Asset-Backed Commercial Paper (ABCP)
A type of commercial paper that is collateralized by financial assets like marketable securities
What Is Asset-Backed Commercial Paper (ABCP)?
Asset-Backed Commercial Paper (ABCP) is a type of short-term financial instrument secured by tangible assets, typically marketable securities. Major financial institutions issue ABCPs, and they are considered secure investments, attracting lower interest rates. The collateralization of these papers allows for the potential recovery of dues by selling the underlying financial assets.
The underlying assets (receivables) might include payments that the corporation expects to collect from advances it has made, such as customer credit card balances outstanding, personal loans, home loans, student loans, etc.
On the other hand, standard commercial papers are a different category. They are unsecured short-term money market instruments with a maturity of up to 270 days. Promissory notes, issued by highly rated corporate borrowers like banks and large public companies fall under this category. These are typically used to address short-term financing needs and lack backing by specific assets or collateral.
Commercial papers are issued at a discount from their face value and are redeemed at face value upon maturity. The difference between the issuing price and the face value represents the interest earned by the investor. These instruments are favored by highly credit-worthy companies, carrying a low risk of default.
The interest rates on commercial papers are generally lower than those on bonds due to their shorter-term nature. The maturity period influences the interest earned, with longer periods correlating to higher interest rates.
Key Takeaways
Commercial Paper vs. ABCPs
Commercial paper is a form of short-term, unsecured debt typically used by businesses to finance inventories and short-term obligations. Maturities are limited to 270 days.
ABCPs, on the other hand, are a type of commercial paper backed by a range of financial assets' potential future cash flows. The entity that formed the ABCP program uses the securities issued under the ABCP program to fund its short-term needs up to 180 days after issuance.
As discussed, the primary difference between both is that the ABCPs are collateralized, backed by the company's receivable assets; on the other hand, any assets do not back standard commercial papers.
As the standard commercial papers are not backed and are only issued with excellent credit ratings, a recognized credit rating agency will be able to make investors invest in their commercial papers at a reasonable price.
To enhance liquidity, a company or a financial institution may sell receivable assets to conduits/SPVs, which in turn issue them to their investors as asset-backed commercial paper.
The originator is expected to pass over the expected cash inflows from the receivables to the SPVs/conduits responsible for disbursing the funds to ABCP noteholders.
Important Considerations
ABCP is often issued through an asset-backed commercial paper program, such as a conduit or structured investment vehicle, and has a maturity between one and 270 days (on average 30 days) from the date of issuance (SIV)
A sponsoring financial institution creates a conduit. A conduit's sole function is to acquire and hold financial assets from various asset sellers.
Selling asset-backed commercial paper to outside investors like money market funds or other "safe asset" investors like retirement funds allows the conduit to finance the assets.
Apart from these features and characteristics, below are some aspects that should be considered when evaluating ABCPs.
Structure
The structure of ABCPs is based on the issuance, requirement, placement, and investors. The issuance can be either a single seller or a multi-seller. A multi-seller comprises a pool of sellers, which lowers risk through diversification.
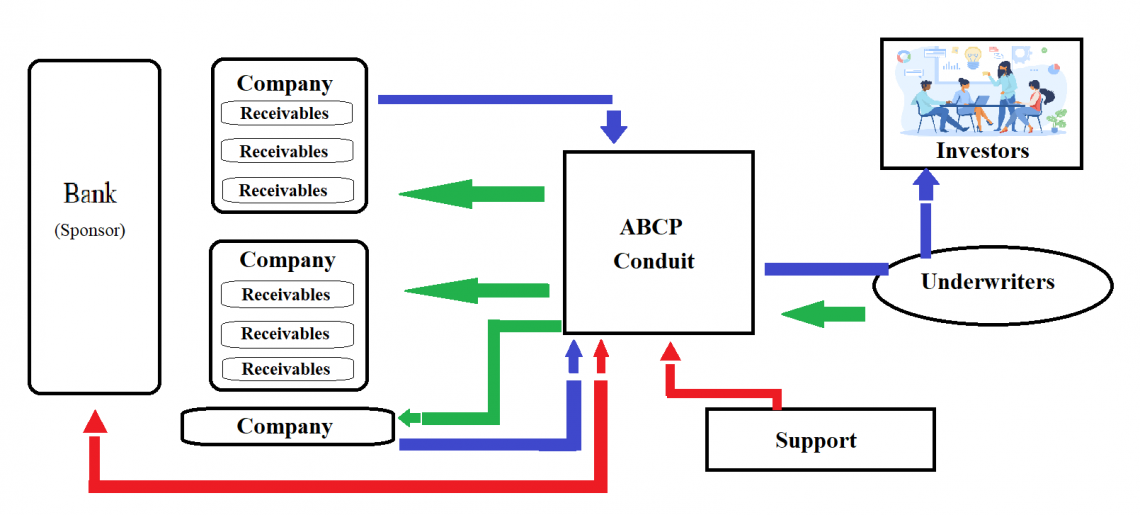
Multi-sellers usually adopt credit enhancement where a sponsor, a third-party bank, or a financial institution provides cash reserves or guarantees. A liquidity provider is also involved in issuance by providing the funds to meet the ABCP payment obligations under certain specified situations.
Investment banks usually do placement agents. They provide the required instructions for issuance and selling ABCP to investors as prescribed and rules & regulations laid down by the appropriate authority. There might be more than one investment banker involved in the process.
Investors pay for investing in these by ABCPs to conduits, and the conduits repay the investors through the placement agents. The repayment to the investors is collected from the principal or interest from the underlying assets.
Till the fulfillment of obligations of the investment, the sponsoring financial institution that is set up as the conduit monitors the development that could affect the performance and credit quality of the assets in the SPV.
Their primary task is to ensure that the investor receives their interest payment with the principal amount on the maturity, take over the necessary decisions, and analyze the assets from time to time to look at the quality and credit rating of the receivables.
Interest payments made to investors originate from the pool of assets backing the security; on maturity, the investors receive their interest payment with their principal amount invested in the security.
Sponsors (Financial Institutions)
The sponsors play two major roles:
- Manage Assets and
- Provide liquidity
Sponsors range from large U.S. commercial banks to non-bank institutions, like mortgage lenders and asset managers. Large US banks have long sponsored ABCP programs; some smaller U.S sponsors a modest share.
Foreign banks also sponsor a substantial share of ABCP; in 2007, it was around 40%. Such programs' non-bank institutional sponsors grew more rapidly than other programs doubling the assets participated by non-bank institutions.
A few largest sponsors are as follows-
Advantages Of Asset-Backed Commercial Papers (ABCPs)
The benefits of this specific class of commercial cards include their ability to provide liquidity in the short term at low risk (by the very nature of a short-term instrument). They are also more secure than conventional commercial papers because the latter lack assurances.
1. More liquid
These commercial papers are more liquid in the market as they provide more security and thus lower risk. In the short term, these liquidities are high from 90 to 270 days, which is easily convertible to cash as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Also, sellers are flexible with the terms of financing and the amount of ABCP conduits/SPVs and are adjustable to the amounts sold with the change in the financing needs.
2. Short-term debt instrument
These are short-term instruments of not more than 270 days of maturity which makes it easy for wider segments of investors to invest in and smaller ones to gain from surplus short-term excess funds.
3. Safer
Commercial Papers are issued by large and highly credit-worthy corporations, which bring high security but are unsecured. This limitation is waived by ABCPs, which are secured and safer than standard commercial papers.
4. Extra protection
The structure provides extra protection to this promissory note to investors. The Special purpose vehicle hired for the issue of CPs isolates the collateral assets from the asset seller's bankruptcy risk.
Disadvantages Of Asset-Backed Commercial Papers (ABCPs)
On the other hand, the nature of the financial assets put up as collateral is one of the key issues. Some of the disadvantages are as follows:
1. False sense of security
Sponsors of ABCP conduits/SPVs sometimes develop a false sense of security and may end up not adhering to strict and inflexible lending standards applied to them if the loans were on their balance sheet.
2. Increasingly Leveraged
During the 2008 Financial crisis, it was seen that companies highly leveraged their assets for issuing illiquid, hard-to-value, long-term maturity, or even unsecured assets like personal loans and credit cards outstanding of consumers, which are assets of banks as underlying collateral.
Disruptions in these unsecured assets and highly leveraged banks make these ABCPs junk and unrecoverable is one of the reasons for the 2008 financial crisis and huge losses for the investors and banks for leveraging it in an ungovernable manner.
3. Market Disruptions
These securities are backed by underlying assets, which are subject to market fluctuations. During the disruption, these assets might lose their value, and the underlying assets used to secure these securities lose their significance.
Under these conditions, investors lose their position in the ABCPs and are riskier than other traditional lenders and unsecured commercial paper, even though they are asset-backed.
4. Lower Credit Score
As the companies mortgage their assets to issue these commercial papers backing their securities, a lower credit-rated company might be issuing such promissory notes than a highly credit-rated company issued standard commercial papers.
This increases the risk of short-term bankruptcy of the company for not fulfilling the payment obligations. Winding up assets to recover the amount due might cause a shortfall and, thus, losses to the investors.
Concerns About Asset-Backed Commercial Papers (ABCPs)
An ABCP's collateral assets' nature and quality play a significant role in determining credit risk. The credit enhancement facility also influences the overall credit risk of an ABCP program in addition to the collateral.
1. Nature and quality of Underlying Asset
The nature and quality of collateral assets of an ABCP determine the credit risk. Usually, these ABCPs are a pool of multiple asset sellers and different types of assets, which helps in diversification and attaining the benefit of it.
Using various risk weights, different classes and risk assets are pooled to reduce the chances of market disruptions and lower the risk associated with the CPs.
2. Credit Enhancement facility
The credit risk of an ABCP program is also based on the credit enhancement facility to maintain the credit and improve upon it. Complex terms in credit enhancement contracts make it more difficult to assess the overall risk.
Issuing companies do this to have better terms for repaying their debt and reduce the risk to the investors of specified structured products in the financial market.
3. Mismatch in Cash Flows
The timing mismatch between cash inflows from the receivables of underlying assets and the payment obligation to ABCP investors is a major concern. Wide gaps and improper analysis may lead to defaults and plunging in credit scores.
Collateral for ABCP should be used so that short-term as the payment to investors would have still not been received from the receivable in full. A short-term receivable removes this hindrance, and the creditor could fully pay out the investors on maturity.
Mortgages should not be used as collateral for ABCPs.
4. Risk aversion
ABCP has a major concern that the expected future receivables are packed and sold to investors in the secondary market, thus transferring the risk associated with those assets to investors buying in the secondary market, which these banks are not keeping up with the standards on risk assessment.
Special Considerations For Asset-Backed Commercial Papers (ABCPs)
Recently funding sources have been extremely diversified, including other debts in ABCPs, like medium-term notes, extendable commercial paper, and subordinated debt to provide credit enhancement.
An ABCP's collateral assets' scale and nature play a significant role in determining credit risk. Although diversifying is an advantage of a pool with multiple asset sellers and various asset kinds, it can be particularly challenging to evaluate the risk for a distinctive or complex asset composition.
ABCP has major concerns about the possibility of high liquidity risk. As discussed earlier, if the value of underlying assets decreases, it imposes a great threat to safety, and the value of the ABCP might also suffer.
This makes it impossible for investors, especially small and retail investors, to understand the safety and how to value underlying assets that were affected due to market distress.
The credit enhancement facility of an ABCP program affects its overall credit risk and collateral. Additionally, it is more challenging to evaluate the overall risk due to the credit enhancement contract's complex conditions.
During high inflation in most developed and developing nations, it is difficult to know whether their investment interest is desired or not to gain in real money value terms.
Present Scenario Of ABCPs
As of now, inflation has crossed 8.6% in the U.S., which is among the highest in the world and which is 40 years high, as per Bloomberg in the CPI report. The U.S. economy has not faced such inflation in 40 years. The outcome of this would be disastrous with the signs of recession.
The Fed has constantly raised the repo rates and, in the last meeting, only raised the interest rates by 50 basis points. With increasing rates and rising inflation, the U.S. economy is facing a recession and has already reported a decline in GDP for Q1 2022.
The Q2 results will be crucial for the economy’s further prediction. Also, as huge as the U.S. economy is, a recession in the U.S. economy will have devastating results on the world economy, especially for developing and manufacturing countries.
Due to the current scenarios, the investors are speculative over the ABCPs and weighing the risk of it as the economic recession would mean a big disruption in the market and especially in the underlying assets of these debt instruments.
The rate increases have further increased to 5-year treasury bills, which have soared to 3.25%, making them more attractive to investors as these can provide them the safety for their investment and guarantee interest during such times.
This is reducing investments in these securities over the risk of market disruptions and losses, increasing the cost of acquiring these funds and only being issued by really large and credit-worthy corporations that, too, at a higher cost.
Researched and authored by Aman Bansal | Linkedin
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:





or Want to Sign up with your social account?