MDURATION Function
It is used to calculate a security’s modified Macauley duration.
The MDURATION function, utilized through Microsoft Excel, is a function used to calculate a security’s modified Macauley duration.

Similar to the MDURATION function, you can find other excel functions that must utilize the maturity duration to compute crucial aspects such as the number of periods for a matured security and the amount of payment.
A couple of similar functions closely related to the calculations and returns of the MDURATION function include the NPER function and the PPMT function.
All three functions include the computational components of a security’s initial date, its expiration date, and the annual yield of the security.
The NPER function and PPMT function also include additional variables that are important in noting the number of periods or the number of payments of a given security.
The NPER function uses a security’s maturity to calculate the number of periods. The PPMT function calculates the number of payments needed for maturity.
A couple of instances where you should avoid using the function is when the dates are incompatible. For example, the security dates might have dates that are not consecutive or occur in different time zones.
In these instances, trying to calculate the MDURATION will lead to an error.
The MDURATION formula will be discussed and broken down throughout the article, and an example will be followed. In addition, in the MDURATION function example, a detailed follow-through and navigation series will be included.
MDURATION Function Formula
The calculation for the Macauley security duration is as follows:
MDURATION(settlement, maturity, coupon, yield, frequency, [basis]).
In breaking down the formula, let’s better understand each necessary component and its contribution to calculating the security duration.

To begin, the “settlement” component of the function considers the settlement date at which the security was traded. Typically, the settlement date noted is the date following the security purchase and is a required part of the function.
Following the “settlement”, also as another required aspect of the function is “maturity.” The “maturity” variable considers the security’s expiration date.
Next is the “coupon rate,” which the security must pay annually and is a required part of the function.
The “yield” is also known as the security's annual yield. There are a couple of ways the annual yield can be known if it is not already given in the security information. Below are how the annual yield may be used, whether you are looking at a matured security or a discounted security.
To calculate the annual yield of a security with interest rates, the YIELDMAT function can return the answer. If calculating the annual yield of a discounted security, use the YIELDDISC function.
Lastly, of the required components of the excel function is “frequency” – the number of coupon payments paid each year.
One optional input of the MDURATION function is “basis,” as noted above in the brackets. The “basis” component measures the day count of the security use.
A follow-through example
In the example below, the security calculated involves crucial information such as:
- A coupon rate of five percent (5%)
- A calculated annual yield of three percent (3%)
- A coupon frequency rate of two, a biannual coupon rate
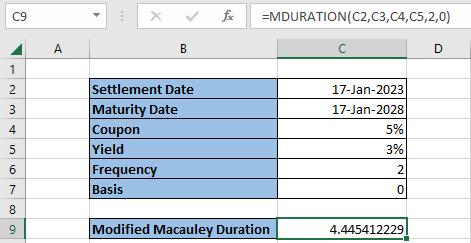
After inputting the necessary information in the Excel sheet, as demonstrated, the five-year security returns a modified Macauley duration of 4.445412229.
To reiterate and also shown in the highlighted cell, in C9, the formula used is as follows:
=MDURATION(settlement, maturity, coupon, yield, frequency, [basis]).
You can locate the function by selecting the desired cell in which you wish to input the modified duration.
In the example above, the modified duration or use of the MDURATION function is located in the “Modified Macauley Duration” above.
To make things easier to locate and keep the Excel sheet organized, creating labeled tables, such as the ones pictured, can help you navigate the returns you are looking for. Simply type in the cell “=MDURATION,'' and the function should appear. By double-clicking the function, you can now include the components.
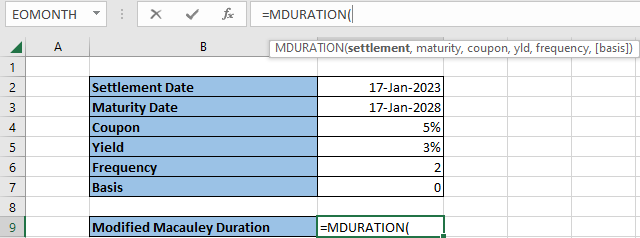
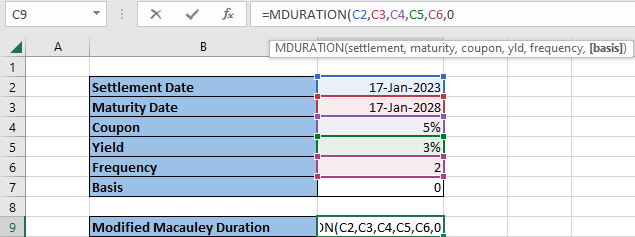
For reference, highlight each component of the table, from cells two through seven, to include the required data of the function.
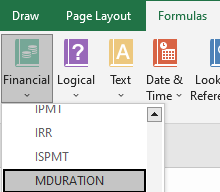
Another way to locate the MDURATION function is to follow the steps as directed in the instructions:
- In the Excel sheet, locate the Formulas tab at the top bar
- Click on Financial
- In the drop-down bar, a list of functions will appear in alphabetical order. Simply scroll down and locate “MDURATION.”
Suppose your returns are receiving errors like #NUM! or #VALUE! the data may be inputted incorrectly. Ensure the coupon rate and annual yield are numerical sets greater than zero.
Also, the frequency must be one, two, or four, as the frequency component relates to the annual payment period: annual, biannual, or quarterly.
As for the settlement and maturity dates, double-check that the purchase date (settlement) occurs earlier than the security’s expiration date (maturity).
Remember that the frequency period can differ from annually, semiannually, or quarterly. The example above demonstrates security with semiannual coupon payments.
- MDURATION functions calculate the modified matured duration of a given security
- The settlement and maturity dates must be entered as serial numbers, or it will return an error.
- The basis component, an optional input, must be a numerical set of one through four.
- There are several ways to calculate the annual yield through excel functions like YIELDMAT and YIELDDISC.
- Other similar functions to MDURATION that utilize modified matured durations are NPER and PPMT.
Reviewed & Edited by Ankit Sinha | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:





or Want to Sign up with your social account?