DEGREES Function
Helps convert any radian angle to its equivalent in degrees.
What is the DEGREES Function?
Math can sometimes be a real pain in the brain, especially when trying to convert from one unit to another. But if you're an Excel user, you're in luck! There's a solution to your radian to degree woes: the DEGREES function!
With this magic formula, you can easily convert any radian angle to its equivalent in degrees. Ensure the angle you're starting with is in radians, or you might get some unexpected results.
And, the significant part is, you can use this function in various ways. You can use it alone, in a formula, or even combined with other functions and operators in Excel. It's compatible with all recent versions of Excel, so no matter what computer you're on, you're good to go!
Just a few tips to keep in mind when using the DEGREES function:
- Make sure the input angle is in radians
- The output will be the angle in degrees
- It can be used as a standalone function or in a formula
- It works with other Excel functions and operators
- It's compatible with Excel 2007 and later versions
So, don't sweat the small stuff. Let the DEGREES function do the work for you. And always double-check your inputs and outputs to ensure you're getting the suitable units. Happy calculating!
Key Takeaways
- The DEGREES function in Excel converts angles expressed in radians to degrees.
- The function takes one argument, the radian value, to be converted.
- The input angle must be in radians, and the function returns the angle in degrees.
- The DEGREES function is compatible with Excel versions 2007 and later.
- They are practical to use in many technical fields, such as navigation and weather forecasting and are an understandable unit of measure for people with no technical background.
- A simple mathematical formula converts radians and degrees: 1 radian equals 180/π degrees.
- To use the DEGREES function in Excel, you enter the radian value into a cell in your spreadsheet and then use the formula "=DEGREES(cell_reference)" in another cell, where "cell_reference" is the cell that contains the radian value.
What is a Degree?
Let's momentarily step back into high school and relive the age-old debate between the popular kid and the math whiz. Degrees vs. Radians, it's time to settle this once and for all!
Picture yourself walking into the gymnasium; on one side, you've got degrees, the cool cat, the crowd favorite, symbolized by that ubiquitous ° symbol. On the other side, we've got radians, the quiet but brilliant mind, the unsung hero of angles.
Now, when it comes to the world of mathematics, radians are like the nerdy valedictorian; they may not be the most popular. Still, they're based on the idea of using a circle's circumference to measure angles, which gives them a unique level of accuracy.
Although the radian is generally preferred more in the scientific field for its ease of calculations, not everyone understands what it is. This is why we need degrees.
However, in practical applications like engineering, degrees take the crown as the king of angles; they're easy to understand and use.
So, the next time you find yourself measuring an angle, don't be afraid to let your inner math geek or popular kid shine. Both degrees and radians have unique qualities and strengths, so choose wisely and embrace the diversity of angles!
History of the Degree
Step back in time, my friend, to a world where angles were measured by the length of fingers and the number of days in a year! The ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Sumerians, to name a few, all had their unique systems for measuring angles.
But the Sumerians, who were ahead of the curve, came up with the idea of dividing a full circle into 360 parts, each part being one degree. Now, why 360, you ask? Well, because it's highly divisible, which makes for some pretty precise measurements.
As time passed, this idea caught on, and pretty soon, the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks were all using degrees to measure angles. The Romans and Chinese added their own spin, and before you knew it, even the Islamic scholars of the Middle Ages were on board!
Fast forward to today, and degrees are still the go-to unit of measurement for angles, a testament to its ancient roots and widespread acceptance. Who knew a simple idea could stand the test of time?
Why Do We Need Degrees?
Using degrees as a unit of measure for angles is very practical. In many technical fields, angles are usually measured in degrees. It is a more intuitive and valuable unit of measurement for applications.
- In navigation, angles are measured in degrees to determine the direction of a ship or plane.
- The degree is an accepted standard unit of measure. It makes it easy to understand even for people with no technical background.
- Degrees are also used in most daily life measurements, such as measuring the angles of a ladder when painting a house or measuring the angles of a camera lens.
- A degree is an understandable unit of measure, and its familiarity makes it easy to communicate and understand.
- Degrees are also used in weather forecasting, where the wind direction is measured in degrees.
In general, a degree is an understandable unit of measure. It provides a convenient and intuitive way to measure angles in many practical applications.
What is a Radian?
Ah, radians! A lesser-known but the fundamental unit of measurement. Have you ever heard the one about degrees and radians going on a date? Degrees says, "I've got 360 personalities!" And radians replies, "Oh, I'm just a straight line."
Jokes aside, radians are a crucial component in the world of mathematics, especially when it comes to trigonometry.
You see, the sine function, for instance, is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite an angle to the length of the hypotenuse. And this relationship is much easier to understand and apply when the angle is measured in radians.
But why radians? Well, for starters, radians are a more natural choice when it comes to circles. That's because the circumference of a circle is 2π times its radius. So, measuring angles in radians just makes more sense in this context.
Radians are defined as the ratio of the length of an arc of a circle to the radius of that circle. This definition makes them an ideal unit of measurement for trigonometric functions, which are based on the ratio of the sides of a right triangle.
In short, radians are the natural choice for measuring angles in mathematics. They may not be as well-known as degrees, but they are just as, if not more important. So, next time you work with circles and triangles, don't forget those trusty radians!
Radians to Degrees
Radians and degrees, oh my! You're probably already familiar with these two angle measurement units if you're a math geek.
For those who are new to the world of trigonometry, here's the deal: Radians are the standard unit in mathematics, but sometimes you need to convert to degrees because, well, that's what we're used to.
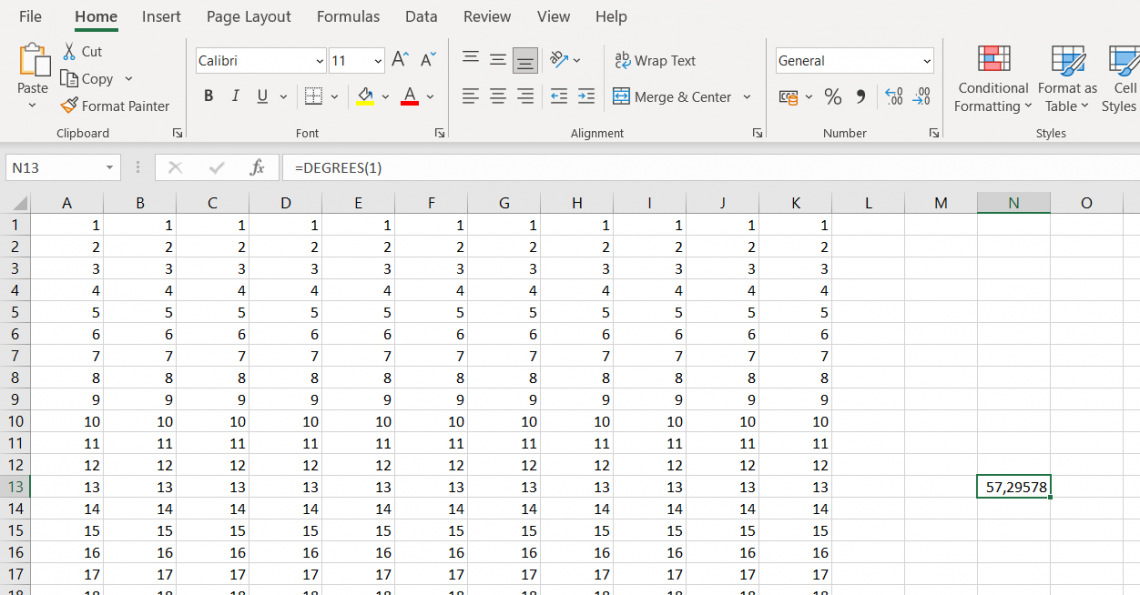
When working with trigonometry, converting between radians and degrees is often necessary. Here are a few key points to remember when converting between these units:
- 1 radian is equal to 57.29577951308232 degrees
- To convert from radians to degrees, you can use the formula: (radians x 180) / π
- To convert from degrees to radians, you can use the formula: (degrees x π) / 180
And here's the most important tip: Ensure you're consistent with the unit of measurement you use throughout your calculation. Trust me; you don't want to end up with a wonky answer because you switched units halfway through. That's just frustrating!
Why do we use the Degree Function?
In Excel, it is a valuable tool for converting angles from radians to degrees. It is more intuitive and useful for many applications as it is used and understood daily.
Here are a few reasons why we use the DEGREES function in Excel:
- In many technical fields, angles are usually measured in degrees. For example, in navigation, angles are measured in degrees to determine the direction of a ship or plane.
- Degrees are more used and understood in everyday life, which makes it easier to understand angle measurements. For example, the angle of a slope is measured in degrees.
- Many trigonometric functions in Excel and programming languages expect the input angle to be in degrees. It makes it more convenient to work with trigonometric functions in Excel.
- The degree is an accepted standard unit of measure, making it easy to understand even for people with no technical background.
- It provides a convenient and intuitive way to measure angles in many practical applications. For example, Measuring the angle between two lines in degrees is easy.
It is a helpful tool in Excel to convert angles from radians to degrees. Using it ensures that your calculations and formulas are accurate and easily understood by others.
Note
Remember that it's essential always to remember the unit of measure you are using and check your inputs and outputs.
How to use the DEGREES Function in Excel?
Turning radians into degrees with Excel is a breeze! There are a few different ways to use it, so let's take a look at a few examples.
Converting an Angle from Radians to Degrees:
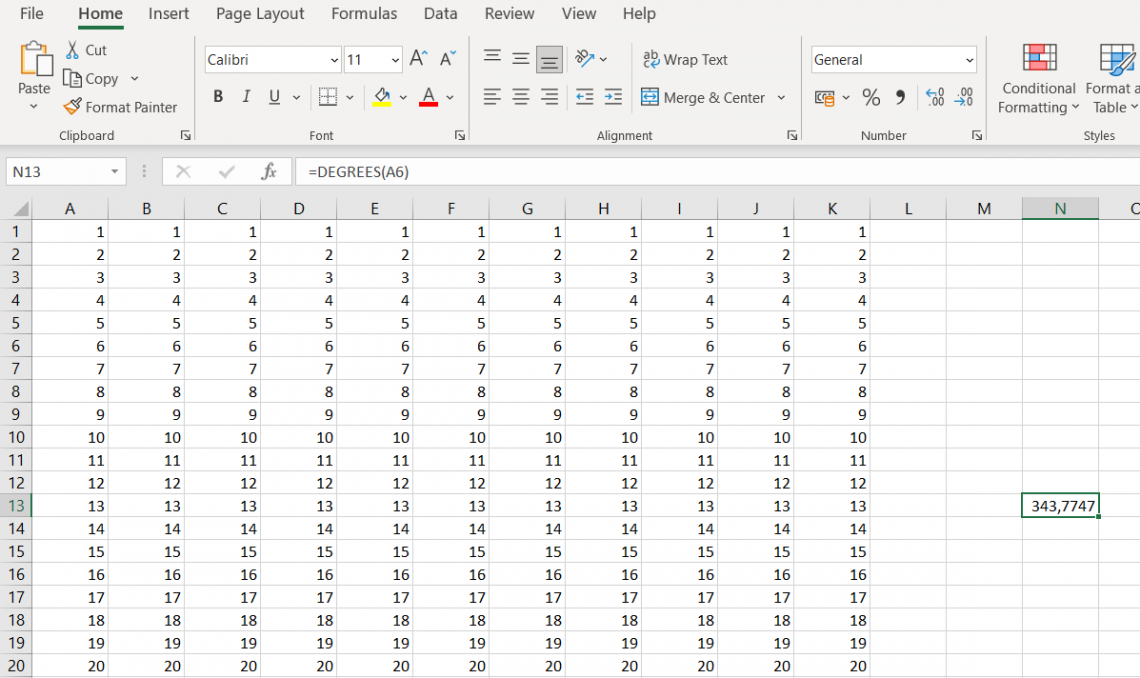
- Let's say you have the radian value in cell A6. To convert it into degrees, all you have to do is use the formula =DEGREES(A6) in another cell. Easy peasy!
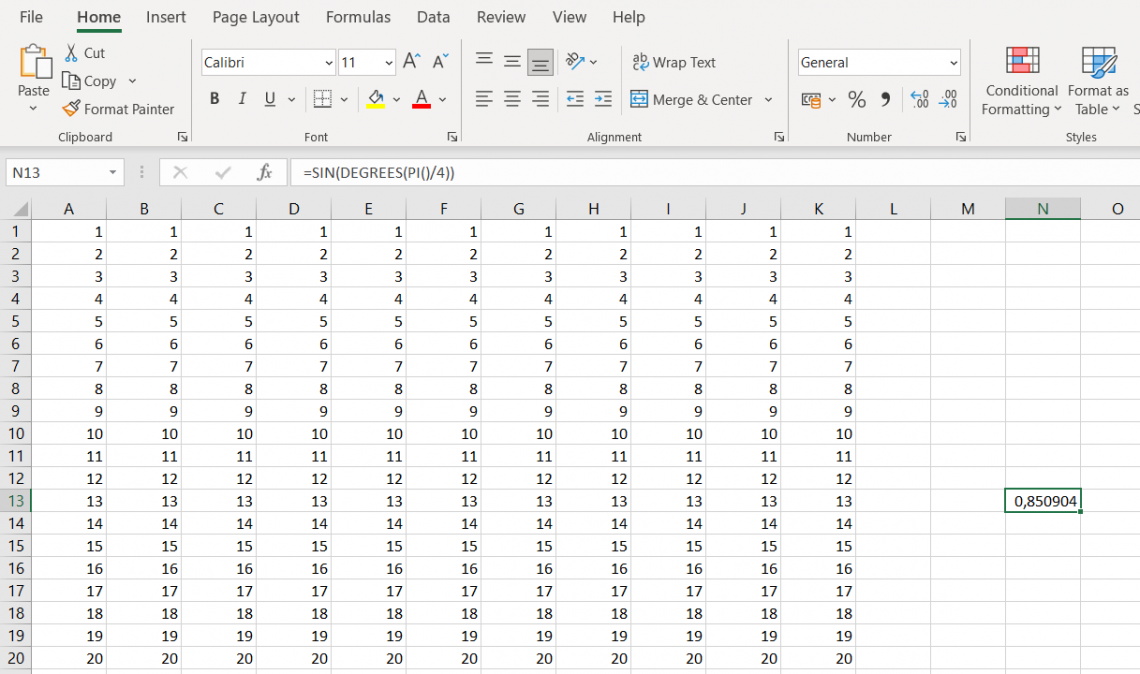
Using Trigonometric Functions:
- If you want to find the sine of a pi/4 angle, you can use the formula =SIN(DEGREES(PI()/4)), and you'll get the value 0.850904. It's like a magic trick!
Creating a Formula to Convert an Angle Measured in Radians to Degrees:
- If you want to convert an angle measured in radians to degrees in column B, use the formula =A1*(180/PI()). It's that simple!
It's essential to remember that Excel's trigonometric functions, like SIN, COS, and TAN, expect angles to be in degrees.
So, by using the function, you're ensuring that your trigonometric calculations are accurate and easy to understand. No more confusion or frustration, just pure mathematical joy!
When to use the DEGREE Function?
For example, let's say you are designing a ramp for a building that needs to have a slope of 8 degrees. You have a laser level that measures the ramp's angle in radians and needs to convert it to degrees.
To do this, you would use the function in Excel as follows:
- In cell A1, enter the value of the slope in radians (e.g., 0,1396)
- In cell B1, enter the formula =DEGREES(A1)
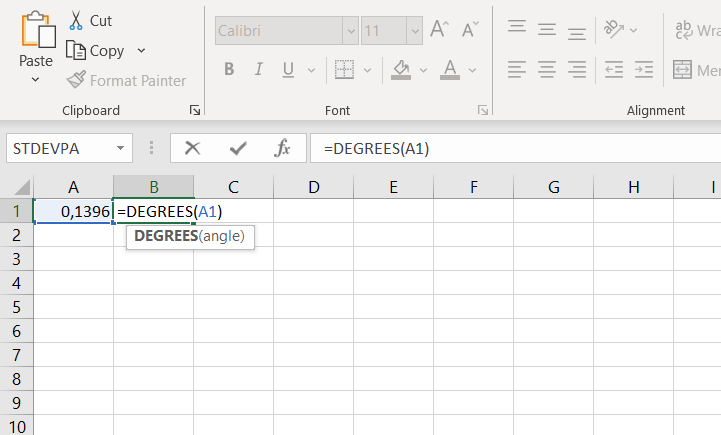
- Press Enter, and cell B1 will show the value of the slope in degrees (7,998491)
- Alternative, you can use the formula =A1*(180/PI()) to convert radians to degrees in cell B1
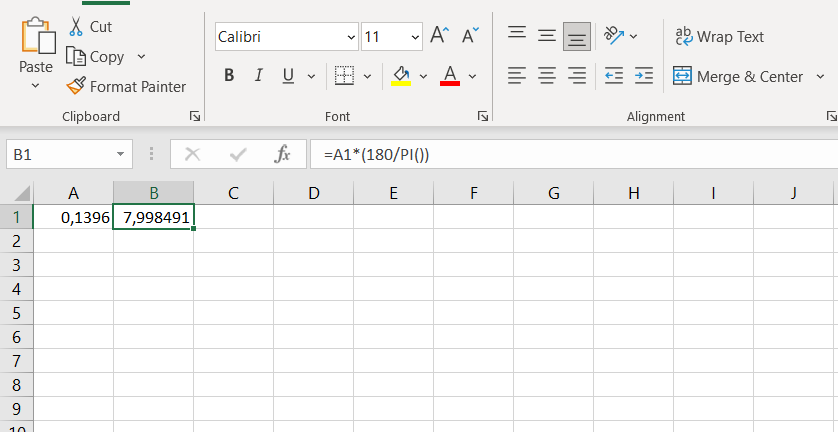
By using the function, you can convert the ramp's angle from radians to degrees; then, you can compare it to the design specification of 8 degrees to ensure that the ramp is built to the correct slope.
Using the Degrees Function
Say goodbye to complicated math conversions because converting radians to degrees in Excel is easy! Just think of it like spinning a wheel, but instead of measuring speed, you're measuring angles.

Here's how you can put the DEGREES function to work:
Locate your radian value and place it in a cell in your Excel sheet.
In another cell, enter the formula:
"=DEGREES(cell_reference)" with "cell_reference" being the cell that holds your radian value.
For instance, if your radian value is in cell A1, your formula would look like this:
"=DEGREES(A1)".
Hit the enter button, and voila! The cell will now show the corresponding degree value.
Now, the DEGREES function is a bit picky, so keep in mind that it only accepts one argument. This argument must be a numeric value, or you'll receive a #VALUE! Error.
It is important to remember that a function is only a conversion tool. It converts radians to degrees, but it won't perform any calculations independently.
The syntax of the DEGREES function in Excel is as follows:
DEGREES(angle)
Where:
- angle: This is the angle you want to convert from radians to degrees. It can be a number, a cell reference, or a formula that returns a number.
All in all, it is your go-to tool for easy radian-degree conversions in Excel. So, next time you're working with trigonometry, remember to remember it; it'll make your life much easier!
DEGREES(angle)
Advantages of the DEGREE Function
Say goodbye to the days of struggling with radians and hello to the good old degree. Yup, you heard that right; we're talking about the DEGREES function in Excel, the lifesaver for all angle-related problems.
Do you know what they say? When life gives you angles measured in radians, just convert them to degrees. Converting angles from radians to degrees has never been easier.
Think of it as the trusty sidekick to your Excel adventures. It's got your back with the ease of use, only requiring one argument and making it simple to understand. And let's not forget degrees are the preferred unit of measure in many technical fields, making it even more convenient.
But wait, there's more! Not only does the DEGREES function make your life easier, but it also makes your angles easier to understand. Say goodbye to the frustration of wrapping your head around radians and hello to the intuition of degrees.
And if that wasn't enough, Compatible with other Excel functions and formulas, giving accurate and error-free results. The superhero of angle transformations!
The DEGREES function is a must-have tool for anyone looking to simplify their angle-related calculations in Excel. So go ahead, try it, and embrace the power of degrees!
Disadvantages of the DEGREE Function
While the DEGREES function in Excel has many advantages, it has some potential disadvantages.
These include:
- Confusion with Radians: The DEGREES function can confuse when working with angles measured in radians. Some people may not be familiar with radians or understand how to convert them to degrees.
- Limited Use: The DEGREES function is most useful in technical fields, such as engineering and physics. But, in other areas, such as mathematics, angles are measured in radians.
- Inability to use Radian Formulas: When using the DEGREES function, you cannot use formulas based on radians, which may limit the types of calculations you can perform.
- Limited precision: A degree is not as precise as a radian; the degree may give you an error when it comes to a certain level of calculations. As with any tool, it's essential to use the DEGREES function appropriately and to be aware of its limitations to avoid potential errors and confusion in your calculations.
Overall, while the DEGREES function can be a valuable tool for converting angles from radians to degrees in Excel, it is essential to be aware of its limitations and use it.
Researched and Authored by Ahmet Taşdemir | Linkedin
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:





or Want to Sign up with your social account?