Net Tangible Assets
All assets that are physical in nature and have a monetary value
What are Net Tangible Assets?
Financial accounting is a part of accounting that entails recording, summarizing, and reporting various transactions arising from corporate operations throughout time.
These activities are summarized in financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which document the company's operating performance over time.
Under Financial accounting, assets and liabilities are divided into current and noncurrent assets and liabilities based on their physical nature.
The word "tangible" describes anything perceptible by touch. Tangible assets, also known as fixed assets, are a company's physical assets.
Tangible assets include properties of a business, vehicles, cash, inventory, plants and equipment, and investments.
A word opposite to tangible is intangible. These assets are the value-holding assets of a company that is not physical. Intangible assets include accounts receivables, pre-payments, patents, copyrights, and goodwill.
Similar to these assets, tangible and intangible liabilities do not exist in physical or physical forms. Examples of tangible liabilities are accounts payables, bills, taxes, and employee payables.
All non-monetary commitments associated with stakeholders that the corporation must fulfill to avoid the depreciation of its intangible assets are referred to as intangible liabilities.
GAAP stands for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. These are a set of rules set up for accounting and financial reporting. Financial statements are also produced according to rules and regulations set by GAAP.
Key Takeaways
-
Tangible assets also known as fixed assets are the assets of a company that is physical in nature.
-
Intangible assets are the assets of a company that are not physical in nature.
-
GAAP stands for generally accepted accounting principles, these are a set of rules set up for accounting and financial reporting
-
Financial statements of a company such as - balance sheets, income statements, etc, can be used to assess the liquidity and efficiency of a business along with the rate of return it is providing to its shareholders.
-
Ratio Analysis in which fixed assets are used is fixed asset turnover, it is used by management, investors, and creditors to make financial decisions for a company.
-
There are a few differences between tangible and intangible assets based on definition, valuation, liquidity, residual value, depreciation, and amortization.
-
Tangible assets are used as collateral for loans for banks. They can be subdivided into two categories known as current and non-current tangible assets.
Formula for Net Tangible Assets (NTA)
Net tangible assets are all assets that are physical in nature and have a monetary value. It can be formulated as taking away net intangible assets and all liabilities from total assets. The formula is listed as follows:
Net Tangible Assets = Total Assets - Net intangible assets -Total liabilities
Where can you find tangible assets?
A balance sheet or statement of financial position is a document provided to the company's stakeholders, such as - investors, creditors, etc. This document shows the financial part of a company, and it includes critical information about the company, such as - assets, liabilities, equity, etc.
The formula for the balance sheet is as follows:
Shareholder's Equity = Assets - Liabilities
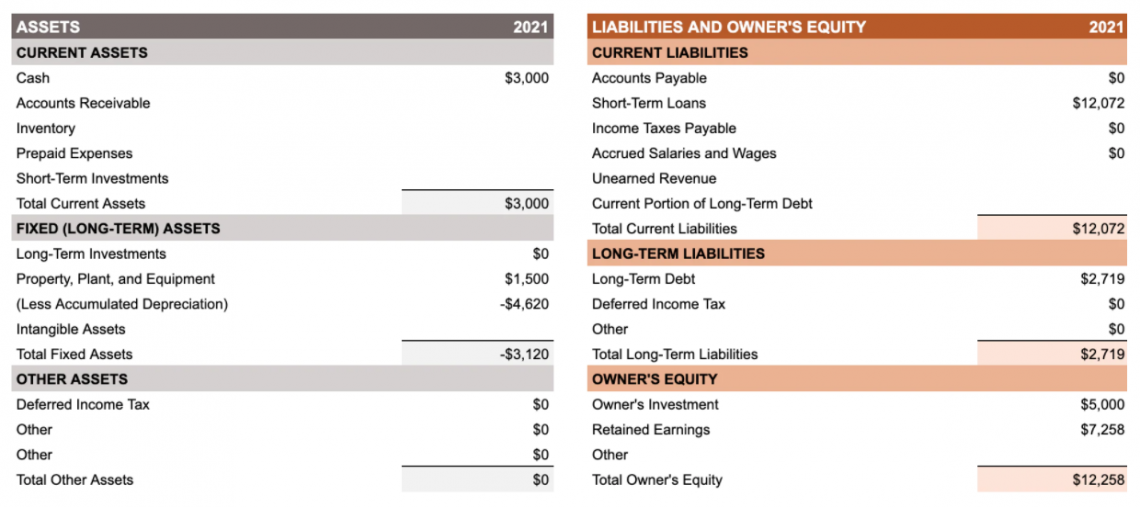
Financial statements of a company such as - balance sheets, income statements, etc, can be used to assess the liquidity and efficiency of a business along with the rate of return it is providing to its shareholders.
The income statement, also known as the Profit & Loss Statement, and the statement of operation contain the main elements of a business such as sales, revenue, income, profit and loss accounts, expenses, costs, and expenditures.
This financial statement helps stakeholders determine the company's health and projected financial trajectory, which impacts investment decisions. It also can provide information for business owners, such as to cut costs or increase sales within a department.
As observed from the above figure, we can clearly see net tangible assets, also known as total fixed assets, under the category of investments. Assets are further divided into current assets and other assets. However, we will be discussing tangible assets.
Similar to the balance sheet, another important financial statement is the income statement, which firms use to analyze their financial performance. This statement is generated annually and can highlight equity, which various user groups use in making their decisions.
Microsoft Excel is one of the most used applications to prepare financial statements for a company. It is because it offers various features to assist users in creating or editing financial data.
Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
The most popular ratio which involves the calculation of tangible or fixed assets is the fixed asset turnover ratio. The efficiency with which a corporation generates net sales from its fixed-asset investments is measured in the fixed asset turnover ratio.
This ratio is used by the investors and creditors to know how efficiently management uses the assets. The fixed asset turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio that can be formulated by dividing total revenue by the value of fixed assets.
The formula is as follows:
Fixed Asset Turnover = Revenue / Fixed assets
Fixed Asset Turnover = Net Sales / Average Fixed Assets
Certain values are considered good from the point of view of investors and creditors. Any business with a ratio value greater than 1 is considered good, meaning the business can generate good revenue by efficiently using its plants, equipment, and other assets.
A ratio value lower than 1 usually means the management is not using its fixed assets efficiently. Therefore, it is not worth investing in.
For example, if a company has a fixed asset turnover of 1.6, it means it is generating $1.60 in sales for every dollar of assets the firm possesses.
Tangible Vs. Intangible assets
Tangible and intangible assets are both value-holding possessions of a firm that are used to fund operations and in case of any financial crisis that could interfere with the functioning of a firm.
| Basis | Tangible Assets | Intangible Assets |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The value holding assets of a company that are physical in nature. | The value holding assets of a company that are not physical in nature. |
| Depreciation & amortization | They are subject to depreciation. | They are subject to amortization. |
| Residual value | Possess a residual value. | Have no residual value. |
| disadvantage | They can be destroyed by natural calamities. | They can be lost due to poor decision-making. |
| Valuation | The value of these can be determined easily. | Valuation is harder in comparison to tangible assets. |
| Liquidity | Easier to cash out due to their physical nature. | Are not easy to liquidate as they are not physical in nature |
| Usage | Creditors, banks accept tangible assets as collateral for loans. | These types of assets are not considered suitable for collateral by the banks and creditors. |
| Financial statements | Creditors, banks accept tangible assets as collateral for loans.Found under assets in the balance sheet under both current and noncurrent assets. | Found in the balance sheet under current assets. |
| Examples | Vehicles, cash, inventory, plant and equipment, and investments. | Accounts receivables, pre-payments, patents, copyrights, and goodwill. |
Tangible assets are assets that an organization acquires that have monetary worth and are physically present. Intangible assets are intangible assets with a specific useful life and monetary worth.
The physically present assets within the organization or the corporation are known as tangible assets. Intangible assets, on the other hand, are assets that do not exist physically and are instead stated as abstract.
Because tangible assets have a large material presence, they can be easily converted into cash when needed or in an emergency. However, selling intangible assets such as a trademark or goodwill, for example, would be challenging.
Uses and types of Tangible Assets
As understood from the above paragraphs, we know that tangible assets are physical in nature, and possess money value in them.
Tangible assets are used to supply a service or product, contribute to the financial flow of a company, and raise funds in the event of an emergency in order to achieve your company's aims and ambitions.
The company also uses tangible assets as collateral for getting loans from banks. Tangible assets are further divided into current and non-current tangible assets as explained below:
-
Current tangible assets - These assets can be quickly converted into cash. These will be reported as revenue in an earnings report. An example of an existing asset can be company inventory.
-
Non-current tangible assets - Fixed assets, often known as long-term assets, are assets that can not be converted into cash within a year. As a result, their worth will deteriorate over time, and their cost will be spread out across the years of use. A good example of a long-term asset is machinery.
Because it can be difficult to swap tangible assets for cash, different types of tangible assets will be treated differently in accounting. Fixed assets, such as real estate, have less market liquidity and are more difficult to sell.
Example of Net Tangible Assets (NTA)
Following is some financial information about company X. We will be calculating the net assets of the company:
| COMPANY X’s Tangible assets | |
|---|---|
| Cash | $ 120,000 |
| Inventory | $ 200,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $ 320,000 |
| Property | $ 250,000 |
| Equipment | $ 220,000 |
| Machinery | $ 100,000 |
| Furniture | $ 23,000 |
| Bonds | $ 135,000 |
| Total Fixed Asset | $ 728,000 |
| $ 7000 + $320,00028 | |
| Net Tangible Assets | $ 1,048,000 |
From the above calculation, we can conclude that we can calculate the total value of tangible assets from a company’s balance sheet.
This information calculated from this formula is not enough for investors and creditors to decide on their investments or provide loans.
Therefore, we have record data calculated from the fixed asset turnover ratio to provide investors and creditors with the relevant and necessary information to help make their decision about investments and giving out a loan.
Net Tangible Assets FAQs
Tangible assets, also known as fixed assets, are the assets of a company that is physical in nature. Tangible assets include properties of a business, vehicles, cash, inventory, plants and equipment, and investments.
The entire assets of a corporation are equal to the sum of its liabilities and shareholders' equity, according to the accounting equation. This is the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity.
Price to tangible book value (PTBV) is a valuation ratio describing the price of a security compared to its tangible net assets' book value as recorded in the company's balance sheet.
The company's entire book value less the value of any intangible assets, such as patents, goodwill, and intellectual property, is equal to the tangible book value number.
Equity, also known as shareholders' equity or owners' equity for privately held businesses, is the sum of money that would remain in the hands of a company's shareholders in the event that all of its assets were sold off and its liabilities were fully settled.
Depreciation is an accounting technique for spreading out the expense of a tangible item over the course of its useful life. How much of an asset's value has been used is shown through depreciation.




or Want to Sign up with your social account?