Cryptocurrency
A form of currency operated by a system of blockchains, which has the characteristics of being digital, encrypted, and decentralized.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a form of currency operated by a system of blockchains, which has the characteristics of being digital, encrypted, and decentralized.
Blockchains act as public ledgers, a method of storing data so that it is difficult or impossible to alter, hack, or cheat it. A blockchain is a digital log of transactions duplicated and distributed across the blockchain's complete network of computer systems.
Crypto implies a form of currency that is encrypted in cryptography. Therefore, it is also referred to as crypto-currency or crypto. The first kind of crypto is Bitcoin, invented in 2009 and has become world-known nowadays.
Cryptocurrency characteristics
The characteristics are as follows:
1. It is used for settling transactions without financial intermediaries
Unlike typical financial transactions, crypto transactions are conducted using decentralized blockchain technology, which means that the transaction is settled publicly. As a result, without the use of financial middlemen to function as a fair medium, transactions can be resolved.
2. It is a form of security that store value
As a basic money form, crypto also acts as a form of storing value, which means the value of assets will not be substantially affected by other factors.
After the 2008 economic recession, Bitcoin was invented as an alternative to fiat currency. Due to its deflationary nature, the total supply of Bitcoin is fixed. Therefore, investors perceive Bitcoin as a store-of-value currency comparable to traditional gold.
3. The crypto trilemma limits it
The Blockchain trilemma postulates fundamental errors in the understanding of cryptos. This further entails the concept's foundations. The proposition of Vitalik Buterin states the set of three main issues.
These include decentralization, security, and scalability.
These refer to various errors or challenges encountered during the construction of blockchains. Thus, it postulates a trade of the following aspects to construct cryptos.
Cryptocurrency examples
Bitcoin has been a trendsetter and has ushered a wave of alternative cryptos, which are also known as altcoins, since its launch. Yet, only several contemporaries will stay in the long run.
There are over 18,000 cryptos as of March 2022. Most of them have little trading volume. But, they enjoy a certain popularity among the investor community.
The variety can make it an overwhelming experience at first. However, this doesn't make it hard to understand or dwell on digital finance.
The top 10 best cryptocurrencies in May 2022, as per Forbes, are:
- Bitcoin (BTC)
- Ethereum (ETH)
- Tether (USDT)
- US Dollar Coin (USDC)
- Binance Coin (BNB)
- XRP (XRP)
- Binance USD (BUSD)
- Cardano (ADA)
- Solana (SOL)
- Dogecoin (DOGE)
Bitcoin remains the most secure, expensive, and oldest among various cryptos. As a result, bitcoins stay in the market as the dominant player.
The value of a single Bitcoin remains roughly 44,000 dollars. The market capitalization is more than 830 billion dollars. (as of February 2022).
Ethereum offers a wide range of applications offering solutions demanding the usage of blockchains. This includes smart contracts.
Tether continues to be offered with stability backed with the support of fiat currencies. US Dollar Coin is also backed up but by US Dollar only. The Binance Coin offers trade across the Binance exchange platform.
XRP continues to be used as an exchange platform. The other coins continue their operations with numerous benefits.
How does cryptocurrency work?
The Cryptos have found penetration in various spheres of digital inclusion and finance. This has included games, applications, and trade.
The facility enabled the concept. However, the challenge remains in its usage and development with protection.
The encrypted data string denotes a form of currency. The difference with conventional currencies is the lack of regulatory and control institutions.
The mining process uses a network of computers. These include specialized hardware. They are common application-specific integrated circuit processes that ensure the validation of transactions.
This acts as an incentive for miners who run the transactions for cryptos.
What are Cryptos? Cryptocurrency is also referred to as crypto. It is digital assets that circulate without the prerequisites. These include central authorities and financial intermediaries.
Cryptos are through technology termed blockchains. The blockchains maintain a tamper-resistant record of transactions. In addition, it maintains the track record of the owners.
The controversial aspect of cryptos remains in recognition and protection. These include restrainment in the creation of copies of its holdings. It also includes refraining from currency spent times.
Crypto holds fundamental aspects. The traits or characteristics of the system of cryptos are as follows.
The system doesn't have a central authority of regulation or control. These include various central banks and financial intermediaries. This implies it doesn't have the financial authority to regulate the system of currencies. This is the fundamental difference between traditional currencies.
Cryptos are a manner in which the designers are self-dependent. The system keeps a check on the ownership and overview of the units.
This poses another problem. The question of origin rests in the creation and lies with the ownership of the units. This can prove cryptography.
Also, it's state-maintained through a distributed consensus. Transaction of cryptos occurs only in the clear status of ownership. In case two transactions are entered at the same time. The system performs one at a time.
Structural classification of cryptos
The structural classification of cryptos consists of individual units. These units are coins or tokens. It is applied depending on the usage.
It is classified into various applications. Some of them are as follows:
- Usage to be units of exchange for goods and services. XRP facilitates various forms of exchanges backed up by fiat currencies.
- Denotation for stores of value. Cardano shows proof of stake validation. As a result, it is known for its storage value with less energy expended.
- They are into participation in specific software programs or applications. For example, Ethereum is used for smart contracts.
Cryptocurrency Creation Methods
The creation of cryptocurrencies involves various means of procedures. However, the common prevalent method is the process of mining.
It further elaborates on the mechanism of the addition of new cryptos into the system of blockchains with the usage of the proof of work technique.
This works each time a new crypto is added to the system. This method is employed due to a lack of centralized authority in functioning cryptos.
Mining is an energy-intensive process involving applications. Computers solve complexity in the form of puzzles. The purpose is the verification and authentication of transactions over the network. The owners of these computers receive new crypto due to mining.
It employs a proof-of-stake methodology that adopts a consensus mechanism for adding cryptos. This works on processing transactions for validation of procedures on distribution and security. This is in proportion to the quantity of stake of holdings associated with the currency.
The other types of cryptos use various methods of creation and distribution. These have a lighter environmental impact.
Cryptocurrency History
The concept of virtual currencies remains contemporary yet quite popular among investors. As a result, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple are quite prevalent in modern times, constituting large components.
Cryptography consists of encryption techniques that protect cryptos. The trace of its origins is in 2009. The transformation from academic illustrations to virtual reality led to the birth of Bitcoin. This wasn't the scenario a few decades back.
1. The 1980s - 2009 The Pre-Bitcoin Era: Academic transformation to virtual reality. The core idea was to allow the transfer of currencies from one medium to another.
2. Post-2009 Purpose of Initial Cryptos: It was to create an instant and direct transfer of money between two parties. The initial developers remained anonymous. It enabled the benefit of lower banking costs and transfer fees.
3. Post-birth of Bitcoins Subsequent implications: The Birth of Bitcoins led to subsequent media attention and speculations.
It brought a revolution, opening the doors of change. These included smart contracts, smart property, Notary services, and Bonded Identity services. This was present in the inherent value of crypto.
4. 2010 and after the Boom Era: Bitcoins peaked at a record high value. The value remained at $266 per bitcoin. It surged 10-fold over the previous value. Yet, what followed was not anticipated by followers of Bitcoin.
It had a market value of over $2 billion. This was at its peak. But, there was a later plunge of over 50 %. This sparked a raging debate over its usage, long-term goals, and applications.
The large, diverse arena of cryptos exists globally for a variety of reasons:
- It employs open-source code and censorship-resistant architecture, which promotes development differently from Bitcoin.
- It is decentralized in nature. It allows anonymity to exist in the network. Anybody to join the network without showing their identity.
controversies of cryptocurrency
The arguments against them are as follows:
- The anticipation and forecasting of alternative currencies offered by bitcoins and cryptos.
- The possibility of replacement of conventional currencies with virtual currencies. This refers to creating new arenas other than cryptos employing blockchains or similar.
- It is used in illegal transactions due to anonymity in nature.
- Mining promotes the large consumption of electricity, which creates a significant release of carbon footprint. Crypto has extreme price volatility.
- Unexpected exchange hacking prevails.
There are various models of postulations of functioning mechanisms. Some of them revolve around investors offering tokens as collateral.
Few revolve around the designers being regulators. Instead, the other sparks of controversy circulate its existence in a non-physical form.
There are currently over a thousand cryptos all over the world. It has a fluctuating market seeing steep rises and falls. Of these, seventy have a market value exceeding a billion dollars.
The academic conceptions included various papers and postulations in the last decades of the twentieth century.
Chaum's postulations in the 1980s consisted of electronic cash, called e-cash. The 1990s paper further elaborated on the minting process for electronic money. Dai's further postulations on the anonymity of electronic money.
The debate over Legality: The Debate remains in its meaning and evolution. Is it a fad or meant to stay as an ever-lit flame? The question remains unanswered with bitcoins.
In the first quarter of Fiscal Year 2022, cryptos show a flat movement. Yet, it is not the only financial instrument facing the bear phase, as referred to by the experts.
The world of cryptos is ever-revolutionizing, and new cryptos are coming daily.
The prime faces of importance revolve around two aspects. First, it allows engagement in a peer-to-peer network of transactions. Also, it provides permissibility to enter into contracts.
Global Cryptocurrency Adoption
The Chain Analysis Report 2021 illustrates crypto's geographic distribution and acceptance globally.
This capitulates some of the following insights:
- The countries acting as users of cryptos are weighted. These are on various parameters. This includes purchasing power and peer-to-peer usage.
- Countries are ranked on the grounds of purchases and transactions.
- Vietnam ranks first, followed by India's adoption and usage of cryptos.
- The other incentives faltered by Venezuela, Argentina, and Turkey. This is further inclusive of African countries. They have been at the forefront of the adoption of payment-to-payment transfer options.
- The 2021 Global Cryptocurrency Adoption Index put forth by the above-mentioned illustrates. This shows an increase in world adoption via P2P platforms. It is inclusive of savings, trading, and investment speculation.
- There is growth in cryptos concerning emerging economies markets.
- The growth in centralized services and expansion of digital finance sparked the explosion.
- There is a questionable aspect associated with Defi. This refers to decentralized finance. This extends to the presence of financial concepts with centralized regulatory institutions.
The Cryptocurrency Adoption at various levels of intensity, as per the Report
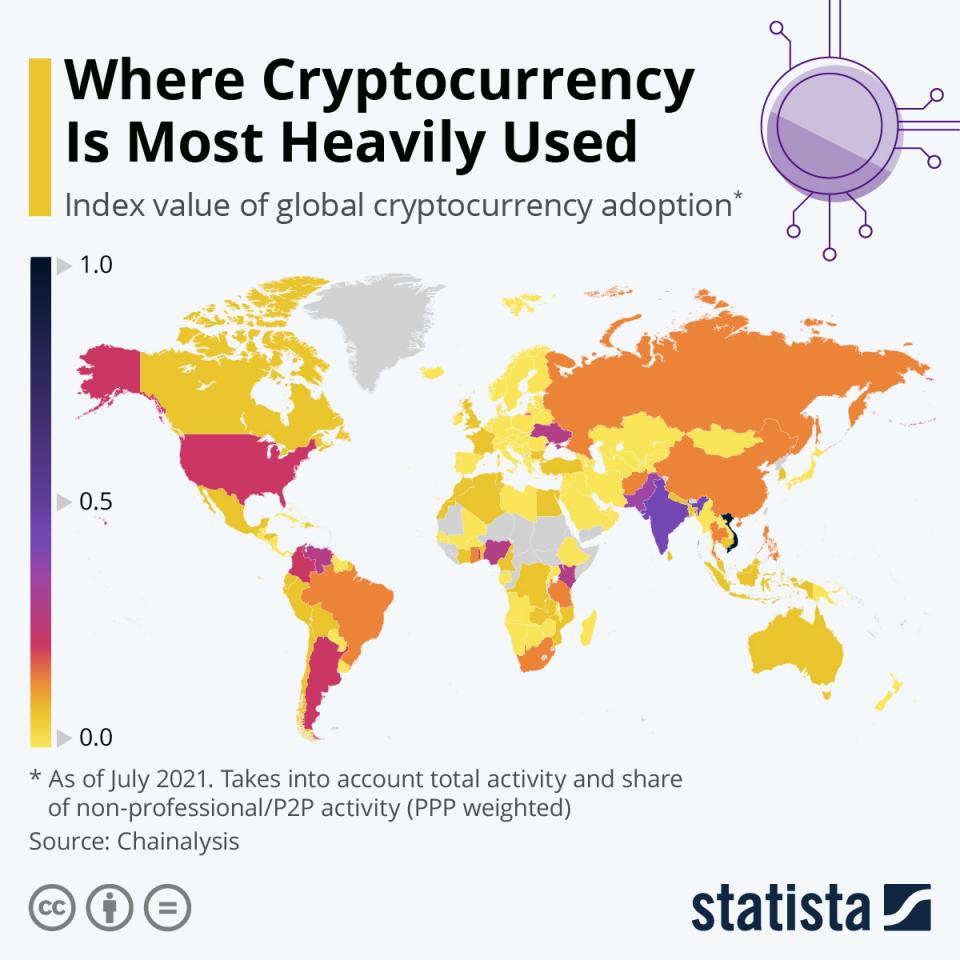
The index value of crypto adoption reflects the grade on a scale of 0 to 1.0. It further broadens the horizon on the grading scale of the intensity of grade ingredients of colors.
North America's Crypto Economy
It is the second-largest crypto economy. It received about seven hundred and fifty billion dollars in crypto. This was between July 2020 and June 2021. As per the Global Cryptocurrency Adoption Index, it ranks eighth globally.
The large usage in North America is due to the following reasons:
- The value of total currency received.
- The value of proportions of retail-sized transactions to the population using the internet.
- Purchasing Power Parity.
Yet, in North America and globally, crypto has several fundamental issues:
1. In Economic terms, cryptos can't be classified or termed money
- It is not universally accepted as money. Also, it doesn't serve the three main functions of money
- It doesn't have legal tender status
2. It acts as a medium for speculative motives only
- It doesn't have an income or practical usage
- It serves as an investment purpose without precautionary motive backup
3. It doesn't have a storage value
- Lacks liquidity and stability
- The trading suffers from manipulation due to whale wallets
4. It has a fixed supply problem
- Its fixed supply is often seen as a potential benefit. Yet, economists and monetary specialists see it as a posing problem
- This is due to a lack of coordination between fixed supply and the speed of amount fluctuations. This stable supply creates a threat to create counter-cyclical policies
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cryptocurrency
The benefits and disadvantages offered by cryptos are numerous.
Benefits include:
- It erases the need for financial intermediaries. This implies the absence of instruments and institutions. The transfer of money is possible.
- It offers a cheaper substitution. This functions with fewer costs of operations compared to other online transactions.
- It offers a safer alternative with anonymity. Yet, it has posed threats of ransomware.
- The lack of regulatory institutions offers immunity. This is against any form of manipulation or interference by central banks.
- The problems associated with cryptos due to lack of regulation are numerous. These include frequent manipulation, easy exploitation, and fraud associated with it.
- Among security issues, it has several regulatory issues. These are a lack of crypto pairs, inconvenient user interfaces, and high withdrawal fees.
This includes:
- Maintenance by distributed networks in the absence of regulatory institutions.
- It has a record of crypto owners.
- The system of maintenance is by cryptography.
Disadvantages are:
- The industries and institutions offering the most significant scope of the mining process face common threats.
- This is due to crimes, threats, and constant war between regulators. The battle to regain control to reduce monetary threats.
- The free-wheeling decentralized crypto market poses several fundamental questions.
- The lack of regulatory institutions.
- Digital currency allows permits for luxury goods only and access to a few websites.
- The increase in scams associated with the currency.
Cryptocurrency FAQs
This has numerous steps. This includes:
- Find a crypto exchange or broker.
- Create an account and deposit cash, buy cryptos. Be clear about the selection of storage methods.
The Cryptography system makes it a secure means of securing transactions and availing digital currency. However, the experts postulate the risks due to decentralized structure and regulations. It further adds to the risks of causing disruptions in finance and law.
Researched and authored by Anannya Sahani
Edited by Ka Chun CHIU | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:









or Want to Sign up with your social account?