Macaulay Duration
It measures the weighted average time for an investor to recover the initial investment in a bond through its cash flows.
What is Macaulay Duration?
Macaulay Duration, often referred to as duration, is a significant principle within fixed-income investments. It computes the length of time, based on bond prices and nominal interest rates, needed to recover the initial investor outlay from a bond via the periodic cash inflows.
The idea was first put forward by Frederick Macaulay back in 1938, and what was invented back then became hugely important for the market as it allows us to understand the behavior of bonds in the given context of the interest rates changes.
In order to find the duration, weighted averages of cash flows are considered, and then the weighted sum of averages is taken out, which in turn will lead to the final answer.
Stated another way, the weighted mean duration of investment includes both the coupon payments and the return of the principal plus accrued interest, which happen at the date of maturity.
The metric is expressed in years, offering investors a time-related benchmark for evaluating and comparing different bond investments. An important aspect of this measure involves its inverse relationship with interest rates.
In the case when the rate of interest rises, the value of the future cash flow is lowered, and as a result Maturity Duration time is shortened.
On the contrary, a cut in the interest rate increases the value of uncertain future revenues and has the effect of lengthening the duration.
To succeed in portfolio investing, the sensitivity of assets to various rates is a fundamental element to appreciate. Analyzing maturity for bonds and bond portfolios helps gain perspective on the level of price movements that may arise due to changes in underlying interest rate.
Macaulay Duration, an important bond characteristic, is used by institutional & retail investors when they are trying to determine risk of debt securities due to interest rate changes. The actual formula is an awesome tool to use for investors in case of bonds to determine profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Macaulay Duration measures the weighted average time for an investor to recover the initial investment in a bond through its cash flows.
- Macaulay Duration has an inverse relationship with interest rates, resulting in a lower duration as interest rates rise and a higher duration as rates fall.
- Macaulay Duration aids in managing interest rate risk in bond portfolios. It allows investors to assess potential price changes in response to fluctuations in interest rates, enabling them to tailor their investment strategies accordingly.
- In bond immunization, Macaulay Duration is crucial for matching portfolio duration with an investor's time horizon. This minimizes the effects of interest rate changes, maintaining a stable financial position by balancing capital gains and losses.
Understanding Macaulay Duration
Macaulay Duration helps the investor understand how long it would take to recover their initial expenditure through a bond’s cash flows with an average weightage.
This metric goes beyond the scope of a plain yield by providing an all-encompassing judgment on the responsiveness of a bond to changes in interest rates.
Understanding this concept fully means that there is a proper comprehension not only of its calculation but also of the potential consequences it presents to investors navigating through the evolving terrain of fixed-income markets.
Here are the key aspects of Macaulay duration that you should be mindful of:
1. Time-Weighted Average
It calculates the time-weighted average of a bond's cash flows, including both coupon payments and the return of principal at maturity. This nuanced approach distinguishes it from other yield measures.
2. Interest Rate Sensitivity
This metric stands as a dependable indicator of a bond's responsiveness to shifts in interest rates. Grasping this intricate relationship is paramount for investors who anticipate market fluctuations and seek to adeptly navigate and manage interest rate risk.
Note
By comprehending how the metric reflects sensitivity, investors can strategically position themselves in the dynamic landscape, making informed decisions to mitigate potential risks and optimize returns.
3. Inverse Relationship with Rates
Macaulay Duration exhibits an inverse relationship with interest rates. With rising interest rates, the present value of future cash flows decreases, leading to a shorter Macaulay Duration. Conversely, when rates decrease, the duration lengthens.
This characteristic functions as a compass for investors adjusting their portfolios to evolving interest rate environments.
4. Portfolio Optimization
This metric enables investors to refine their bond portfolios. By assessing the duration of individual bonds and the overall portfolio, investors can align their holdings with risk tolerance, investment horizon, and market expectations, optimizing their overall investment strategy.
5. Risk Management Tool
Macaulay Duration is a significant risk management tool and plays one of the most important roles in helping investors make an educated choice about their fixed-income investments.
Note
Macaulay Duration helps investors measure and reduce the risk of changes in interest rates, making their strategies for managing risk more effective.
First of all, this tool allows them not only to predict but also to manage adequately the possible changes in prices due to fluctuations of interest rates on the market so that their investment portfolio becomes even more robust.
In the field of bond investment, it serves as an informative manual for investors looking to gain a full picture of their holdings.
By concentrating on the concepts of time-weighted averages and bond interest rate sensitivity, it presents investors with a broad picture.
This comprehensive position allows investors to strategically approach the market making decisions that mesh perfectly with their financial goals.
How to Calculate Macaulay Duration
Macaulay duration is a way of measuring the average time it takes for a bond to pay back its original cost through the total present value of received cash flows.
This calculation considers the time based on weights and provides insights into the relationship between the bond's cash flows and the market price paid for the bond at the current moment.
To calculate it, add up the products of the present values of cash flows and their respective time periods, then divide the sum by the market bond price. The formula is as follows:
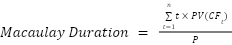
where:
- PV(CFt) is the present value of cash flow (coupon) at period t,
- t is the time period for each cash flow,
- n is the total number of periods to maturity,
- P is the market bond price.
Macaulay Duration is often used in bond immunization strategies. It has a positive correlation with the time to maturity and an inverse correlation with the bond's coupon rate and interest rate.
In contrast, modified duration gauges how a bond's price reacts to fluctuations in interest rates.
Example of Macaulay Duration
Suppose you have a bond with the following characteristics:
- Face value (N): $1,000
- Annual coupon payment (CF): $80
- Yield to maturity (r): 6%
- Time to maturity (n): 5 years
- Current price (P): $950
Remember the present value of a bond is just the present value of all its cash flows, this includes the final face value. In this example, the present value of the bond is $1,084.24.
Create a table to organize the cash flows, present values, and weighted present values for each period.
| Period (t) | Cash Flow (CF) | Present Value (CF)[CF/(1+r)^t] | Weight [PV(CF) / PV Bond] | Weighted Average of Time [t x Weight] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $80 | $75.47 | 0.070 | 0.070 |
| 2 | $80 | $71.20 | 0.066 | 0.131 |
| 3 | $80 | $67.17 | 0.062 | 0.186 |
| 4 | $80 | $63.36 | 0.058 | 0.234 |
| 5 | $1,080 | $807.04 | 0.744 | 3.722 |
| Total | 1084.24 | 1 | 4.343 |
The duration of this bond is 4.342 years. Investors would recover their initial investment over 4.3 years through the bond's cash flows. This measure assists investors in making well-informed decisions based on the time-weighted average of its cash flows.
Factors that Affect Macaulay Duration
Macaulay Duration is influenced by a few factors. Knowing these can help you understand how your bonds might react to changes in interest rates. Now, let's check out some of these important factors.
Yield to Maturity (YTM)
It works in opposite ways with YTM. When YTM goes up, the value of future money from the bond goes down, making the waiting time shorter, and the duration lower. Conversely, a lower YTM results in a higher duration.
Time to Maturity
Imagine "Time to Maturity" as the time you need to wait for a bond to pay up. The longer you wait to get the money, the higher the duration of the bond. It's like saying the longer you wait for something, the more important that future money becomes when we calculate things.
Coupon Rate
Imagine the coupon rate as the bonus you receive for owning a bond. If the bonus is big (higher coupon rate), it actually makes the waiting time for the bond's money shorter. This is because those larger annual bonuses play a big role in the bond's current value, making the overall time to get the money less when we do the math.
Frequency of Coupon Payments
Bonds with more frequent coupon payments, say semi-annual instead of annual, tend to have a diminished duration. This is due to the more frequent effects of compounding, lowering the present value of future cash flows.
Current Yield
Think of it as a simple comparison – the annual bonus you get from a bond compared to what it costs right now. Now, the Current Yield influences how long you have to wait for the bond's money. If the Current Yield is higher, it usually means you don't have to wait as long to get your money, making the waiting time, or duration, shorter.
Callable or Putable Features
Picture bonds with special features such as call or put options. The callable ones might have a shorter duration if there's a chance they'll be redeemed early. On the flip side, putable bonds could have a longer duration because they might stick around for an extended period.
Market Interest Rates
Think of it like this: when the interest rates in the market change, it has a ripple effect on how long you might have to wait for your bond's money.
When they rise, the waiting time for bond money shortens, lowering duration. Conversely, if rates drop, the waiting time lengthens, increasing duration.
Redemption Features
Bonds with features such as sinking funds or other redemption provisions can affect duration. Imagine having the option to say goodbye to your bond earlier than expected. This choice can shake up when and how much money you get, tinkering with the waiting time or duration.
Macaulay Duration And Bond Immunization
Macaulay Duration is super important when it comes to bond immunization. It's a tool that investors use to protect themselves from the danger of changing interest rates.
So, what exactly is bond immunization? Well, it's a strategy that investors rely on to ensure that if interest rates decide to climb or drop, their bond investments don't get too shaken up by the ride.
Investors aim to keep things stable so they can achieve their financial goals without getting too stressed out about the frequent shifts in interest rates that can occur in some areas.
Now, let's dig into how these two concepts, Macaulay Duration and Bond Immunization, are connected:
1. Bond Immunization Objective
The big idea behind bond immunization is to shield your bond collection from the twists and turns of interest rate shifts. But it's also about ensuring you hit your future money targets, whether saving away cash for retirement or paying off debts.
2. Implementation of Bond Immunization
Bond immunization is about ensuring the Macaulay Duration of your bond collection matches how long you plan to hold onto them. This way, how your bonds react to interest rate changes fits right in with what you aim for.
3. Duration Matching
When you pick bonds that match how long you plan to keep them, your portfolio can handle interest rate changes without messing up your ability to cover future money needs.
4. Reducing Interest Rate Risk
Bond immunization, with Macaulay Duration as its guide, helps lessen how much interest rate shifts change with your portfolio's value.
The plan is to set up an " immunized portfolio," meaning any gains or losses from interest rate changes balance out, keeping your portfolio's overall value steadier.
Note
By matching bond durations with Macaulay Duration, investors can reduce how much changes in interest rates affect their portfolio's value, ensuring it stays steady even when the market shifts.
5. Reinvestment Risk Consideration
When you're dealing with bond immunization, you should also think about reinvestment risk. That means you figure out what to do with the money you get from bond payments and when bonds mature.
You assume you'll put that money into new bonds at the rates that are around at the time. This is important for keeping your portfolio safe and steady over the long haul.
Macaulay Duration is like your trusty sidekick in the bond immunization game. It helps you set up your portfolio to match how long you want to keep your investments and what you're aiming to achieve financially.
When you line up the duration of your portfolio with your investment timeline, you can lower the risk of interest rates messing things up. Plus, it makes it easier to know what cash you can expect down the road, making your financial situation more predictable and solid.
The interested reader can check out this article, which considers whether Macaulay Duration provides the most cost-effective immunization method.
Comparing Macaulay Duration and Modified Duration
Both Macaulay Duration and Modified Duration are essential metrics for assessing how bond prices respond to fluctuations in interest rates. When you purchase a bond and provide a loan, you effectively become the bondholder.
These measures serve to gauge how a bond's value may fluctuate in response to potential changes in interest rates.
Macaulay’s Duration provides insight into the average period it takes to recoup the initial investment from a bond, factoring in both interest payments and the return of principal.
On the other hand, Modified Duration primarily focuses on the bond's sensitivity to changes in interest rates.
In simpler terms, Macaulay Duration offers a comprehensive overview of the repayment process, akin to tracing the entire journey of retrieving your investment.
Conversely, Modified Duration offers a more concise snapshot, emphasizing how much the bond's value could alter with interest rate shifts.
Both metrics are indispensable for bond investors, enabling them to assess risks effectively and make informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
Macaulay Duration aids in bond investing because it helps investors know when they'll get their money back from the bond payments. It's like a little helper to see how a bond will handle changes in interest rates.
To figure it out, you must do a bit of math, adding up all the cash you'll get and bringing this back to the present value.
You should get an overall measure in years.
This average takes into account both coupon payments and getting back your original investment when the bond matures, giving you a fresh perspective that goes beyond the usual ways of measuring gains.
Most importantly, this measure is closely linked to interest rates, making it necessary for investors dealing with unpredictable market ups and downs.
You should remember that a lot of things can affect Macaulay's duration, such as how much money the bond gives you, how many years until it's done, and what the interest rates are right now.
If you're an investor and you want to know how your bonds will act when interest rates change, it's important to know about these things and maybe adjust your investment accordingly.
The connection between duration and bond immunization shows how useful it is in managing risks. With bond immunization, you can adjust the duration of your bond collection to match up with how long you plan to keep your investments.
This helps reduce the risk of interest rate changes and keeps your financial situation more stable.
In the end, Macaulay duration is one of many tools investors can utilize to analyze their bond investment.
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:



or Want to Sign up with your social account?