Series Exams
Securities professionals who want to register must pass FINRA-administered qualifying tests to prove their proficiency in the specific securities
What Are Series Exams?
Securities professionals who want to register must pass FINRA-administered qualifying tests to prove their proficiency in the securities activities they plan to engage in. A person must pass the tests to participate in various aspects of the business.
When you decide to sell investment products, whether you are a registered representative or an investment advisor, the first step you need to take is to choose an appropriate securities license.
Some criteria can help you filter out suitable licenses, such as:
- The type of investment product to be sold
- The method of subsidy
- The scope of services
These tests cover various topics related to markets, the securities sector, and its regulatory framework. This entails familiarizing with FINRA and other self-regulatory bodies' rules (SROs).
The exams aim to ensure that a person has at least a basic comprehension of the material. In this article, we'll look at the many licensing options and demonstrate how to choose the one that's best for you.
Key Takeaways
- Securities professionals need to pass FINRA exams to demonstrate expertise in securities activities for various roles.
- Choosing appropriate securities licenses involves considering factors like investment type, subsidy method, and service scope.
- Key Series exams include Series 7, 63, 6, 57, and 24, each catering to different aspects of securities trading.
- The SIE exam serves as a foundational step, assessing basic knowledge of the securities industry, regulatory agencies, and prohibited practices.
- NASAA exams like Series 63, 65, and 66 focus on state and investment advisor law, leading to roles as Registered Representatives or Investment Adviser Representatives in the diverse financial industry.
Different Types of Series Exams
Series 7 is the General Securities Representative Examination, a required license for financial personnel stipulated by the United States government.
The required securities qualification examinations include Series 7 and Series 63, New York State Securities Law, which is similar in content and methodology to CFA Level I.
The US stock market is a significant global financial investment center and the focus market of international investors. Overseas people who step into some markets and become brokers, investors, or analysts in these markets will have endless development opportunities and space for asset appreciation.
With these licenses, there is a wide range of American employment and development opportunities. Well-known financial institutions such as Citigroup, Merrill Lynch, and other foreign banks or brokerages are listed as one of the required qualifications for employees.
The Financial Regulatory Authority (FINRA) reviews all securities licensing processes and requirements. The body is a self-regulatory body that certifies those who pass the exam as licensed financial professionals.
The FINRA also maintains relevant discipline and performs data management duties. FINRA offers different qualifications for sales representatives and management. Each qualification corresponds to a specific security or investment type.
The length of time allotted to finish each exam is listed in the Duration column below. The instructional and post-test surveys each take 30 minutes, in addition to the exam appointment time.
Additional ungraded (pretest) questions may be present on some tests. The kind of securities license you require will largely depend on the goods, transactions, and recommendations you make.
A license enables you to increase the scope of your financial products and services and enhance your management style. We'll only briefly touch on them here, but if you're interested in learning more, see this list of FINRA licenses.
Securities Industry Essentials Exam (SIE)
SIE is the latest and most basic exam among all financial certificates. It is an entry-level certificate for financial practitioners. The exam is not difficult and is the most suitable stepping stone for new financial professionals.
The SIE is an entry-level examination that assesses knowledge of basic information about the securities industry, including:
- Types of products and their risks
- The structure of the securities industry market
- Regulatory agencies and their functions
- Prohibited practices for securities practitioners
SIE allows you to have basic knowledge of finance and an introduction to the securities industry. The SIE license can be transferred to various financial jobs, such as investment banking, securities analysis, private placement, industry research, securities trading, etc.
| SIE (Securities Industry Exam) | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 1 hour 45 minutes |
| Questions | 75 |
| Exam Cost | $80 |
| Passing Score | 70 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
Eligibility: Anyone over 18 is welcome to participate in SIE, including students and job hopefuls who want to show prospective employers that they have a basic understanding of the business.
Note
You can register for an account on the FINRA website and participate in SIE without being associated with the company.
The individual must submit Form U4 by the company they belong to take the qualifying exam. The following picture shows the sections that the exam will cover:
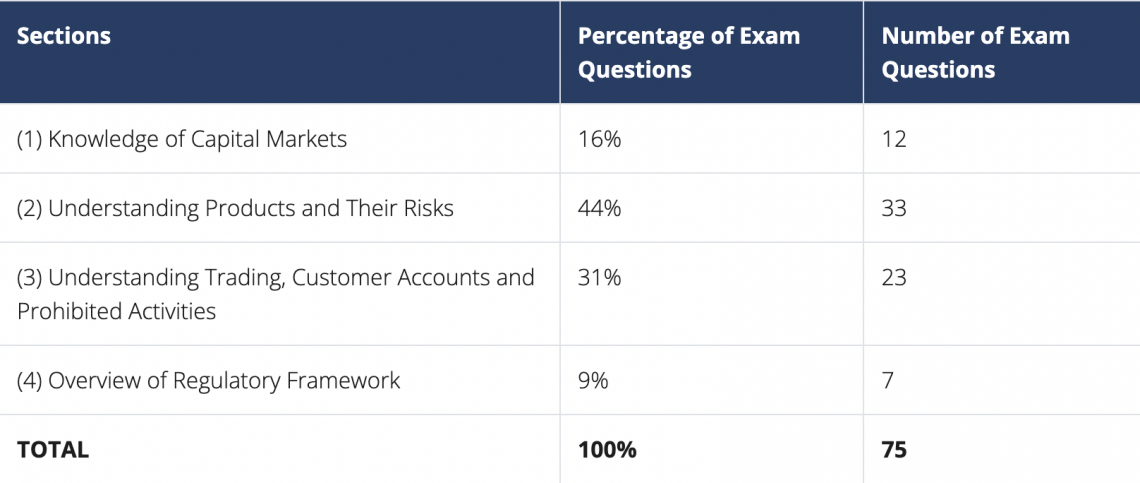
In the following paragraphs, we will further describe the exams regarding their content, exam duration, the number of questions, exam cost, exam format, and how they differ:
- Series 6 (Investment Company and Variable Contracts Products Representative Exam)
- Series 7 (General Securities Representative Exam)
- Series 57 (Securities Trader Representative Exam)
- Series 24 (General Securities Principal Exam)
- Series 79 (Investment Banking Representative Exam)
Series 6: Investment Company and Variable Contracts Products Representative Exam
The Series 6 Content Outline offers a thorough overview of the breadth of subjects examined on the test and the level of expertise necessary.
The exam time for Series 6 qualification certification is 135 minutes. The exam content covers basic information, such as:
- Packaged investment
- Securities management regulations
- Ethical standards
It is also one of the most common licenses. Many students will choose the first license.
| Series 6 | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 1 hour 30 minutes |
| Questions | 50 |
| Exam Cost | $75 |
| Passing Score | 70 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
The four primary responsibilities of an investment firm representative and a representative of variable contract products are included in the framework. The distribution of exam questions for each significant job function is shown in the table below:
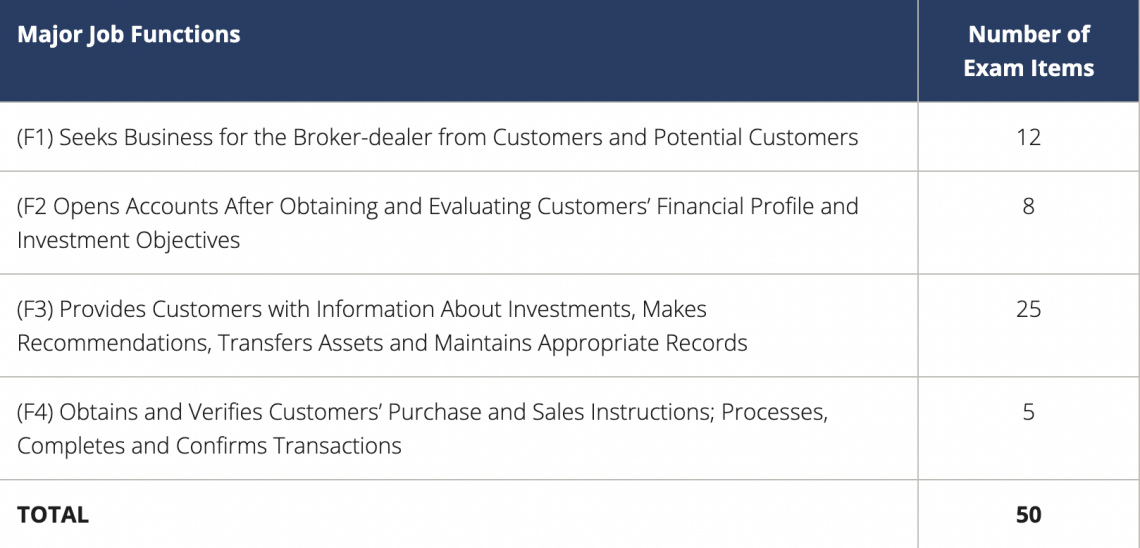
Refer to FINRA Rule 1210 for more details on registration requirements. The Series 6 test requires the SIE exam as a prerequisite. To receive the Investment Company and Variable Contracts Products registration, candidates must pass both the Series 6 exam and the SIE exam.
Series 7: General Securities Representative Exam
The general securities broker license is another name for this certificate. The licensee is given the authority to sell practically all categories of personal securities.
These include:
- The most popular stocks
- Ordinary and preferred stocks
- Options (calls and puts)
- Bonds
- Other personal fixed-income investments
Note
However, it should be noted that despite holding Series 7 licenses, they are not permitted to sell life insurance, real estate, or commodity futures.
The exam gauges how well each applicant is prepared to carry out the essential duties of a general securities representative, including:
- The sale of corporate
- Municipal, and investment companies
- Variable annuities
- Direct participation programs
- Options
- Government securities
| Series 7 | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 3 hours 45 minutes |
| Questions | 125 |
| Exam Cost | $300 |
| Passing Score | 72 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
The Series 7 Content Outline offers a thorough overview of the breadth of subjects examined on the test and the level of expertise necessary. The general securities representative's four primary job functions are listed in the outline.
The distribution of exam questions for each significant job function is shown in the table below.
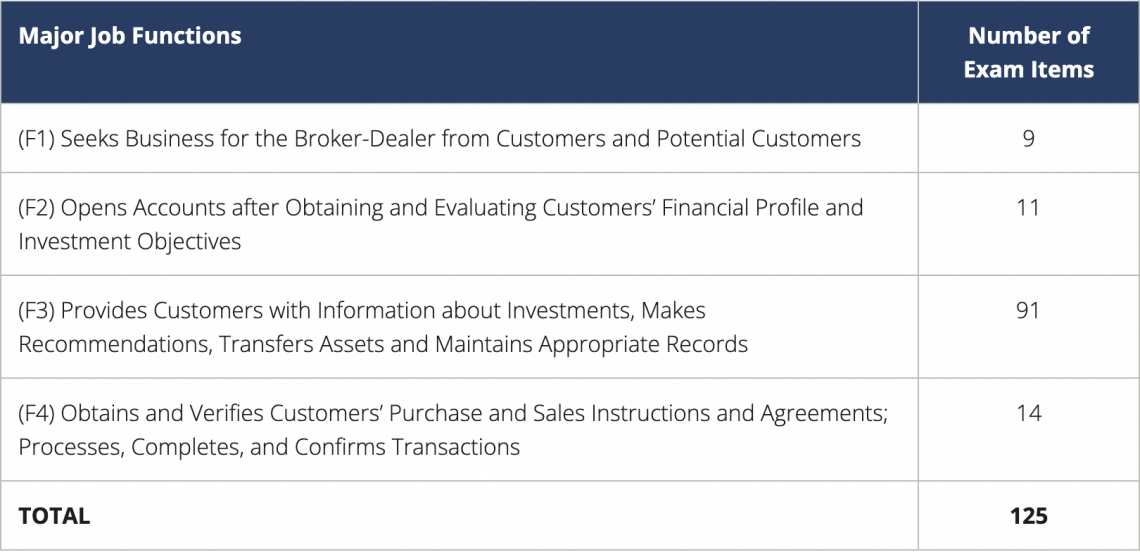
The SIE test is a corequisite to the Series 7 exam. Therefore, candidates must pass both the Series 7 exam and the SIE exam to receive the General Securities registration.
Series 57: Securities Trader Representative Exam
By ensuring that professional traders satisfy a necessary quality of professional knowledge and competency, the Series 57 exam serves to protect the public. Aspiring traders must also pass the Securities Industry Essentials (SIE) test and the Series 57 exam.
After passing both exams, beginning traders are authorized to engage in proprietary trading and trading on the Nasdaq exchange and over-the-counter (OTC) transactions.
Note
The Securities Trader Representative Exam, or Series 57 exam, evaluates a registered representative's ability to carry out their duties as a securities trader representative at the entry level.
The Series 57 exam assesses a candidate's knowledge of the essential duties of a securities trader, including the ability to execute transactions in equity, preferred, or convertible debt instruments that are not carried out on a securities exchange (proprietary trading).
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 1 hour 45 minutes |
| Questions | 50 |
| Exam Cost | $80 |
| Passing Score | 70 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
The Series 57 Content Outline offers a thorough overview of the breadth of subjects examined in the test and the level of expertise necessary. In addition, the two primary duties of a securities trading representative are included in the framework.
The distribution of exam questions for each significant job function is shown in the table below.

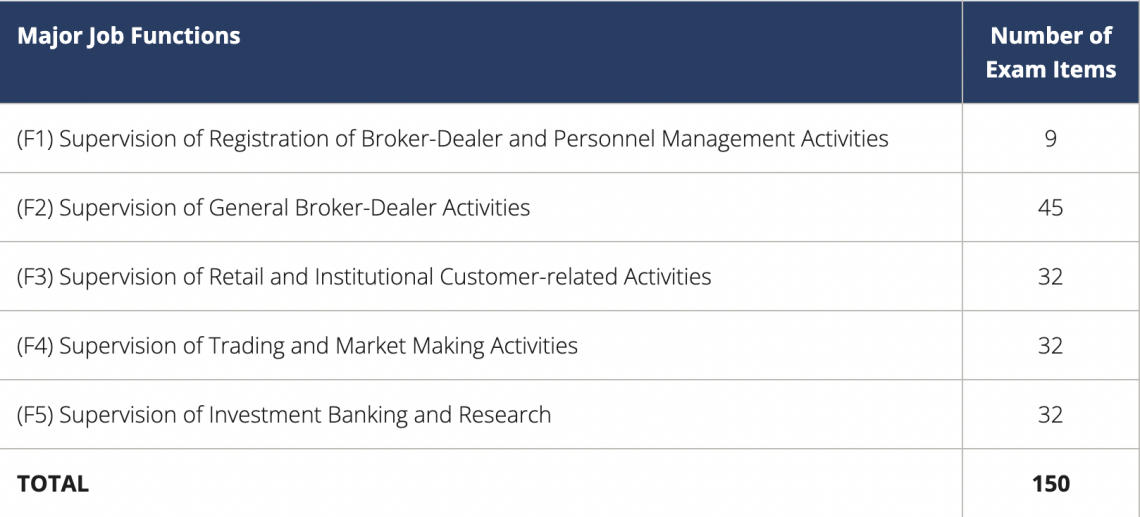
Series 24: General Securities Principal Exam
The General Securities Principal Qualification Exam (GP), part of the Series 24 exam, evaluates an entry-level principal's ability to carry out their duties as a principal in light of their core registrations.
The exam gauges how well each candidate is prepared to carry out the crucial duties of a principal, including their understanding of the laws and regulations that govern the management of a general securities broker-dealer.
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 3 hours 45 minutes |
| Questions | 150 |
| Exam Cost | $175 |
| Passing Score | 70 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
For candidates to possess an appropriate principal registration, they must also complete the Securities Industry Essentials (SIE) Exam, a representative-level qualifying exam, or the Supervisory Analysts Exam (Series 16).
After passing the Series 24 exam, candidates will be granted one of the following significant registrations based on their corequisite qualification(s):
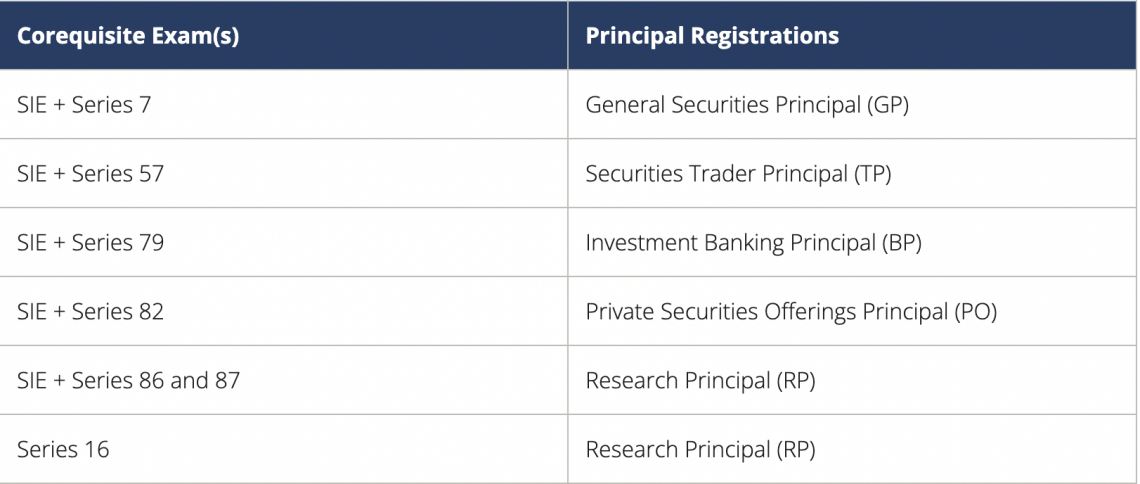
The Series 24 Content Outline offers a thorough overview of the breadth of subjects examined on the test and the level of expertise necessary. In addition, the five primary responsibilities of a general securities principal are listed in the outline.
The distribution of exam questions for each significant job function is shown in the table below.
Series 79: Investment Banking Representative Exam
Candidates seeking entry-level positions as investment banking representatives must pass the Series 79 exam. This test, along with the Securities Industry Essentials (SIE) exam, is a requirement to become registered for the position.
Although it's considered a "lighter" version of the Series 7 exam, Series 79 is rather challenging. Continue reading for more information about the Series 79 exam, including prerequisites, passing requirements, and a test breakdown.
The Investment Banking Representative Exam, commonly known as the Series 79 exam, assesses a registered representative's capacity to perform the tasks of an entry-level investment banking representative.
As a representative exam, the Series 79 exam satisfies the Series 24 prerequisite. The Series 24 General Securities Principal can only perform investment banking supervisory duties if they have passed the Series 79 test, an investment banking-specific examination.
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 2 hours 30 minutes |
| Questions | 75 |
| Exam Cost | $300 |
| Passing Score | 73 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
North American Securities Administrators Association (NASAA) Exams
In the following paragraphs, we will further describe the content, exam duration, number of questions, exam cost, exam format, and how they differ from each other:
- Series 63
- Series 65
- Series 66
A) Series 63 - Uniform Securities Agent State Law Exam
Each state mandates the Series 63 license, also known as the Uniform Securities Agent license, which entitles licensees to conduct business inside the state.
This license is also required for Series 6 and Series 7 license holders. On the 75-minute exam, the Uniform Securities Act's provisions are assessed.
| Details | |
|---|---|
| Exam Duration | 1 hour 15 minutes |
| Questions | 60 |
| Exam Cost | $147 |
| Passing Score | 43/60 |
| Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
Despite being significantly shorter and covering less content than the FINRA tests, this test is renowned for its "trick" questions, which force candidates to clearly understand the distinction between transactions and situations that are allowed and those that must adhere to the rules.
B) Series 65 - Uniform Investment Advisor Law Exam
Anyone planning to offer any form of financial advice or service on a non-commission basis must hold a Series 65 license. This group includes hourly-paid financial planners, counselors, stockbrokers, and other registered representatives who deal with managed money accounts.
| Details | |
|---|---|
|
Exam Duration |
3 hours |
|
Questions |
130 |
|
Exam Cost |
$187 |
|
Passing Score |
94/130 |
|
Exam Format |
Multiple Choice |
The 180-minute exam for this licensure includes the laws and standards governing registered investment advisors, different types of investments and investment disciplines, economics, ethics, and analysis.
Since many of the advisors who take this exam are not already licensed as Series 7 advisors and may never be, they need exposure to the investment information given there. Much of the material is also covered on the Series 7 exam.
C) Series 66 - Uniform Combined State Law Exam
The most recent test that NASAA offers is Series 66. The Series 63 and 65 tests are combined into a single 150-minute exam. The Series 66 license is only available to candidates who have already obtained their Series 7 license; hence this test does not include any investment-related topics.
| Details | |
|---|---|
|
Exam Duration |
2 hours 30 minutes |
|
Questions |
100 |
|
Exam Cost |
$177 |
|
Passing Score |
73/100 |
|
Exam Format |
Multiple Choice |
Note
A securities license's prominence and esteem also aid in developing your clientele. A security license will advance your career regardless of how experienced you are or how new to the field you are.
Conclusion
The US futures market is established and highly regulated.
All industry members must adhere to the guidelines strictly; otherwise, the regulatory bodies will harshly penalize them. Passing several relevant exams is the first requirement for future-related activity in the US.
There are many different kinds of securities qualification exams, depending on the type of business you are in. Some companies have two paths to choose from:
- SIE + S6 + S63
- SIE + S7
Passing the qualification examination of these two combinations can obtain the qualification of Registered Representative (RR) and engage in the financial services provided by Broker-Dealer.
Obtaining an S65 (or S66 based on SIE+S7) can obtain the qualification of Investment Adviser Representative (IAR), and the business attribute is the financial service provided by an Investment Adviser.
There are also many financial certificates, and the above can only be briefly introduced.
The market size of the financial industry is considerable, and the types of financial products are very diverse. Obtaining the certificates mentioned above can already bring very comprehensive planning to customers.
Finally, I would like to remind all of you. For all information, please refer to the official website to find the most real-time and accurate information.
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:


or Want to Sign up with your social account?