Stop-Loss Order
It is a buy/sell order placed by a trader to exit a trade at a predetermined price to avoid losses.
A stop-loss order (SL Order) is a buy/sell order placed by a trader to exit a trade at a predetermined price to avoid losses.

The traders use this order to exit a running trade to book profit or avoid losses. There are two types of stop-loss orders:
- Sell Stop-Loss order
- Buy Stop-Loss order
1. Sell Stop-Loss Order
This is used to book profit or avoid losses on a running buy-side trade.
For example, A bullish trader has bought security at $100. He is willing to take the risk of 10% and expects a 20% profit from the trade, which sets his target at $120 and his probable loss at $90.
There is also a chance that the trade goes in the opposite direction, and the trader loses much more than his risk capacity. Therefore, to avoid big losses, the trade will place a sell stop-loss order so that if the price crosses the SL price, the security will be sold automatically at $90.
Hence, a trader can avoid losses beyond his risk-taking capacity by placing an SL order.

2. Buy Stop-Loss Order
This is used to book profit or avoid losses on a running short-sell trade.
For Example:
A bearish trader has short-sold security at $100. He is willing to take the risk of 10% on this trade. Hence, to avoid bigger losses, the trader has placed an SL at $110.
Now, if the trader wishes to book his profits when the price hits $80, he will place a buy SL order at $80 so that if the price hits the SL price, the security will automatically be bought, and the profit will be booked.
With the help of this order, the trader would not have to track the price and wait for it to hit the target. Instead, he can just place the order so that the trade is automatically settled when the price hits the target price.
How does a Stop-Loss Order work?
Stop loss is a very powerful tool, and it is used very frequently by traders. However, this type of order works best when the trade is backed by technical analysis and price action.

A trader often uses technical analysis and price action to determine a particular security's support and resistance prices. Then, the trader places an SL order only after studying the price behavior and measuring the market volatility.
The trader must first decide on a trigger price with the SL price to place an SL order.
Trigger price: As its name suggests, a trigger price is slightly lower than the SL price at which the order gets triggered and is sent to the exchange for execution when the SL price is met.
A trigger price proves to be very helpful in volatile markets. Many times, due to high volatility, the price shoots in one direction in a couple of seconds with a huge margin which leaves the already placed SL order unexecuted, and the trader suffers huge losses.
To avoid this, a trigger is placed a few points below the volatility of the security being traded so that when the price suddenly jumps, the order is triggered and sent to the exchange for settlement. This ensures the execution of the order at the desired price.
Let's understand this with the help of an example.
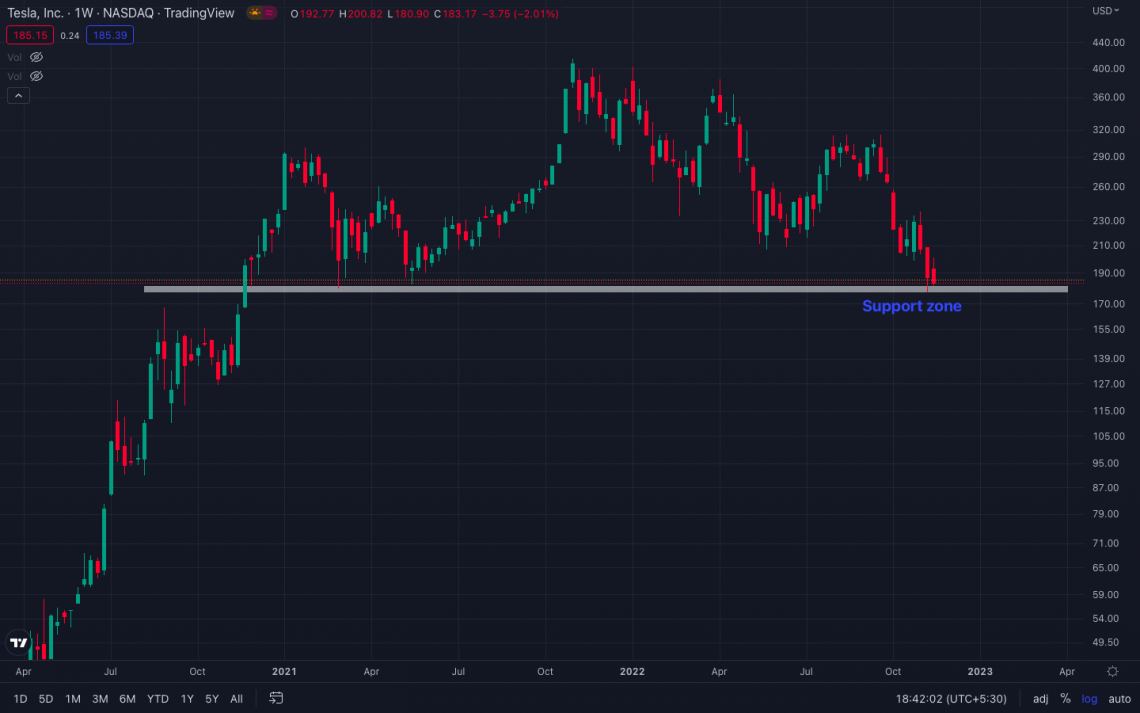
In the image above, it is clear that the share price of TESLA has a support zone of $180 to $177 because the price has surged twice after touching the level.
A bullish trader on TESLA would go long on here because the price is trading near a support zone below which they can place a stop-loss order to limit the losses if the price falls below the support zone.
Hence, the trader will place the SL order at $176 and the trigger price at $177. Doing this will help the trader minimize risk and ensure that if the price drops sharply below the support zone, the order will get executed at the desired price.
Pros and Cons
A stop-loss order is a beneficial tool that enables a trader to enter and exit a trade at a predetermined price to book profit or avoid loss. It is a very powerful tool and builds discipline in the trader.

However, there are a few disadvantages to using a stop-loss order.
1. Partial Execution
It does not ensure 100 percent execution of the order. Sometimes an order might get partially executed, and the trader would keep losing money on the remaining quantity.
This could happen due to low market liquidity, where fewer sellers or buyers are at the asked price.
2. Market Volatility
Sometimes, the market gets too volatile when there are huge fluctuations in the price of a security in a short period. In such cases, the order might get triggered due to a false fluctuation in the price.
Although a stop-loss order sometimes fails due to market volatility and lack of liquidity, there are much more benefits than risks.
Here are a few advantages of using an SL order:
1. Desired price
The trader using this tool to exit his positions from trade is insured that the order will be executed at the desired price. This would limit his losses and save his capital from sinking.
2. Automated system
It helps a trader exit a position at their desired price without always having to trace the security price. Instead, the order is automatically executed when the security price hits the SL price.
3. Builds discipline
This type of order enables the trader to follow the proper risk-to-reward ratio and builds discipline within them. This also keeps the trader's greed in check and protects capital.
Researched and authored by Pratik Chandra | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:



or Want to Sign up with your social account?