Strategic Financial Management
It involves the long-term planning and management of an organization's financial resources to achieve its strategic objectives.
What Is Strategic Financial Management?
Strategic Financial Management (SFM) is planning, oversight, and management of an organization's financial resources to accomplish its long-term goals and objectives.

Strategic Financial Management involves aligning financial decisions with the organization's overall strategic direction, ensuring financial stability, sustainability, and value creation.
Effective financial management is essential for organizations to thrive and remain resilient in today's dynamic and competitive business landscape.
Organizations can chart a strategic course that supports growth, innovation, and market expansion by setting clear financial goals and developing comprehensive financial plans.
It involves analyzing the external environment, market trends, and industry dynamics to identify opportunities and mitigate risks.
Strategic Financial Management requires assessing the financial implications of various strategic options, evaluating investment projects, and aligning financial resources to capitalize on opportunities that align with the organization's vision.

Moreover, SFM plays a crucial role in managing financial risks and uncertainties. It involves developing risk management strategies to protect the organization from market volatility, credit default, liquidity challenges, and other potential threats.
Another aspect of SFM is optimizing the capital structure of an organization. This involves determining the appropriate mix of debt and equity financing to fund operations and investments.
By analyzing the cost of capital, capital markets, and the organization's risk appetite, strategic financial management enables organizations to strike a balance between financial leverage, cost of funding, and shareholder value.
Furthermore, it enhances decision-making processes across the organization.
It gives decision-makers fast access to reliable financial data, empowering them to analyze project viability, evaluate investment opportunities, and make decisions that align with the organization's strategic goals.
Key Takeaways
- Strategic financial management involves the long-term planning and management of an organization's financial resources to achieve its strategic objectives.
- SFM requires setting clear and measurable financial goals using frameworks like SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound).
- SFM includes developing long-term financial plans and budgets to guide resource allocation and capital investment decisions.
- SFM involves making strategic decisions related to capital structure, investment strategies, mergers and acquisitions, and other financial initiatives.
- SFM considers external factors such as market conditions, industry trends, and regulatory requirements when formulating financial strategies.
Features of Strategic Financial Management
Here are some key features of strategic financial management that contribute to running a business effectively:

1. Financial Planning
Strategic financial management entails creating thorough financial plans that complement the overall aims and objectives of the organization. This includes forecasting future financial needs, setting budgets, and establishing financial targets.
2. Capital Structure Management
Strategic financial management involves determining the optimal mix of debt and equity to finance the company's operations.
This entails determining the cost of capital, examining various funding options, and managing the business's capital structure to maximize shareholder value.
3. Investment and Project Evaluation
Strategic financial management involves assessing potential investment opportunities and evaluating the financial viability of various projects.

This entails performing cost-benefit assessments, estimating investment returns, and determining how best to distribute resources among various initiatives.
4. Risk Management
Strategic financial management includes identifying and managing financial risks that could impact the organization's performance.
This involves implementing risk management strategies such as diversification, hedging, and insurance to mitigate potential financial risks and uncertainties.
5. Financial Performance Analysis
Strategic financial management involves monitoring and analyzing the company's financial performance to assess its overall health and make informed decisions.
This includes analyzing financial statements, key performance indicators (KPIs), and financial ratios to evaluate profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and other important financial metrics.
6. Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
This includes conducting due diligence, valuing potential targets, negotiating deal terms, and integrating acquired companies to achieve synergies and enhance shareholder value.
7. Stakeholder Management
This involves effectively communicating with and managing relationships with various stakeholders, including shareholders, lenders, investors, and regulatory authorities.
This includes providing timely and accurate financial information, addressing concerns, and maintaining transparency to build trust and confidence.
8. Long-Term Financial Strategy
This includes setting financial objectives, formulating strategies to achieve them, and regularly reviewing and adjusting the strategy based on changing market conditions and business dynamics.
Strategic vs. Tactical Financial Management
Strategic and tactical financial management are two distinct approaches to managing finances within an organization.

While they are related, they differ in terms of their scope, focus, and time horizon. Here's an overview of the difference between strategic and tactical financial management:
| Strategic | Tactical | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Long-term goals and objectives of the organization | Short-term operational decisions and actions |
| Timeframe | Extended time horizon (e.g., 3-5 years or more) | Immediate or near-term (e.g., days, weeks, or months) |
| Scope | A comprehensive view of the organization | Specific areas or functions within the organization |
| Decision making | High-level and strategic decisions | Specific areas within the organization |
| Goal-setting | Setting overall financial direction and objectives | Implementing strategies to achieve the overall financial direction |
| Risk management | Assessing long-term risks and mitigation strategies | Addressing immediate risks and operational issues |
| Financial planning | Developing long-term financial plans and budgets | Creating short-term financial plans and budgets |
| Capital allocation | Determining the allocation of resources for long-term growth | Allocating resources for immediate needs and day-to-day operations |
| Performance metrics | Evaluating financial performance against long-term goals | Monitoring financial performance in relation to short-term targets |
| Decision hierarchy | Top-level executives and the board of directors | Middle management and operational staff |
Goal-Setting Process
When setting goals for strategic financial management, it is important to adopt a systematic and comprehensive approach. Here are two key approaches to consider: SMART goals, fast goals, and the integration of both approaches.
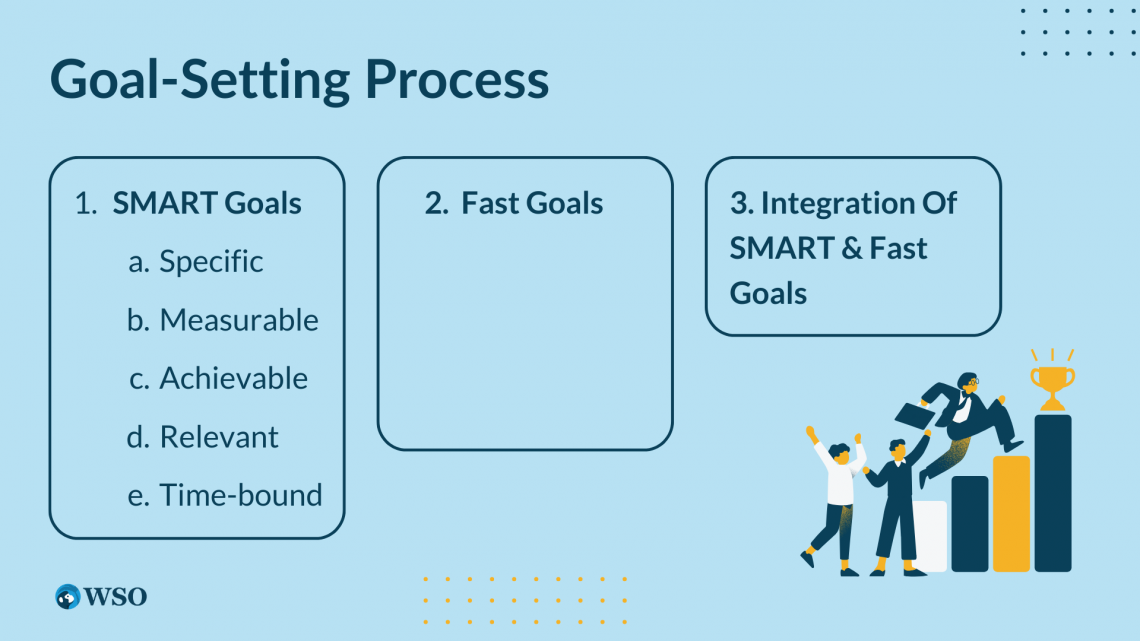
1. SMART Goals
SMART is an acronym that stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Let's break down each component:
- Specific: Goals should be precise and focused. Define your goals in terms of money, such as boosting sales by a given percentage or cutting costs in a particular region.
- Measurable: Establish concrete metrics to track progress and determine success. Quantifiable targets allow for objective assessment and enable you to make informed decisions based on data.
- Achievable:Goals should be realistic and attainable within the resources and capabilities of the organization. Assess the feasibility of your goals based on available resources, market conditions, and the organization's capabilities.
- Relevant: Align financial goals with the overall strategic objectives of the organization. Ensure that the financial goals contribute directly to the broader mission and vision of the company.
- Time-bound: Set a clear timeline for achieving your financial goals. Deadlines help create a sense of urgency and accountability. Breaking down long-term goals into shorter milestones can facilitate progress tracking.
2. Fast Goals
In addition to the SMART framework, organizations can benefit from adopting fast goals emphasizing speed, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
Fast goals are characterized by agility and flexibility, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changes in the business environment.
Instead of concentrating primarily on long-term goals, they involve defining short-term goals that can be accomplished within a few weeks or months.
Note
Fast goals encourage experimentation, learning, and iteration, allowing for rapid adjustments based on feedback and emerging opportunities or challenges.
3. Integration of SMART and Fast Goals
An effective approach is integrating the SMART and fast goal-setting methods. By combining the clarity and precision of the SMART framework with the nimbleness and adaptability of fast goals, organizations can strike a balance between long-term planning and short-term responsiveness.
Set overarching SMART goals that align with the organization's strategic direction, and complement them with a series of fast goals that can be adjusted and updated more frequently.
This approach enables organizations to maintain focus on long-term objectives while remaining agile in an ever-changing business landscape.
When setting goals for strategic financial management, it is advisable to employ the SMART framework for clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives.
Additionally, integrating fast goals can provide the flexibility and agility required to respond quickly to market dynamics and drive continuous improvement.
Benefits of Strategic Financial Management
Because it involves analyzing, planning, and controlling an organization's financial resources to effectively achieve its objectives, SFM has many benefits.

Here are some key benefits of strategic financial management:
1. Improved Financial Performance
The main purpose of strategic financial management is to optimize the allocation of financial resources for improved performance.
By effectively managing cash flow, budgeting, and investment decisions, organizations can maximize their profitability and generate higher investment returns.
2. Optimal Capital Structure
Strategic financial management involves determining the optimal capital structure of an organization. Capital structure is the complex structuring and balancing of debt and equity used to financially support a business's operations.
Specifically, it assists in achieving a balance between debt and equity financing while taking into account elements like capital costs, risk tolerance, and tax ramifications.
Maintaining an optimal capital structure can minimize the cost of capital and maximize shareholder value.
3. Risk Management
Strategic financial management incorporates risk management practices to identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks. It involves developing strategies to manage risks associated with market volatility, credit default, liquidity, and operational challenges.
Organizations can safeguard their financial health and protect their assets by implementing effective risk management measures.
4. Efficient Resource Allocation
Strategic financial management involves prioritizing financial resources to achieve strategic objectives. It helps allocate funds to projects or initiatives that align with the organization's goals and have the highest potential for returns.
This ensures efficient utilization of resources and minimizes wasteful spending.
Effective strategic financial management instills confidence among stakeholders, including shareholders, investors, lenders, and regulators. It demonstrates the organization's ability to manage its finances prudently, meet financial obligations, and generate sustainable growth.
This can lead to improved access to capital, better credit ratings, and increased investor trust.
Strategic financial management contributes to the organization's competitive advantage by optimizing financial decisions and resource allocation. Additionally, it facilitates strategic partnerships and mergers/acquisitions that can enhance market position and growth prospects.
Conclusion
Strategic financial management is a critical component of organizational success, encompassing various processes and practices that align financial goals with overall strategic objectives.

One of the key advantages of strategic financial management is improved financial performance. By effectively managing cash flow, budgeting, and investment decisions, organizations can maximize profitability and generate higher investment returns.
This leads to increased shareholder value and financial stability.
Strategic financial management also enhances decision-making by providing decision-makers with timely and accurate financial information. This enables informed assessment of investment opportunities, project viability evaluation, and identification of potential risks.
With better decision-making, organizations can make choices that align with their strategic direction and create long-term value.
Furthermore, strategic financial management contributes to the long-term sustainability of organizations.

By aligning financial management practices with strategic goals, organizations can adapt to changing market conditions, manage risks effectively, and seize growth opportunities. Essentially this attempts to ensure a business's resilience and longevity in a dynamic business environment.
The ability to optimize capital structure is another benefit of strategic financial management. By determining the right mix of debt and equity financing, organizations can minimize the cost of capital and maximize shareholder value.
This enables efficient utilization of financial resources and supports sustainable growth.
Effective strategic financial management also includes robust risk management practices. Organizations can identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks through proactive measures.
This helps safeguard the organization's financial health, protect assets, and maintain stakeholder confidence.
Furthermore, it enables efficient resource allocation by prioritizing financial resources based on strategic objectives. This ensures that funds are directed towards initiatives that align with the organization's goals and have the highest potential for returns.
All in all, strategic financial management, and more specifically efficient resource allocation, is necessary for optimizing organizational performance and minimizing wasteful spending.









or Want to Sign up with your social account?