Contribution Margin After Marketing (CMAM)
It is an essential metric for evaluating the success of marketing campaigns
What Is Contribution Margin?
The contribution margin is the amount of money that is left over after these expenses are paid. It can be used to cover additional expenses, such as marketing, or it can be used to increase profits.
When a company sells a product or service, it has to cover its costs of goods sold (COGS) and its other operating expenses.
Marketing is vital to any business, but it can be expensive. Many companies choose to invest a portion of their contribution margin into marketing to increase brand awareness and drive sales. The question is, how much should a company spend on marketing?
The answer depends on several factors, including the company's overall marketing strategy.
Once a company has decided how much to spend on marketing, the question then becomes how to allocate that budget.
The contribution margin after marketing represents the amount of revenue that is left over after marketing expenses are deducted. This metric is important because it helps businesses to understand how much money they have available to reinvest in other areas.
Key Takeaways
- Contribution margin is what's left after expenses, used for marketing or profits. Businesses invest it in marketing to boost sales and brand awareness.
- CMAM measures marketing's profitability, calculated by deducting marketing costs from revenue. It informs resource allocation and pricing strategies.
- Distinguishing Metrics Differentiates between profit margin and contribution margin. Profit margin focuses on net income as a percentage of total revenue, while contribution margin assesses individual product profitability.
- CMPO/CMPC calculates gross profit per customer; CMAM adds marketing expenses. Both aid pricing, marketing, and decision-making.
- High contribution margins indicate growth potential. CMAM helps investors assess product performance and guide investment choices.
Contribution margin VS profit margin
These two metrics are commonly confusing, but they have their distinct definitions.
Contribution margin measures how profitable individual products are within a company, and profit margin is the total amount of revenue left after subtracting production costs.
1. Profit Margin
Profit margin is a measure of a company's profitability. It is calculated by dividing a company's net income by its total revenue. Profit margin is usually expressed as a percentage.
A company's profit margin can be a helpful metric to track over time. It can give insights into a company's overall financial health and performance. A company with a high-profit margin is typically more profitable than a company with a low-profit margin.
Profit margin is a measure of a company's profitability. It is calculated by dividing a company's net income by its total revenue. Profit margin is usually expressed as a percentage.
A company's profit margin can be a valuable metric to track over time. It can give insights into a company's overall financial health and performance. A company with a high-profit margin is typically more profitable than a company with a low-profit margin.
A higher profit margin means that a company is more efficient at generating profit from its revenue.
Profit margin is a crucial metric for investors and businesses because it provides insight into a company's profitability and ability to generate profit from its sales. It is also a helpful metric for comparing companies in the same industry.
While profit margin is a valuable metric, it is essential to remember that it is just one metric and should not be used in isolation. To get a complete picture of a company's financial health, it is essential to look at other metrics such as revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
2. Contribution Margin
The contribution margin is a financial metric that measures the profitability of a company's products or services. It is calculated by subtracting the total variable costs from the total revenue. The difference is the contribution margin.
The resulting number is the amount of money that the company has left over to cover its fixed costs and generate a profit.
The contribution margin is a financial metric that measures the profitability of a company's products or services. It is calculated by subtracting the total variable costs from the total revenue. The difference is the contribution margin.
The resulting number is the amount of money that the company has left over to cover its fixed costs and generate a profit.
The contribution margin can be used to assess a company's financial health and make pricing and cost decisions. It is also a helpful tool for planning and budgeting. It can also be used to evaluate pricing strategies and decide on product mix.
Additionally, the contribution margin can be used to calculate the break-even point.
Contribution margin per order/customer (CMPO/CMPC)
Contribution Margin Per Order/Customer(CMPO/CMPC) comes before Contribution Margin After Marketing (CMAM) and shows how much gross profit is produced per customer.
A business's contribution per order or customer is the total revenue from that order or customer, minus the costs associated with fulfilling that order or providing that service.
The contribution per order can be a helpful metric for businesses to track, as it can give them insight into how much each order or customer is worth to the company.
Assuming that each order/customer has an equal chance of generating a return, the contribution per order/customer can be calculated as follows:
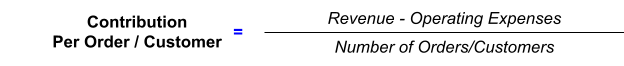
This metric helps evaluate the overall profitability of each order/customer. If the contribution per order/customer is positive, the company makes a profit on each sale.
The company loses money on each sale if the contribution per order/customer is negative.
Businesses should track their contribution per order/customer over time to see if there are any trends. For example, if the gift per order/customer begins to decline, then the company will need to take action to improve its profitability.
For example, if a business has a total revenue of $100,000 and the costs associated with fulfilling that payment is $80,000, then the business's contribution per order or customer is $20,000.
This means that, on average, each order or customer is worth $20,000 to the business.
If a business is tracking its contribution per order or customer, it can use this metric to make pricing, marketing, and more decisions.
Understanding Contribution margin after marketing (CMAM)
Businesses need to calculate their contribution margin after marketing to gauge the success of their marketing campaigns. (CMAM) is the same as (CMPO/CMPC), with the exception that the former includes marketing expenses
After marketing, the contribution margin is left over after all marketing expenses have been paid. This metric assesses the profitability of a company's marketing activities.
The contribution margin after marketing can be calculated by subtracting all marketing expenses from total revenue. This metric is usually expressed as a percentage.
The contribution margin is calculated by subtracting the variable costs associated with a product or service from the selling price. This number can be used to help businesses determine how much profit they are making from each sale.
Marketing campaigns often involve variable costs, such as advertising and promotional expenses. By subtracting these costs from the selling price, businesses can get a better idea of how much profit they make from each sale.
This information can be used to make decisions about where to allocate marketing resources and how to price products and services.
Businesses should track their contribution margin after marketing regularly. This will allow them to see whether their marketing efforts are paying off.
Suppose you can increase your contribution margin after marketing. In that case, it means you'll have more money to reinvest in your business or use for other purposes that can significantly impact your bottom line.
So if you're looking for ways to boost your business profits, pay attention to your contribution margin after marketing, it just might be the key to success.
If the contribution margin after marketing is low, it may be time to reevaluate the marketing strategy.
How to calculate CMAM
It is an essential metric for evaluating the success of marketing campaigns. It provides insights into the profitability of a campaign by calculating the revenue generated minus the marketing costs incurred.
There are a few different ways to calculate CMAM, but the most common method is to divide total revenue by total marketing spend. This will give you a ratio that you can use to compare the profitability of different campaigns.
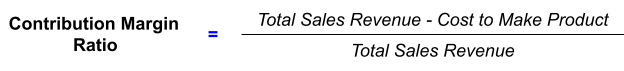
Another way is to take the total revenue from sales and subtract the total amount spent on marketing. This will give you the contribution margin before any other expenses are deducted.
CMAM = (Revenue - Direct Variable Costs - Marketing Expenses)
A more involved way to calculate the contribution margin after marketing is to take the gross margin from sales and subtract the marketing expenses as a percentage of sales. This method is more accurate because it considers that marketing expenses can vary depending on the level of sales.
How CMAM is used
It is one of the most important metrics that businesses use to assess the profitability of their products and services.
CMAM tells a business how much revenue is left over after all marketing expenses have been deducted from total income. This metric is important because it allows businesses to see how much revenue they generate from their marketing efforts.
CMAM is also helpful for businesses to evaluate different marketing strategies. For example, companies can see which method is more profitable by comparing the CMAM of two different marketing strategies.
This helps businesses make better decisions about where to allocate their marketing resources. CMAM is a valuable tool for businesses to determine which marketing campaigns are most effective and which ones are not meeting their goals.
By evaluating the CMAM of each marketing campaign, businesses can make more informed decisions about where to allocate their marketing budgets. While CMAM is helpful, it is essential to remember that it is just one metric that should be considered when assessing the success of a marketing campaign.
Other factors, such as customer satisfaction and brand awareness, should also be considered.
Overall, CMAM is a critical metric for businesses to understand the profitability of their products and services. By understanding this metric, companies can make better marketing strategy decisions and allocate resources more effectively.
Why is the contribution margin significant?
The contribution margin is an excellent place to start if you want to understand your company's financial performance better.
There are two main reasons why the contribution margin is so significant.
- Firstly, it allows businesses to see how much revenue is available to cover fixed costs. This is important because it can help determine a company's breakeven point - the end at which payments cover all costs and the business starts to make a profit.
- Secondly, contribution margin can also be used to assess a company's profitability. By knowing the contribution margin, businesses can see how much revenue is available to cover fixed costs and make a profit.
Contribution margin also lays the framework for breakeven analysis, which companies use for cost and sales price planning for their product lines.
Contribution margin distinguishes profit components from fixed costs which come from product sales and is used to tell what the selling price range of a product should be.
CM also shows us what profits can be expected from sales, and how to structure sales commissions for sales team members.
By understanding how much revenue is generated after all of your variable costs are deducted, you can get a better sense of your company's profitability.
Contribution margin for investors
Investors often want to know how much a company can grow without additional investment. One way to measure this is by looking at the contribution margin. The contribution margin is the amount of revenue available to cover fixed costs after variable costs are paid.
Companies with a high contribution margin can usually grow faster because they have more money available to reinvest in their business. For example, a company with a contribution margin of 50% can grow twice as fast as a company with a contribution margin of 25%.
Investors use the contribution margin to measure a company's potential for growth without additional investment.
There are many different ways that investors can use contribution margin to their advantage.
For example, it can be used to help assess a company's profitability, calculate breakeven points, or make pricing decisions. By understanding contribution margin and how it works, investors can make more informed investment decisions and maximize their returns.
CMAM is explicitly helpful in analyzing product performance as well. For example, imagine one company producing a product that consistently achieves a high CMAM compared to other competitors' products.
Potential investors could look at that information and make conclusions to guide what their next investment might be.
Companies that maintain low or negative CMAM suggest that their product or service is non-viable or that they are spending too much on their marketing campaign to compete with other competitors' products.
Researched and authored by Jake Heimowitz | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:










or Want to Sign up with your social account?