Black Market
A transaction platform, either physical or virtual, where services or goods are exchanged illegally.
What Is a Black Market?
A black market is a transaction platform, either physical or virtual, where services or goods are exchanged illegally. The component that makes a market ‘black’ can be either the illegal nature of goods and services, illegal transactions, or both.

This market can also be an area of the economy where illegal transactions take place without the knowledge of any governing body, government, or tax authority. These transactions involve the violation of certain laws.
These violations can include filing proper tax returns, violating gun and ammunition laws, animal laws, human and criminal laws, and more.
This market is also known by other terms. Such as:
- Underground Market
- Hidden Economy
- Unreported Markets
- Shadow Market
It is distinct from a grey market, defined as the legal trade of goods through various channels, either unauthorized, unofficial, or legal yet unintentional by the original manufacturer.
The transactions of this market usually happen “under the table” so that the participants can avoid government controls or taxes. The goods or services sold at this market are either lawfully banned, or they can be legal, but the transaction takes place to avoid taxes.
Key Takeaways
- The black market refers to an illegal platform, physical or virtual, where goods or services are exchanged outside the purview of government regulations and taxation.
- Black markets involve transactions that violate laws and regulations set by governing bodies. They are often conducted discreetly to avoid detection.
- AKA, the underground market, unreported market, unreported market, or shadow market, encompasses various illegal transactions such as trade in illicit substances, weapons, human trafficking, and more.
- Black markets facilitate trade in illegal substances, human trafficking, organ trafficking, firearms, counterfeit currency, and more. They operate beyond government-sanctioned channels, leading to economic distortions and social harm.
Understanding the Black Market
Black markets are involved in the illegal trade of illicit substances, ammunition, human trafficking, organ trafficking, and more. These markets conduct businesses that are outside the government-sanctioned channels.
These markets came into existence to counter the overregulation, price ceilings, and the need to buy or sell goods deemed to illegal by the government.
Black markets function outside the perimeters of legal channels, involving the illegal exchange of goods and services. These markets can exist because of various socio-economic conditions.
These factors may include
- Government prohibitions
- Tax avoidance
- Licensing restrictions
- Trade limitations
- Unemployment, and
- Other economic conditions.
Since the history of the black markets, every transaction has been conducted in cash. It was one of its defining aspects and was done to avoid any paper trail.
After the rise of technology and the internet, most underground market transactions are now conducted online, such as on the dark web, with the help of digital currencies.
These markets can take a toll on the economy as they are considered shadow markets whose economy is not recorded and taxes are not paid.
Also, these assets bought and sold are out of government control, which means the government cannot control the supply of these assets in the economy. This is what makes them dangerous and harmful to economic stability.
The common assumption is that a country's actual Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is not the actual one, as the businesses conducted in these markets are not considered
History of the Black Market
The existence of the black market can be traced back to the early 1900s, specifically between the years 1939 and 1955 in Great Britain.
During World War II and the post-war period, the black market came into existence as a response to government rationing and price controls, as well as to the changing interplay between economic regulations, evasions, and societal norms.
These markets included activities such as evading regulations on goods such as food, clothing, and other essentials.
Black markets gained popularity due to shortages caused by wartime conditions and restrictions. Participants found ways to circumvent the rules, regulations, and laws, leading to the emergence of grey markets.
A grey market is a place where certain activities are considered to be legal despite being technically illegal.
This history and background of the black market sheds light on how economic conditions and government policies can shape illegal trade and the morals surrounding it.
Types Of Underground Economic Activities
According to institutional rules that are violated, underground activities are distinguished into different types, which are listed below:
- Illegal Economy: It consists of economic activities that violate legal laws defining the legitimate source of the economy. The participants of the illicit economy produce and distribute legally banned goods and services.
- Unreported Economy: This is defined as fiscal rules that are institutionally established, as mentioned in the tax code. A small example of an unreported economy is the amount of the economy not reported to the tax authority. A measure of such an economy is the tax gap.
- Informal Economy: The cost of such an economy is excluded from the benefits and rights that are included in the laws and rules covering torts, financial credit, labor contracts, and social security systems.
- It is the part of the economy that is not taxed, included in the gross national product (GNP), or monitored by the government. It is hidden from the state for various taxes but is legal in every other aspect.
- Unrecorded Economy: It is the unrecorded income that should be recorded in the national accounting system but is not done. It is very popular in transition countries that switched to the UN standard national accounting system from the socialist accounting system.
The Necessity of Black Markets
The conditions that necessitate the existence of black markets include unmet demands, the want for goods to improve the quality of life, and getting past government regulations.
One reason black markets came into existence was that people wanted to exchange or buy goods and services prohibited by the government.
Unrecorded transactions skew economic data. These markets can disfigure prices, diminish government earnings, and increase crime. The need for buying/selling prohibited goods gives rise to such markets.
For example, this is frequent when the commodity is a niche product with a high utility, like a drug that can cure a rare fatal disease.
These illegal markets also arise when people do not want to pay taxes on purchasing legal or illegal goods and services.
They also exist because people don't follow government laws, such as not reporting the taxable price of transactions and not paying employment tax.
There are various conditions due to which such a market exists, and they are listed below.
Licensure-Driven Black Market Conditions
The different licensing restrictions imposed by the government on various occupations are the reason why some workers have no choice but to venture into the illegal market.
It is because they can not afford or have the will to invest the time and economy to obtain the necessary licenses.
For example, in New York City, a license called a medallion is required to operate a taxi business legally. However, these medallions are too expensive for most entrepreneurs.
Therefore, many people choose to operate illegally without a license until they are caught.
Trade-Driven Black Market Conditions
Every participant in these markets does not want to act illegally, but as they need money, their inability to work legally prohibits them from not reporting their jobs or income to the government.
This situation arises when illegal immigrants obtain jobs, when students traveling abroad avail themselves of employment without a proper work visa or when children of minimum age requirements work for money and survival, also known as child labor.
The governments of many countries have been trying to keep a check on this situation. Still, due to the increasing number of immigrants, it is nearly impossible to eradicate the possibility of this illegal market condition.
Regulations-Driven Black Market Conditions
These markets can also appear due to the shortages created by government-imposed price ceilings.
For example, if the government caps prices at a grocery store, where bottled water is to be sold after a natural disaster, then the store will quickly run out of water. The vendors will then likely sell water at a higher price than the people are willing to pay.
Government overregulation can also create underground markets. These markets are rampant because citizens want to buy goods and services that are hard to obtain through legal channels.
Economy-Driven Black Market Conditions
Underground Markets can also rise due to high unemployment. When workers are unable to find any job in the legal economy, then they turn to the illegal market.
Such jobs can be as simple as babysitting (but being paid in cash and not reporting it to the legal tax authorities) or something as serious as selling cocaine or other drugs (where both the sale and not reporting the income to tax authorities is illegal).
Earning money but not reporting it legally to the tax authorities is the main cause of economy-driven illegal market conditions.
Types of Illegal Markets
An underground market is a place where the exchange of illegal goods and services is conducted. Highly controlled substances or products, such as drugs and firearms, are illegally traded at such venues.
Human Trafficking
Human Trafficking is a vast illegal market. It moves people into prostitution, forced labor, and the market for human organs.
Prostitution is highly illegal and regulated in many countries. An underground market for prostitution is developed due to the consistently high demand from customers, high pay, but labor-intensive and work with low skill, attracting a constant supply of workers.
It is estimated that in 2021, there will be 40 million people trapped in modern enslavement worldwide. Almost three-quarters (71%) are women and girls.
According to a 2014 International Labor Organization (ILO) report, profits of $150 billion a year are earned from human trafficking.
Organ Trafficking
Illegal human organ trafficking occurs when organs are removed from the body, either deceased or alive, for the purpose of commercial transactions, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Despite prohibitions from the government, in 2005, it was estimated that 5% of all organ recipients were engaged in commercial organ transplants.
Illegal Substances
An underground market exists to supply illegal drugs. The demand remains high despite numerous law enforcement efforts, providing huge profits for organized criminal groups.
Many countries have begun to ban the use or possession of recreational drugs. Illegal markets exist despite law enforcement efforts.
The retail market value of illegal drugs is $446 billion, according to the United Nations.
Drug legalization activists drew a parallel between the illegal drug trade and the Prohibition of alcohol in the United States in the 1920s.
Firearms And Ammunitions
The illegal market meets the demands for firearms and ammunition that are either illegal or may only be obtained legally after obtaining different permits and paying fees.
Smugglers of firearms do this from different countries where they are stolen or bought legally or by stealing them from the arms manufacturers themselves.
People can also satisfy requests by gunsmithing their firearms in scenarios where the underground economy cannot smuggle firearms.
Illegal/Counterfeit Currency Market
The nations with strict currency controls are the biggest underground markets for currency.
Currency illegal markets exist in nations that - apart from currency controls - have weaker economic fundamentals (high inflation rate and low currency reserves) and a fixed exchange rate.
Recently, cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin have been a medium of exchange in underground markets. The underground currency market is flourishing in Argentina, Venezuela, and Iran.
Case For And Against Black Market
The case for the black market is debatable and highly subjective, depending on one's moral and ethical beliefs.
Case For
Some people favor the concept of black markets.
Such markets can supply goods and services that, while being illegal (like marijuana), also improve the quality of life (used to alleviate pain for patients who have not found relief from legal drugs).
These markets are useful in providing legal necessities that are in short supply, as in the case of Cuba or a city that is hit by a hurricane.
Also, the underground economy allows people to earn a living who would otherwise seek welfare illegally—people who would be employable under fewer government regulations or in an economy with a higher employment rate.
Case Against
There are many downsides of underground markets, some of which are subjective, but many would agree these are serious problems.
Some goods in underground markets are stolen from legitimate legal markets, taking their business away from law-abiding businessmen and entrepreneurs.
Most consumers would not mind buying stolen goods at a lower rate than the actual price, while others would be appalled at knowing that by buying such products, they were actively supporting the underground markets.
The dark side of such underground markets goes beyond theft and resale of stolen goods and services. Illegal market activities are sometimes used in funding terrorist organizations since the profits can not be adequately traced.
Violence is another problem in such illegal markets. The participants can not rely on legitimate police protection in case of theft or even other serious crimes because these markets are unregulated and illegal.
If another rival gang steals a drug dealer's stash of heroin, he can not approach the police for help in getting his merchandise back. This is how the start of violence takes place in underground markets.
Symbiotic Relationship Between Legal Markets and Black Markets
A symbiotic relationship refers to the existence of elements and people living together in a way that benefits everyone. Indeed, legal markets and black markets have symbiotic relationships.
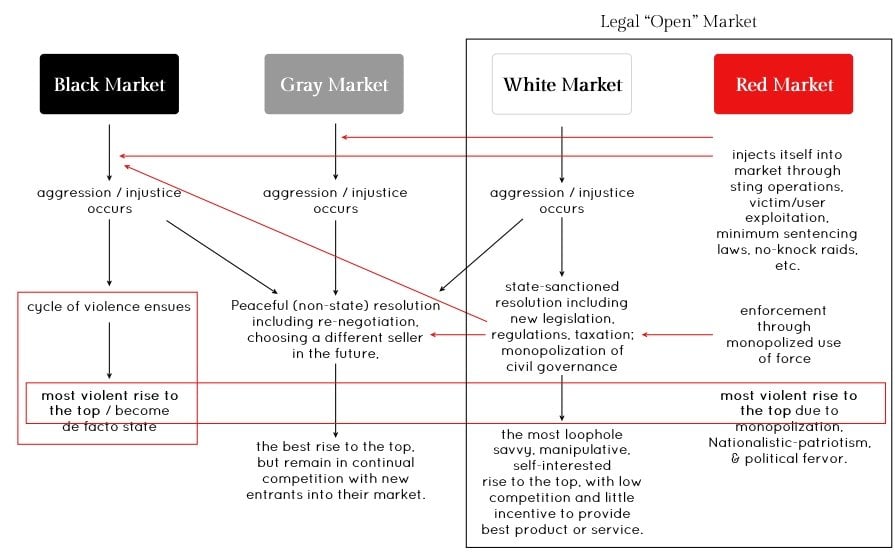
This relationship is possible when there is a legal ban on certain commodities that leads to the genesis of a black market. These markets emerge when goods and services are considered unlawful by the government.
And, since there is an unfulfilled demand through legal channels, people search for back-door channels to fulfill their demands.
Day by day, illegal trading gathers volume, organically allowing more participants to continue the trade and avoid legal penalization. As a result, such illegal markets become more difficult to wipe out when operated for a long period completely.
A National Bureau of Economic Research study stated that the underground market represents almost a fifth of global economic activity.
Authors like Solomon Hsiang and Nitin Sarkar, in "Does Legalization Reduce Black Market Activity? Evidence from a Global Ivory Experiment and Elephant Poaching Data," evaluate the first-ever global legalization experiment conducted in an internationally banned black market.
The findings were quite surprising. The study charted a 66% increase in the trade of illegal ivory that aligned with the announcement of legalizing ivory sales.
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:




or Want to Sign up with your social account?