Stop-Limit Order
It is a combination of a stop order and a limit order, which traders use to enter or exit security at their desired price.
A Stop-limit order is a combination of a stop order and a limit order, which traders use to enter or exit security at their desired price. This order type is used for both – booking profits and minimizing losses.

However, for a better understanding of a stop limit order(SLO), it is essential to be familiar with a stop order and limit order:
1. Stop order
A stop order is an order which is placed by a trader to buy or sell any security after it has crossed the desired stop price decided by the trader. Once the stop price is breached, the order is executed at the next available price in the market.
2. Limit order
A limit order is an order which is placed by a trader to buy or sell a security at a specific price decided by the trader. Once the limit price is reached, the order gets executed at the limit price or a better price.
Using this combination of a stop order and limit order, a trader, with the help of SLO, can decide the maximum amount of profit he wants to make in a particular trade or the total amount of loss he is willing to endure for a specific trade.
Such an order shields the trader from market volatility and ensures the amount lost or gained in a particular trade.
How does a Stop Limit Order work?
A stop-limit order works best when a trader is familiar with technical analysis or if he knows the price action of the security he is willing to trade.
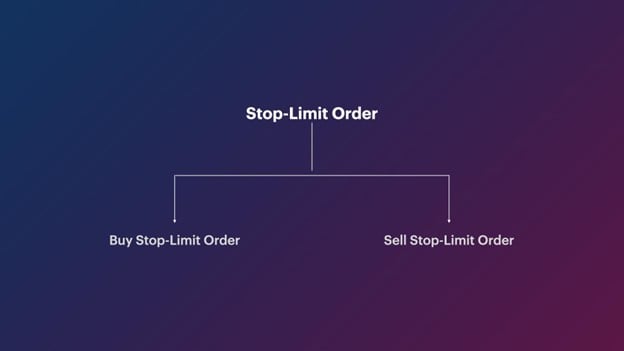
An SLO is not limited to a specific side of a trade. It can be used for buying as well as selling security. For example, a 'Buy stop-limit Order' is used to buy a security at the desired price. Similarly, a 'Sell stop-limit Order' is used to sell a security at an expected price.
Knowing about the support (the price upon reaching which the price shoots up) and resistance(the price upon reaching which the price falls) points of security can be very beneficial for the trader in making the best out of this tool.
Let's go through the following examples to understand better the usage and application of both 'Buy SLO' and 'Sell SLO.'
Example of Buy Stop Limit Order
Let's look at META Platforms, Inc.'s candlestick chart below to understand the application of SLO while buying security.
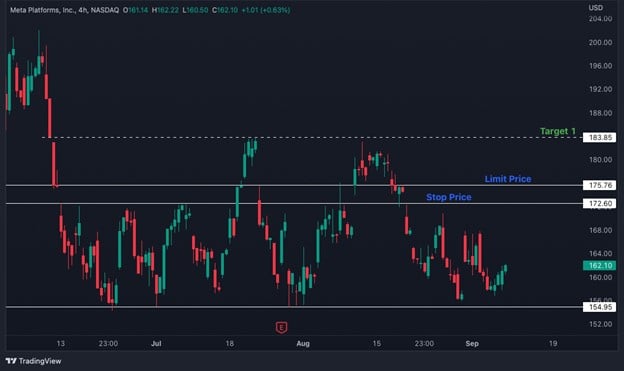
Let's assume that a trader wants to create a long position in META Platforms, Inc.
Looking at the chart above, it is clear that there is strong resistance at the $173 zone because the price falls every time it touches that zone. It can also be observed that there is a minor resistance at the $176 area, and above that, the next resistance is at the $184 zone.
Hence, the trader decides to place an SLO by setting the stop price at $173 and the limit price at $176 so that he can earn at least $8 per share if his target is met.
As soon as the price breaks $173, i.e., the stop price, the order will be triggered and sent to the exchange for execution. However, the order will not be executed if the price shoots up too quickly and crosses $176.
This enabled the trader to control the desired entry price and maintain a good risk-to-reward ratio.
Example of Sell Stop Limit Order
Let's look at the same candlestick chart of META Platforms, Inc used in the above example to understand the application of SLO while short-selling security.
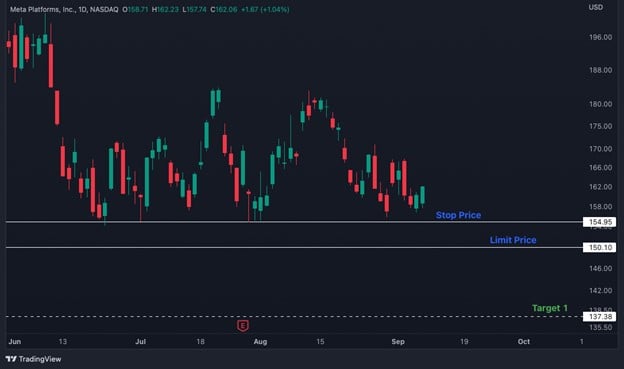
Now, let's assume that a trader wants to create a short position in META Platforms, Inc. and wants to make a minimum profit of $12 in the trade.
Looking at the chart above, it is clear that there is strong support at the $155 zone because the price shoots up every time it touches that zone. Hence, it is possible that the price could fall sharply if it breaks the support zone at $155.
Therefore, the trader will place the stop price at $155 and limit the price to $150 to maintain the minimum desired profit per share.
As soon as the price goes below the stop price, i.e., $155, the order will be triggered and sent to the exchange for execution. However, if there is a sharp fall in the stock price and it crosses the limit price, i.e., $150, the order will not be executed.
Hence, the trader can enter the trade at his desired price per risk-to-reward ratio.
Advantages and disadvantages of using a Stop Limit Order
An SLO allows the trader to control the price at which they want to enter or exit a position. It is very beneficial in planning trades and placing orders based on technical analysis. It also shields traders in highly volatile securities.

The advantages of using an SLO are listed below:
1. Price Certainty
The trader using this tool to make new positions in any security is insured that their order will only be executed at the desired price.
2. Protects capital in highly volatile markets
Due to market volatility, traders who place orders at market price get worse and suffer losses or reduce profits by a considerable margin. Using SLO ensures that the order will only be executed at the required price.
3. Helps in profit booking
This tool helps the traders to place a limit on the profit they want to book and get out of the market as soon as the target is reached. This increases the discipline of the trader and keeps greed in check.
Despite ensuring price certainty, protecting capital in a volatile market,s and helping traders to book a predetermined profit, a stop-limit order invites a few risks for a trader.

It becomes utterly useless in case of low volumes and volatile intraday markets. Moreover, there is also a risk of partial execution or no execution at all in some cases. This puts the trader's capital at risk and decreases profitability.
The disadvantages of using a stop-limit order are as follows:
1. Partial execution of orders
In this type of order, the order starts getting executed when the price crosses the stop price and stops if the price crosses the limit price. Hence, in some cases, the order receives partially filled, and the trader is left with a partial order.
For example, if the order is for 1000 shares of XYZ Co. with a stop price of $50 and the limit price is $60, as soon as the price hits $50, the order starts getting executed.
However, after executing 400 shares, if the prices spike at once and cross $60, the quantity still needs to be executed (600 shares) will be canceled.
Due to partial execution of the order, the trader will have to place the order for the rest of the quantity again, and the broker will also charge a commission on it. This will increase the expenditure of the trader and take a toll on profits.
2. Failure in execution
In some cases, the order might not get executed. For instance, in a buy order, if the stop price is crossed, but the number of sellers is limited at that time, and instantly the limit price is reached, the order might only get executed partially.
Due to this, traders might fail to participate in extensive breakouts and decrease their profitability.
3. False trigger in volatile markets
The order might get triggered if there is some irregular spike in price in the intraday market. However, the trader might get trapped and suffer losses if the price spikes just enough to trigger the order and then fall back to the original price.
Best way to use Stop Limit Order
We have discussed the benefits and the risks involved in using stop-limit orders for placing orders to buy or sell a security.

However, a trader must be accurate and consistent to make profits using this kind of order to buy or sell securities. Therefore, they should be alert to the strategies and market study before placing orders to minimize losses and earn a good profit.
Let's discuss some strategies and factors which a trader should keep in mind to make the best use of SLO:
1. Liquidity
The trader must consider the liquidity of the commodity they want to trade before placing such an order type. There are often insufficient sellers or buyers at a price between the stop price and the limit price.
Due to the lack of liquidity, the orders may get only partially filled or may not get executed altogether.
2. Strong price analysis
This type of order works best with technical analysis and price action. Through technical analysis, chart reading, and determining a stock's price action, traders can identify the support and resistance zones.
According to the trade, placing the stop price and limit price at the support or resistance zone would increase the probability of proper execution of orders and making profits or protecting the capital to the least.
3. Market Volatility
This type of order often fails due to a false trigger of the orders or incomplete execution. Also, it happens due to market volatility.
Hence, a trader must consider the intraday price spikes and volatility of the security they are willing to trade before placing the stop price and limit price.
4. The sufficient gap between the stop price and the limit price
There should be a sufficient gap between the stop and limit prices while buying or selling a security. If the gap between the two prices is too small, the price will hit the limit soon after the stop price, and the order might get canceled or remain unexecuted.
FAQs
Yes, an SLO can be used to buy and sell a security.
An SLO, in case of an intraday trade, remains valid till the closing time. In other cases, it acts as a GTC (Good-till-canceled) order.
A stop limit order is of two types – Buy Stop Limit and Sell Stop Limit.
If there is a huge gap up or down due to which the price crosses both the SL and LP, the order will not be executed.









or Want to Sign up with your social account?