provide us with the company's internal and external interests and practices, such as a company's legal and regulatory status, commercial landscape, environmental regulations, assessing potential environmental risks, etc.
Operational analysis is another critical area of DD, and potential investors must subject the company's day-to-day operations to meticulous scrutiny. This includes management structure, production processes, and supply chain management.
Thorough investigations can yield long-term profitability and success for investors and ensure they have all the necessary information to make an informed decision.
As we got a basic idea of what due diligence means, we will now move toward our main topic.
Key Takeaways
- Due diligence (DD) is an essential process for investors, buyers, and businesses to verify information about a particular matter before making a deal.
- Involves a comprehensive analysis of financial statements and records.
- Thorough due diligence can lead to informed decisions, contributing to long-term profitability and success for investors.
- Due diligence is indispensable for a successful business deal or investment.
Types of Due Diligence
When it comes to investment decisions and analyzing a company according to that, it helps us gain profound enlightenment of the company's trade practices and interests.
We can evaluate a company's health, risks, issues, and product quality based on the type of DD.
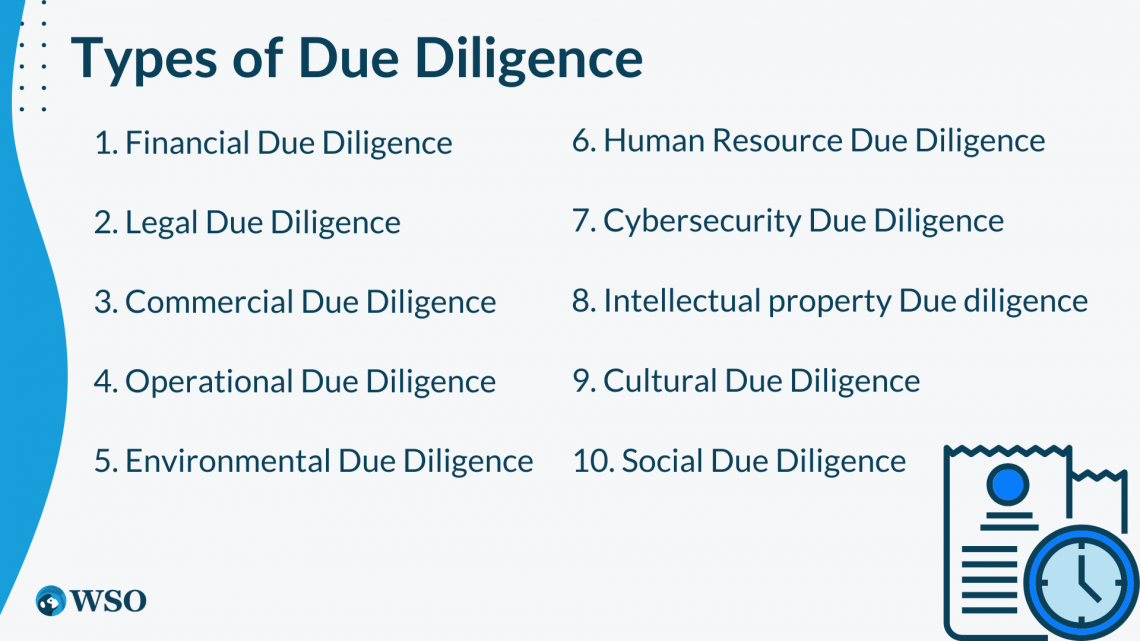
There are some common things we have to look into the company while analyzing it, such as its financial records and statements, environmental practices, operative administration, and the internal and external social variables that may impact future investment opportunities.
DD is the process of conducting an investigation before an investment. Now, we will look at some of the most common and essential types of DD that can be performed in general to find the company's health, future growth, and investment opportunities.
For more reference, you can watch this video:
Financial due diligence (FDD)
FDD is the process of reviewing a company's financial records and statements. It is common to know a company's financial position in the current market before investing in that particular company.
FDD can help an individual or group to access the company's financial health, financial risks, future growth of the company, and investment opportunities, which may occur based on a financial investigation of the company.
It helps the reviewer to understand the company's financial records and statements to find future investment opportunities.
During FDD, a reviewer must review the company’s financial statements, tax records, cash flow statements, accounts payable and receivable, and other financial records.
There are some primary objectives while performing FDD:
- Identifying potential risks and growth of the company.
- Evaluating the company's financial performance and ability to create sales and profits.
- Evaluating the accuracy of financial statements.
- Assessing the company’s risk management.
- Identifying investment opportunities.
Legal due diligence (LDD)
LDD has different approaches to accessing investment opportunities in the company.
When considering an investment in a company or business venture, performing and going through the company's legal and regulatory status is essential to find the risk factors and future growth.
The main motive behind LDD is accessing a firm's legal issues that could impact the investment decision.
The reviewer must go through the company's contract, leases, permits, licenses, and other legal papers while looking for investment opportunities. The reviewer can also do background checks on essential employees, evaluate litigation history, and assess legal and regulatory compliance.
There are some basic objectives we have to consider while performing LDD:
- Identifying potential legal risks and liabilities.
- Evaluating the company's legal contract strength.
- Evaluating the company's adherence to applicable rules and regulations.
- Assessing the company's legal claims and disputes that could impact investment.
Commercial due diligence (CDD)
CDD examines a company to analyze the potential growth and profitability of the investment opportunity by assessing the market conditions, competition, and the overall commercial landscape.
CDD aims to give investors a deep understanding of the company's commercial landscape. It often entails conducting market research, analyzing industry trends and competitive dynamics, and evaluating the target company's client base, sales channels, and product offers.
A reviewer can evaluate the company’s health, risks, and investment opportunities by doing market research and analyzing the market trends.
Some objectives to take note of:
- Identifying the commercial potential of a company or its products.
- Evaluating the market research of the company.
- Assessing current market trends of the company.
- Identifying risk factors.
Operational due diligence (ODD)
The purpose of ODD is to evaluate the company's operating and administrative activities to find investment opportunities and also to find hidden risk factors that could impact investment.
ODD's main motive is to determine if any fraudulent activities are going through the company's operative administration.
The goal of ODD is to provide investors or buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the target company's operations, including its production processes, supply chain management, IT systems, and overall operational efficiency.
By conducting ODD, investors or buyers can gain insight into a target company's operational strengths and weaknesses and develop strategies to mitigate risks and improve performance. This can help ensure a successful investment and maximize the value of the acquisition.
Objectives may include:
- Evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of the company's operational and administrative activities.
- Identifying potential operational risks, such as supply chain disruptions and cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
- Evaluating the company's IT infrastructure, including data security and software systems.
- Analyzing the company's production processes, including quality control, manufacturing capacity, and inventory management.
Environmental due diligence (EDD)
EDD is a vital process that investors and buyers can use to assess the environmental risks associated with a target company. It's an external and internal investigation where the reviewer must find all environmental risks and issues to evaluate future profit.
EDD evaluates a company's compliance with environmental regulations, assesses potential environmental risks, and identifies any potential environmental liabilities.
During EDD, the company's environmental permits and compliance history are reviewed, and site visits and assessments are conducted to identify potential environmental risks or liabilities.
Some objectives of EDD may include:
- Assessing the potential impact of the target company's operations on the environment and identifying potential risks or liabilities.
- Reviewing the company's compliance with environmental regulations and identifying any potential violations or liabilities.
- Evaluating the company's environmental management systems, including pollution prevention measures, waste management practices, and emergency response plans.
- Identifying any potential remediation or cleanup costs associated with environmental contamination.
By conducting EDD, investors or buyers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the potential environmental risks associated with the target company and develop strategies to mitigate those risks and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Environmental management systems, pollution prevention measures, waste management practices, and emergency response plans are also evaluated. This can help ensure a successful investment and minimize the risk of future liabilities.
Human resource due diligence
Human resource DD is the process of evaluating a company's HR practices, policies, and investments to assess the company's human capital and identify potential risks and opportunities.
Human resource DD aims to find the quality of work culture and workforce and the effectiveness of its HR practices.
During HRDD, the reviewer typically examines HR policies and procedures, employee contracts, benefits packages, performance management processes, and other HR-related documents.
A reviewer can ensure any future investment opportunities or profit risks by evaluating the company's HR policies and practices, the employee's contracts, and their reviews about the company.
They may also interview key personnel, such as the company's HR Director or other senior leaders, to better understand the company's HR practices.
The goals of HRDD may vary depending on the transaction, but some common objectives include the following:
- Assessing the quality and depth of the talent pool.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of HR processes and practices.
- Identifying potential employee relations issues or concerns.
- Assessing the risk of non-compliance with employment laws and regulations.
- Identifying potential opportunities to improve employee engagement and retention.
Overall, HRDD is a critical step in assessing the human capital of a company or investment and can help inform investment decisions and mitigate HR-related risks.
Cybersecurity due diligence
Cybersecurity DD is the process of assessing the company's cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities, which could impact the company's future growth. Also, identify potential risks that may affect the security of sensitive data or systems.
Cybersecurity DD aims to evaluate the strength and weaknesses of cybersecurity controls and find the gaps and flaws that could impact investment growth.
While assessing it, the reviewer examines the company's cybersecurity policies and procedures, conducts penetration testing, and assesses the effectiveness of security controls.
Some common objectives include:
- Identifying potential cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities.
- Assessing the effectiveness of the company's cybersecurity controls and processes.
- Identifying potential areas for improvement in cybersecurity practices.
- Assessing the risk of non-compliance with cybersecurity regulations and standards.
- Identifying potential liabilities or legal risks related to cybersecurity.
Intellectual property due diligence
Intellectual property DD is assessing the company's value and legal compliance. It includes the company's intellectual property assets, such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, financial instruments, and trade secrets.
Suppose two manufacturing companies merge, then a reviewer must go through the company's intellectual property DD.
Its purpose is to find if there are any hidden gaps in the company's assets and property portfolio. In addition, it helps to evaluate the strength and enforceability of the company's financial instrument.
During intellectual property DD, the reviewer typically examines the company's intellectual property portfolio, including agreements and licenses, and conducts searches to identify potential infringement or validity issues.
Its goals may vary depending on the transaction. Still, some common objectives include:
- Assessing the strength and enforceability of the company's intellectual property portfolio.
- Identifying potential intellectual property infringement or validity issues.
- Evaluating the risks and liabilities associated with the company's intellectual property.
- Assessing the potential for future intellectual property development and protection.
- Identifying potential licensing or acquisition opportunities for the company's intellectual property.
Cultural due diligence
This involves assessing the cultural fit between companies, particularly in mergers and acquisitions. In addition, cultural DD may involve conducting employee surveys, assessing company values and leadership styles, and identifying potential areas of cultural conflict.
The purpose behind conducting cultural DD, the reviewer typically examines the company's culture and values, management styles, employee engagement levels, and communication processes.
The goals may vary depending on the transaction. Still, some common objectives include:
- Assessing the compatibility of the organizational cultures of the two organizations.
- Identifying potential integration challenges, such as differences in communication styles or management approaches.
- Evaluating the employee engagement and retention levels of the target company.
- Identifying opportunities for cultural synergy and collaboration.
- Assessing potential risks and liabilities associated with cultural differences, such as employee morale and turnover.
Overall, cultural DD is a critical step in assessing a company's or investment's compatibility and integration challenges and can help inform integration strategies and mitigate cultural risks.
Social due diligence
As its name implies, social DD evaluates the companies standing in the current market.
Social DD evaluation includes a company's social impact and reputation to evaluate how it aligns with the values and expectations of the acquiring organization.
It aims to assess the company's social activity in the market, including customer satisfaction, employee reviews, communities, and the environment around the company.
While assessing a company's social DD, a reviewer must examine its social responsibility practices, including its environmental impact, labor practices, human rights policies, and community engagement efforts.
Some objectives to take note of:
- Assessing the potential social and environmental impact of the company's activities.
- Evaluating the company's reputation and social responsibility practices.
- Identifying potential social or environmental risks or liabilities associated with the company's activities.
- Identifying opportunities for the company to enhance its social responsibility practices and reputation.
Social DD is an important stage in examining a company's or investment's possible social and environmental impact. It can assist in informing investment decisions and mitigating social and environmental risks.
In conclusion, DD explains a lot about a company's background, financial growth, investment opportunities, social enforceability, cybersecurity, cultural values, environmental factors, etc.
For a better understanding, you can check out our courses, which will provide a more detailed comprehension of the M&A- M&A Modeling Course.
Now, we will talk about some critical aspects of conducting DD. Some potential elements to consider that can give us a basic idea of how we can investigate the company.
Considerations for assessing company due diligence
Some points to consider while assessing the company's DD:
1. Team
Identify the team responsible for conducting the DD process. This team should be composed of individuals with the necessary expertise and experience to evaluate the target company or investment opportunity thoroughly.
2. Scope
Define the scope of the DD investigation, including what areas and aspects of the target company or investment opportunity will be evaluated. This could include financial, legal, operational, human resource, cultural, and social DD.
3. Documentation
Determine what documentation will be required to conduct the DD investigation effectively. This could include financial statements, legal documents, contracts, operational reports, and other relevant records.
4. Timeline
Establish a timeline for completing the DD process, including deadlines for gathering information, conducting analysis, and presenting findings.
5. Communication
By communicating through the legal council and third parties, a reviewer can evaluate the company's risk-reward ratio. In addition, by assessing the company's risks and issues, the reviewer would better understand the company’s surroundings.



or Want to Sign up with your social account?