Market Positioning
It is a strategic exercise used to establish the image of a brand or product in a consumer's mind
What Is Market Positioning?
Market positioning is a strategic process that revolves around shaping consumer perceptions of a brand or product in relation to its competitors within the market landscape. It involves crafting a distinct identity or image for a brand so that it resonates with the target audience in a specific and meaningful way.

A firm's marketing positioning strategy is influenced by various factors, such as client needs and motives and competitors' actions. Therefore, marketing positioning entails more than creating a category or specialty page on your website.
Market positioning is creating a brand's or product's identity or image so that consumers will view it in a specific way. It takes more than a catchy phrase or eye-catching logo to differentiate your company through brand positioning.
Everything from market research to content generation depends on positioning, which requires living and breathing that information. Building an image of your business is a critical component of positioning in marketing.
It describes how you will distinguish your goods or service from the competition and what market segment you will target.
Key Takeaways
- Market positioning involves shaping consumer perceptions of a brand or product relative to competitors. It's about creating a unique identity to influence how people perceive the brand.
- Market positioning is influenced by customer needs, competition, and market conditions. It goes beyond superficial efforts like creating a website page.
- Effective market positioning is about building a brand's image and identity. It's not just about catchy phrases or logos; it's about differentiation and perception.
- Market positioning impacts everything from market research to content creation. It's a continuous effort that requires deep understanding and integration into all aspects of the business.
Importance of Market Positioning
Positioning is a strategic marketing technique that comprises creating a brand or product's identity/image in the eyes of potential purchasers. It defines how you'll differentiate your product/service from the competition and your target market segment.
From content production to market research and branding your firm to appeal to your chosen target buyer, positioning demands living and breathing that information.
You can communicate and reach your target audience more efficiently and successfully if you have a clear Brand Position.
The positioning of a brand and its products makes them noticeable and desirable to buyers. And positioning creates an emotional response from your target customers, allowing them to quickly trust you, which leads to higher client attention and sales.
The interaction between a brand's identity and the image is called positioning. The customer's brand perception develops only when the market positioning is proper. Therefore, better marketing positioning will provide the organization with a competitive advantage.
A company's positioning will help it stand out in a sea of competitors. This positioning aims to make your brand stand out and be perceived as superior.
People prefer to stick with a brand for years if not decades, so making a good first impression is crucial to your business's success. In addition, market positioning may need to be modified and enhanced regularly for established enterprises to respond to changes in the marketplace.
Types of Positioning Strategies
Developing products and services with the most potential for profit with the aid of strategy. Listed below are some strategies that are crucial for a market:
1. Pricing
Most customers base their judgments on pricing, which is an important consideration. Typically, businesses that provide goods at the lowest prices while maintaining a decent degree of quality prevail.
Your customer base will become more price-sensitive due to your decision to compete with lower prices.
Example: KFC, a fast-food restaurant, has great valued quality food at a reasonable price worldwide. This helps them maximize their profits and boost revenue volumes.
2. Quality
In some industries, like those for high-end apparel or vehicles, the level of quality can define who the competitors are. Because it could relate to a product or service, corporations usually choose this kind of position.
The product's primary selling point in a quality-based product positioning strategy is its quality.
Let's take Rolls Royce, for example. This famous British luxury automobile is associated with luxury and excellence and is popular among powerful and wealthy people.
3. Differentiation
Differentiation is a marketing strategy focusing on the features that make your product or service stand out from your rivals.
Example: Tesla is unique from its rivals because its automobiles are cutting-edge, luxurious, battery-operated electric vehicles.
4. Convenience
Convenience is perceived as being more user-friendly by the consumer base. E-commerce, thoughtful positioning, usability, and free returns are fantastic ways to guarantee comfort.
Example: Every day, eligible Prime members can receive 5% off their purchases made on Amazon and use their Amazon Prime Store Card to access the exclusive flexible benefit.
5. Customer service
A popular strategy is positioning based on a product or service. It emphasizes how your good or service fixes a customer's issue.
For example, Starbucks successfully positioned itself by focusing on giving customers the best experience possible. As part of its culture, it started writing the customer's name on the glass before giving them their beverage.
6. User group
Such positioning justifies why a certain user group would genuinely benefit from and be drawn to the business's goods and services.
For example, Products made by Dove are marketed as personal care products for everyday women worldwide. Therefore, they put a lot of effort into building their brand around appealing feminine characteristics that appeal to the female market.
How to Create an Effective Market Positioning Strategy?
You should have a good idea of what your firm is, how it differs from competitors, market conditions, market potential, and how your company might position itself after going through the preceding stages.
Compare and contrast your company to its competitors to assess its uniqueness and identify prospects. Next, determine your market position and how the new positioning will help you differentiate yourself from the competitors.
Analyzing competitor positioning can help determine how much one competitor can influence the other.
Examine your current product's market position. Identify any changes or distinguishing characteristics that may help your brand stand out. This information should be condensed into a single, well-targeted image: your current location.
After you've assessed your position, find out where your competitors stand in the same market. What role does your company play?
A strong market positioning statement describes the advantages that customers will gain and how your organization offers and delivers products and services that are distinct from those offered by competitors.
It should clearly explain your target client, the products and services you plan to provide them, how you plan to deliver them, and your brand's identity, purpose, and distinguishing characteristics.
How to create a brand positioning strategy
To create an organizational plan to meet client needs, positioning strategy assists in identifying the areas that organizational growth affects. Here are some tips:
1. Create a brand essence chart based on your present brand positioning
Are you currently presenting your product or service as if it were just another commodity on the market or as something unique? Your present brand positioning might help you figure out where you should go next.
A brand essence chart can aid in organizing these concepts, making them clearer and simpler. It has seven parts: attributes, benefits, personas, missions, values, voice, authority source, and testimonials.
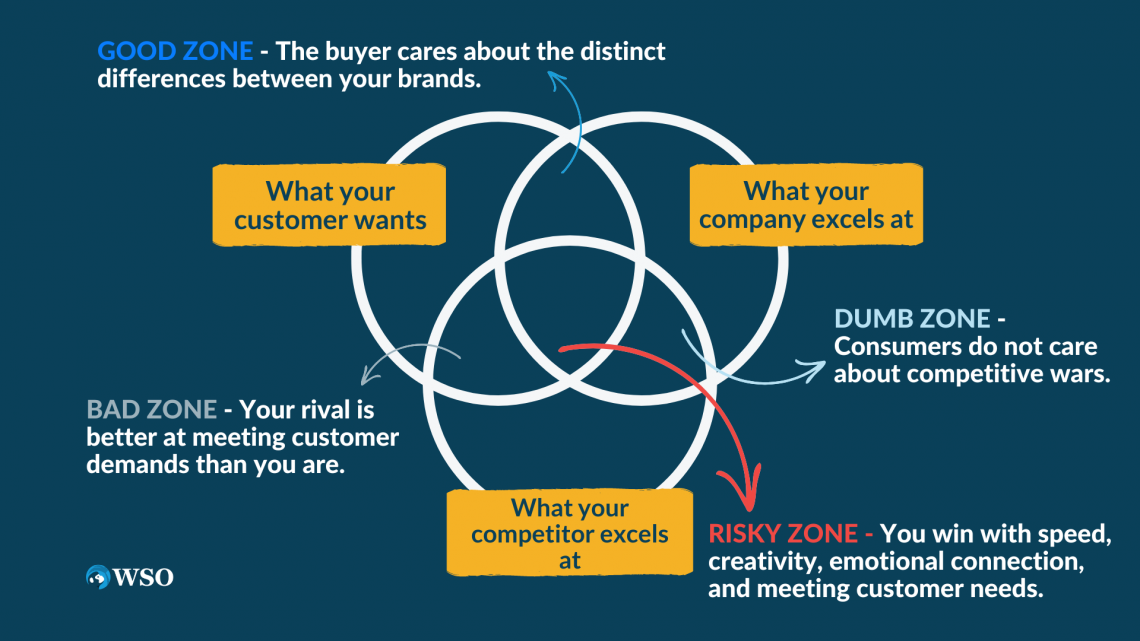
2. Find out who your competitors are and do some research on them
After you've analyzed yourself, it's time to examine your competition through competitor analysis. Market research and social media are two examples of strategies for determining your competitors.
To compete, you'll need to look at how your competitors position their brands. At its most basic level, your study should comprise the following: What items or services do your rivals provide? What are their advantages and disadvantages?
3. Create a brand positioning framework by identifying your unique value proposition
Creating a distinct brand is about figuring out what makes you stand out and what works best for your company. This brand positioning framework might aid your brand positioning strategy.
This methodology takes a top-down approach, starting with the overarching idea and working down to sample touchpoints that may be used in tactical situations like social media captions and headlines.
4. Make your positioning statement and then test it to see if it's effective
It's critical to test, experiment, and actively seek (genuine) feedback from your target clients to see if your positioning is working. Anyone is Amazon's target consumer, despite its enormous scope.
Their main benefit is that they sell a wide choice of things for everyone. And what about the proof? It's all done over the internet.
5. During sales, develop an emotional connection with prospects and consumers and emphasize your brand's distinctive traits
The unique qualities of your company's offering should be easy to comprehend and refer to if you have a strong brand position. However, before you go in for the hard sell, connect with your prospects on a human level.
Sales, for example, should spend time learning about your prospects at the start of the sales process.
6. Create value and make sure your customer-facing workers are brand ambassadors
Employees that interact with customers are your company's most important assets. Therefore, prospects should have an experience that reflects your company's underlying principles.
If your company's branding is lighthearted and playful, you should use this language in your sales talks. Conversely, a tone that is extremely serious or rigid is not consistent with your company's brand.
Market Positioning Advantages and Disadvantages
Establishing a relative position in the market entails product positioning. To differentiate itself from competitors, a brand must convince customers that its product is well suited to meet their demands.
Below are some of the advantages of market positioning:
1. Brand Recall
The ability to show your customers exactly what you want them to know about your brand is known as brand recall.
Example: Volvo has become synonymous with the phrase "safety." The car has been designed for the safety and comfort of the owner
2. Brand loyalty
You can build a devoted customer base if you have a strong brand positioning. Brand supporters are people who value your brand's differentiators. Advocates.
3. Market differentiation
Without differentiation, every company's marketing collateral would tout the same product features. The target market would have a hard time telling the difference.
You must express your worth to sell your products. Your brand should be distinct from that of the competition.
4. Compete on more than just pricing.
It's critical to compete on more than just pricing. However, you become difficult to replace when you concentrate on other variables such as quality, service, and customer care.
Southwest Airlines, specializing in short-haul flights, understood they couldn't compete just on price because that isn't a sustainable advantage.
5. Marketing with an emotional appeal
Good placement will generate emotional responses from your target audience. Even in a data-driven society, we still rely on emotions to make purchasing decisions.
Coca-Cola is an excellent example of a company that employs emotional marketing to influence customers in its positioning and advertising efforts.
6. Marketing that is based on the value
You must convey the value you provide to your customers. You must make it apparent to them what benefit they will obtain if they buy your product.
This can be accomplished by presenting them with a short, engaging customer-focused value proposition that explains the benefits and features of your product.
7. Consistent brand message, identity, and clear direction.
If you don't know where you want to go with your brand, your brand elements and message won't help you get there.
Your marketing staff might use a positioning statement as a reference document when developing a marketing plan. But, again, it's easier to take control of your market position when you're consistent.
Below are some of the disadvantages of market positioning:
1. The dangers of hedge positioning
When brands strive to own two frames of reference simultaneously, they end up not possessing either.
BMW has done a fantastic job owning both the luxury and performance benchmarks. Smaller companies should focus on holding a particular positioning angle with their statement.
2. Failure to grab market share and risk being linked to adversely correlated characteristics.
There is a risk of missing out if your brand isn't built on traits and values that are important to your customer.
Customers have a negative correlation with specific traits, so ensure that the negative correlation won't put off your target customer persona. Wrong positioning can mean failure to capture the market.
What is Market Repositioning?
When a corporation repositions its existing brand or product in the marketplace, it is known as market repositioning. It is frequently done in response to poor performance or significant environmental changes.
Because of the tremendous expense and work required to reposition a brand properly, many companies choose to develop a new product or brand.
The repositioning method is identical to the original process, except that it starts from a different location. Repositioning may necessitate changes to the actual product or its selling price, but this is not always the case.
It frequently attempts to alter public views to make a product or service more appealing to a wider audience. However, repositioning is more than just making something new. Instead, it attempts to preserve the positive aspects of current market positions.
People remember your product, service, or brand because of its history. So some people will try to figure out how the new positioning corresponds to their previous perceptions of the offering.
A brand would want to reposition itself when; it wants to change the customer perception because of innumerable:
- Industry-related
- Brand-related
- Future-related
- Competition-related
- Customer-related reasons
Increased competition in the market results in the lack of perceived differentiation of the brand compared to its competitors. Therefore, when a business invests in a substantial product improvement, it will likely offer additional benefits and cater to a broad audience.
This often requires the brand to reposition itself. Over time, repositioning becomes increasingly important as it helps the brand take on a new (and more profitable) position in customers' eyes.
When a brand's positioning is improper, target customers cannot associate emotions, traits, sensations, and sentiments with it, making it impossible for the brand to survive.
Key steps to take in repositioning your brand
Repositioning a company's brand necessitates extensive planning. It must be based on three pillars to succeed:
- Listening
- Delivering
- Persuading
First, listen to your customers, meet their expectations, and persuade them with your message to reposition your brand effectively.
1. Examine your current position as a brand and redefine your distinct value proposition
The first stage in successful brand repositioning is a detailed examination of your brand's current state. If you know what's wrong with your brand, you can determine what needs to be altered.
Rethink your company's fundamental beliefs and feelings with which you want to be connected. Look for ways to set yourself apart, even if it means recognizing that competition is superior to you. Examine who purchases (or does not purchase) your products.
Who do you think would be the most from your services? Do you want to connect with a new audience? Consider who your present and potential consumers are and what they expect from your company.
Determine the most significant factors. After that, work on developing a new communication plan.
2. Create a brand repositioning strategy, put it into action, and pay attention to your customers
When selecting how to reposition your brand, you have various alternatives. The activities you should take are determined by the factors that impact your decision and the anticipated outcomes.
Because the public image is so important in repositioning a brand, social listening is essential. In addition, good time management, a well-defined budget, and a division of responsibilities are crucial to success.
3. Lastly, examine the results
Once your brand repositioning activities have been completed, it's time to assess their value. A few weeks after making the changes, you can start comparing statistics. Have you noticed an increase in sales? Is your client's business growing?
These indicators might help you determine whether the entire process was successful or needs to be tweaked.
Market Positioning FAQs

The four key market positions that brands frequently assume are market leaders, challengers, followers, and niches.
The five forms are:
- Positioning based on product features
- Price-based positioning
- The quality or luxury-based positioning
- Product positioning or application positioning
- Competition-based positioning
Product positioning methods should be divided into three categories: comparison, differentiation, and segmentation.
Positioning will help a firm stand out from the crowd of sellers. A clearly defined Brand Position enables you to communicate with and reach your target audience efficiently and effectively.
A well-defined market positioning raises the visibility and attraction of the brand and its product to purchasers.
Product Positioning in 5 Simple Steps:
Step 1: Determine why your customers buy your products.
Step 2: Determine your target market and the persona you want to attract.
Step 3: Assess Market Maturity.
Step 4: Determine Others' Emotional States.
Step 5: Put it all together.
There are seven techniques for positioning strategy:
- Using product attributes or consumer benefits
- The price-quality approach
- The use or applications approach
- The product-user approach
- The product-class approach
- The cultural symbol approach
- The competitor approach
5 Brand Positioning Elements
- Brand characteristics are what the brand has to offer in terms of customer features and benefits.
- Customer Preferences, what people expect from the brand
- Characteristics of competitors, what other brands on the market have to offer in terms of features and benefits
- Price
- Perceptions of customers
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:







or Want to Sign up with your social account?