Efficient Markets Hypothesis
The efficient market hypothesis (EMH) suggests that financial markets operate in such a way that the prices of equities, or shares in companies, are always efficient.
What Is the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)?
The efficient market hypothesis (EMH) suggests that financial markets operate in such a way that the prices of equities, or shares in companies, are always efficient. In simpler terms, these prices accurately reflect the true value of the underlying companies they represent.

The efficient market hypothesis is one of the most foundational theories developed in finance. It was developed by Nobel laureate Eugene Fama in the 1960s and is widely known amongst finance professionals in the industry.
There are many implications arising from this hypothesis; however, the main proposition is that it is impossible to “beat the market” and generate alpha.
What does beating the market or generating alpha mean? Broadly speaking, you can think of how much the return of your risk-adjusted investments exceeds benchmark indices.
For example, a proxy for the US market will be the S&P 500, which covers the top 500 companies in the United States or over 80% of its total market capitalization.
If your portfolio of investments generated an alpha of 3%, then it is considered that your portfolio outperformed the S&P 500 by 3% (assuming that you trade in the US market)
How is it possible that share prices are always efficient and reflect the actual value of the underlying company following the efficient market hypothesis?
It is because, at all times, a company's share price reflects certain relevant available information to all investors who trade upon it, and the type of information required to ensure efficient prices depends on what form of efficiency the market is in.
If you are interested in a profession surrounding capital markets, be it asset management, sales & trading, or even hedge funds, the EMH is a theory you need to know to ace your interviews.
However, this is only one topic in the diverse world of finance that you will truly need to know if you want to break into these careers. To gain a deeper understanding of finance, look at Wall Street Oasis's courses. For a link to our courses, click here.
Key Takeaways
- Developed by Eugene Fama, the EMH suggests that financial markets reflect all available information and that it's impossible to consistently "beat the market" to generate abnormal returns (alpha).
- The EMH has three forms: weak, semi-strong, and strong. Each form describes the extent of information already reflected in stock prices.
- Under this form, stock prices incorporate historical information like past earnings and price movements. Investors can't gain alpha by trading on this historical data as it's already "priced in."
- In this form, stock prices reflect all publicly available information, including recent news and announcements. Even with access to this information, investors can't consistently beat the market.
- The strongest form of EMH incorporates all information, including insider information. Even with insider knowledge, investors can't generate abnormal returns. However, some argue that real-world markets may not fully adhere to this hypothesis due to behavioral biases and inefficiencies.
Variations of the Efficient Markets Hypothesis
According to Eugene Fama, there are three variations of efficient markets:
-
Weak form
-
Semi-strong form
-
Strong form
Depending on which form the market takes, the share price of companies incorporates different types of information. Let’s go over what kind of information is required for each form of the efficient market.
Weak form efficiency
Under the weak form of efficient markets, share prices incorporate all historical information of stocks. This would typically cover a company’s historical earnings, price movements, technical indicators, etc.
Another way to look at it is that when a market is weakly efficient, it means - there is no predictive power from historical information.
Investors are unlikely to generate alpha from investing in a company just because they saw that the company outperformed earnings estimates last week. That information was already “priced in,” and there is nothing to gain trading off that information.
Semi-strong form efficiency
The semi-strong form of efficiency within markets is believed to be most prevalent across markets. Under this form of efficiency, share prices incorporate all historical information of stocks and go a step further by including all publicly available information.
This implies that share prices practically adjust immediately following the announcement of relevant information to a company’s stock.
What this means is that investors are not able to generate alpha by trading off relevant information that is publicly available, no matter how recent that piece of information became public.
This partially explains why you’ve probably heard those investment gurus tell you to buy the rumors and sell on the news.
One relevant example would be the reaction from every stock exchange worldwide on specific key dates surrounding the World Health Organization and the Covid-19 pandemic.
The market crashed following specific announcements because, at that time, the market anticipated lockdowns to occur, which would damage every company’s supply chain and sales.
If lockdowns did occur, companies wouldn’t be able to produce goods and services. Furthermore, customers wouldn’t be able to purchase goods, resulting in companies taking a hit on their earnings. And this was exactly what happened.
Although Covid was known since November 2019, If you look at the S&P 500 and the FTSE 100, they both crashed on the same date (21st February 2020), with the impact on markets being equally significant.
It would be safe to say that this was the date that the market started incorporating the impact of Covid-19 on a company’s share price. It is no coincidence that the World Health Organization also hosted a press conference that day.
You can look at the FTSE 100 and S&P 500 index, which represent the UK and US market conditions. The following images show the drop in benchmark indices due to Covid-19:
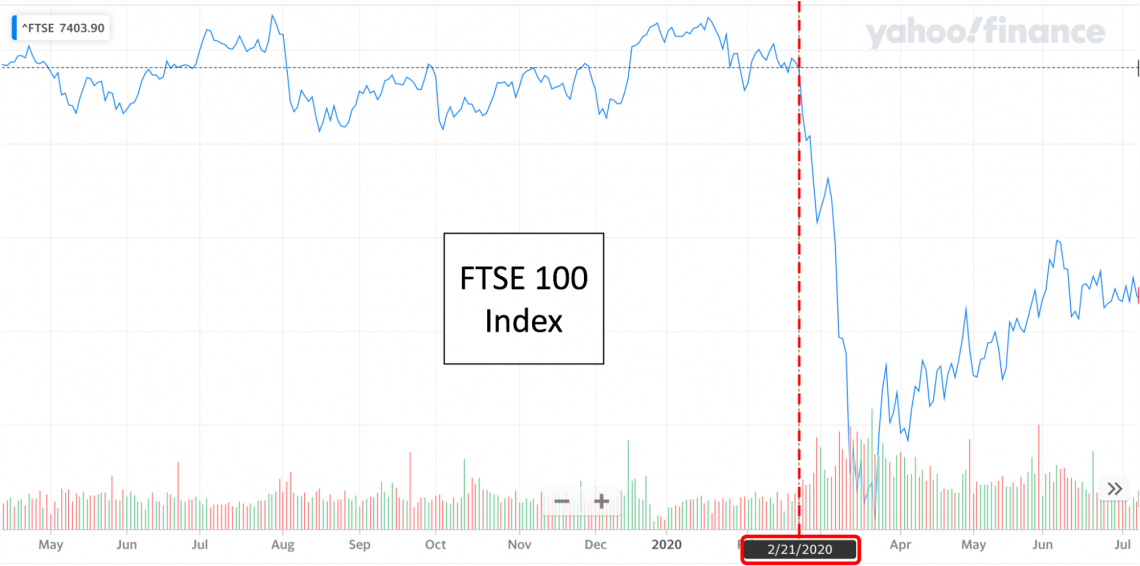
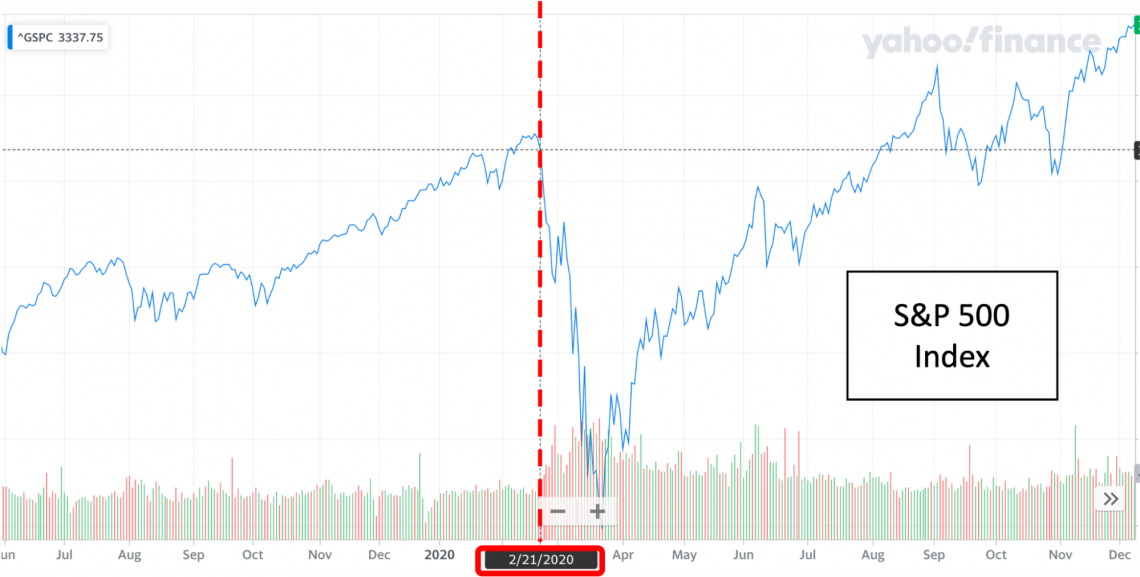
Unfortunately, there are a couple of caveats to this example.
In Eugene Fama’s purest depiction of the semi-strong form of an efficient market hypothesis, prices are meant to adjust instantaneously following the public announcement of relevant information, with the new prices reflecting the market’s new actual value.
When you look at the market’s reaction to Covid-19, the market crash happened gradually over a certain period.
Furthermore, if you look at the FTSE 100 and S&P 500, the index started showing signs of recovery immediately after the market crash.
Broadly speaking, there are two reasons this could have happened:
-
There was an announcement of new publicly available information with a positive impact on markets
-
The market had initially overreacted to the Covid-19 pandemic
An excellent example of newly announced publicly available information with a positive impact on markets would be something like the respective countries’ governments and central banks both promoting aggressive monetary and fiscal policies designed to improve economic situations.
Although it is impossible to say, and every investor will have a different opinion on the market, the consensus is that the market has reacted to monetary and fiscal policies. As a result, there was an initial overreaction to Covid-19 in the market.
This is where the practical example strays away from theory. In the market’s reaction to Covid-19, the impact of new information was gradual (but still quick) and argued to be inefficient at the trough.
However, Eugene Fama’s efficient market hypothesis anticipates rapid price movements following the release of public information, and prices are always efficient, moving from one true value to another.
Market indices that genuinely follow the semi-strong form efficient market hypothesis would look something like this:
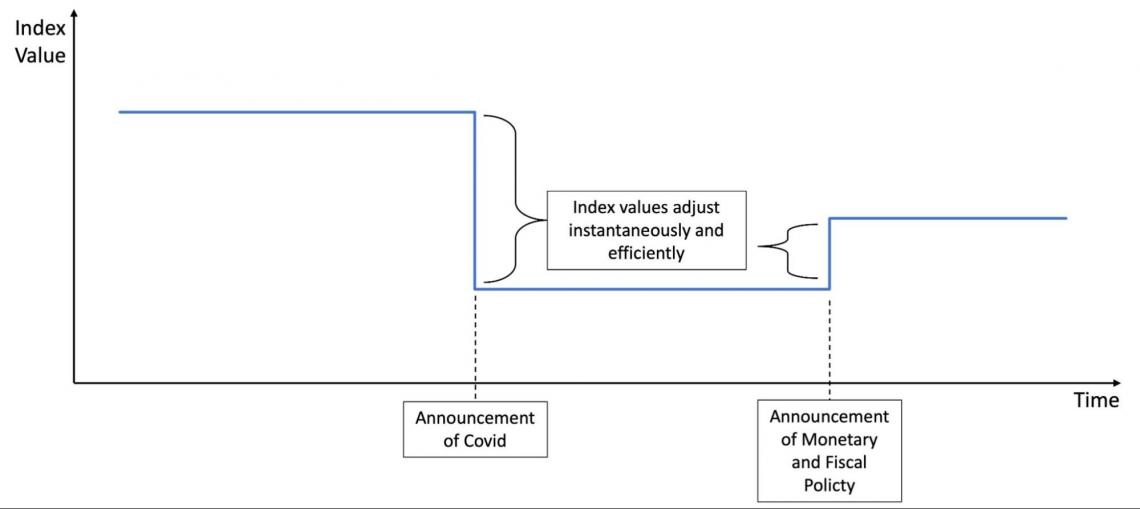
And this is what the true efficient market hypothesis envisions. There is no exaggeration in this graph, and the market index isn't expected to have any daily fluctuation because it reflects the valid, efficient value pricing in all the publicly available information.
Reaction to new relevant information is instant and accurate, leaving no room for values to readjust over time.
NOTE
This example applies to all forms of efficient markets, including the weak and strong forms. However, the difference is the type of information that will cause a company's share price to readjust.
Strong form efficiency
The share prices of companies in strongly efficient markets incorporate everything that the semi-strong form efficiency incorporates but go a step further by also incorporating insider information.
This implies that investors who know something about a company that isn't publicly known cannot generate abnormal returns trading off that information.
Generally speaking, you should expect more developed countries to have more efficient markets, mainly because more asset managers are analyzing stocks and more educated individuals make better investment decisions.
However, if any country were likely to display powerfully efficient markets, you would expect them to exist within more corrupt and opaque countries. This is because countries like the US and UK have implemented sanctions against insider trading purely because of how profitable it is.
Investors with insider information are known to have an edge in markets, which is why there are policies in place dictating that asset managers and substantial shareholders must disclose their trades to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Under Rule 10b-5, the SEC explicitly states that insiders are prohibited from trading on material non-public information.
In November 2021, a McKinsey partner was charged with insider trading because he assisted Goldman Sachs with its acquisition of GreenSky.
The Mckinsey partner had private information regarding the GreenSky acquisition and purchased multiple call options on GreenSky, profiting over $450,000.
Aside from the fact that the man was blatantly insider trading, the fact that he was able to profit off insider information is evidence that the US market does NOT possess strong form efficiency.

The above is somewhat considered to be proof by contradiction. If markets were efficient, trading off insider information would not let investors generate abnormal returns. But in this case, the Mckinsey partner could make almost half a million dollars!
To put that into perspective, $450 thousand is more than two years of the average investment banking analyst’s total compensation and slightly over four years of base pay.
Are capital markets efficient?
After developing a decent understanding of the efficient market hypothesis, the real question is: is the market truly efficient, and do they follow the EMH? This topic is controversial, and many individuals will support different sides of the argument.
Supporters of the efficient market hypothesis generally believe in traditional neoclassical finance. Neoclassical finance has been around since the twentieth century, and its approach revolves around key assumptions like perfect knowledge or rationality among individuals.
In fact, most of the material taught at university and in textbooks are materials that talk about neoclassical finance - one might argue that the world of finance was built by theories such as the EMH.
However, some of the assumptions in neoclassical finance have always been known to be overly restrictive and not at all realistic. For example, humans are not the objective supercomputers that neoclassical finance believes us to be.
The fact is that humans are ruled by emotions and subjected to behavioral biases. We do not act the same as everyone else, and it is absurd to believe that we all behave rationally or even have perfect knowledge about a subject before making decisions.
Some of the latest developments in academics have been surrounding behavioral finance, with Nobel laureates including Robert Shiller and Richard Thaler (cameo in a classic finance film titled The Big Short) leading the field and relaxing unrealistic assumptions in neoclassical finance.
Aside from being unable to generate alpha, another significant implication arising from the EMH is that investors can blindly purchase any stock in the exchange without any prior analysis and still receive a fair return on equity.
That does not make sense because if everyone did that, then it would be safe to assume that the share prices would be wildly inaccurate and far apart from the company’s actual value.
The fact is that there is some reliance upon financial institutions such as asset managers or arbitrageurs to constantly monitor and exploit inefficiencies within capital markets (such as buying underpriced and shorting overpriced equities) to keep the market efficient.
Therefore, another argument arising from this is the idea that markets are efficiently inefficient where money managers who use costly financial information software such as Bloomberg Terminal or FactSet can gain a competitive edge in the market.
These money managers generate abnormal returns by exploiting inefficiencies within markets, such as longing for undervalued stocks or shorting overvalued stocks. A beneficial outcome of this activity is that market prices are slowly shifting towards efficient values.
The biggest argument supporting the efficient market hypothesis is that many money managers cannot outperform benchmark indices such as the S&P 500 on a year-to-year basis.
That argument is further supported when you compare the average 20-year annual return of the S&P 500 to any hedge fund’s average 20-year yearly return. You will find that MOST money managers underperform compared to the benchmark.
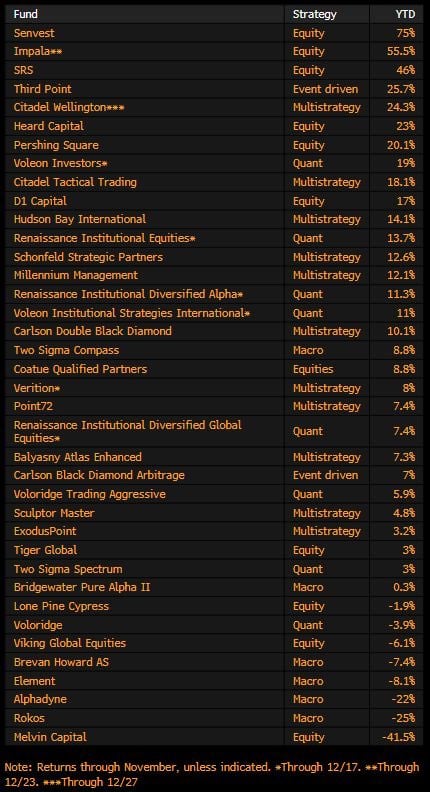
The table below displays the November 2021 return of the top hedge funds. For reference, the S&P 500 had a total return of 26.89%.
Therefore, if you compare the hedge funds to the S&P 500 (ignoring the hedge funds’ December 2021 performance), you can see that only three hedge funds outperformed the index.
Hedge funds are also costly, with many institutions imposing a minimum 2-20 fee structure where there is a 2% fee charged on the AUM of the fund and a 20% fee for any profit above the hurdle rate.
Nevertheless, while the data seems to point to the fact that hedge funds can be somewhat lackluster, a common argument is that the concept of a hedge fund is to “hedge,” which means to protect money.
Therefore, perhaps some hedge funds have a greater purpose of maintaining their AUM rather than growing it despite the fact that hedge funds are known for having the most aggressive investment strategies.
Overall, being a part of a hedge fund is still highly lucrative. For example, Kenneth Griffin, CEO of Citadel LLC, had total compensation of over $2 billion in 2021, whereas David Solomon, CEO of Goldman Sachs, had a total payment of $35 million in 2021.
If you want to make $2 billion a year in a hedge fund one day, you need to polish up your interviewing skills. To impress your interviewers, look at Wall Street Oasis’s Hedge Fund Interview Prep Course. For a link to our courses, click here.
Researched and authored by Jasper Lim | Linkedin
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:









or Want to Sign up with your social account?