Inflation Hedge
A term used by investors that protects their assets or investments from the threat of inflation.
What is an Inflation Hedge?
An inflation hedge is a term used by investors that protects their assets or investments from the threat of inflation. In times of high inflation, investors look for assets like gold to prevent losses from the devaluation of the purchasing power of money to keep their assets safe.
Over time, inflation drives up the price of goods and services in an economy. It is quantified as the rate of change over an extended period that results in a decline in the purchasing power of a unit of currency.
A security whose value you anticipate persisting or increasing over time, taking the impacts of inflation into account, is what you purchase when you invest in an inflation hedge.
Investing in a commodity whose value is anticipated to drop more gradually than the value of the underlying currency could also be meant by this phrase.
Hedging means establishing a contrary position in a comparable asset, investors can use the risk management technique of hedging to offset losses on their investments. Potential gains are often reduced as a result of the risk reduction offered by hedging.
Even though a certain investment can seem to have a respectable rate of return, if inflation is higher than average, the investment will eventually lose value.
Key Takeaways
- Investments that shield investors against the loss of buying power brought on by inflation are referred to as inflation hedges.
- During periods of inflation, it is anticipated that the investments' value will hold steady or perhaps rise.
- Inflation hedging is a strategy used by investors to safeguard the value of their holdings and keep overall operating costs to a minimum.
- An effective inflation hedge plan frequently relies on diversification and a long-term outlook.
How to Hedge Against Inflation
Over time, inflation reduces the value of money, which means that a given quantity of money loses purchasing power and will no longer be able to purchase the same number of products or services. The impact of inflation can reduce your investments' true value.
An inflation hedge looks for returns that are larger than the rate of inflation to guard against this deterioration, assist in maintaining the worth of your money, and guarantee that you may continue to buy the products and services you require and desire in the future.
An asset that will increase in value during inflationary times is the ultimate inflation hedge. However, it is important to recognize the fact that there is no single asset that is always inflation-proof.
To maintain low operational expenses during times when they anticipate rising inflation, many businesses adopt inflation hedges. Companies may be obliged to raise prices, reduce operating expenses, or accept lower profit margins as input costs rise.
For instance, rising prices for oil might be a result of inflation. For businesses in sectors with high fuel costs, like the aviation sector, this is a considerable expense.
To lessen the possibility of increases in the price of jet fuel, aviation businesses may even go so far as to purchase oil refineries. This indicates that they can create their fuel rather than paying market prices to obtain it from outside vendors. They might also just raise the cost of tickets.
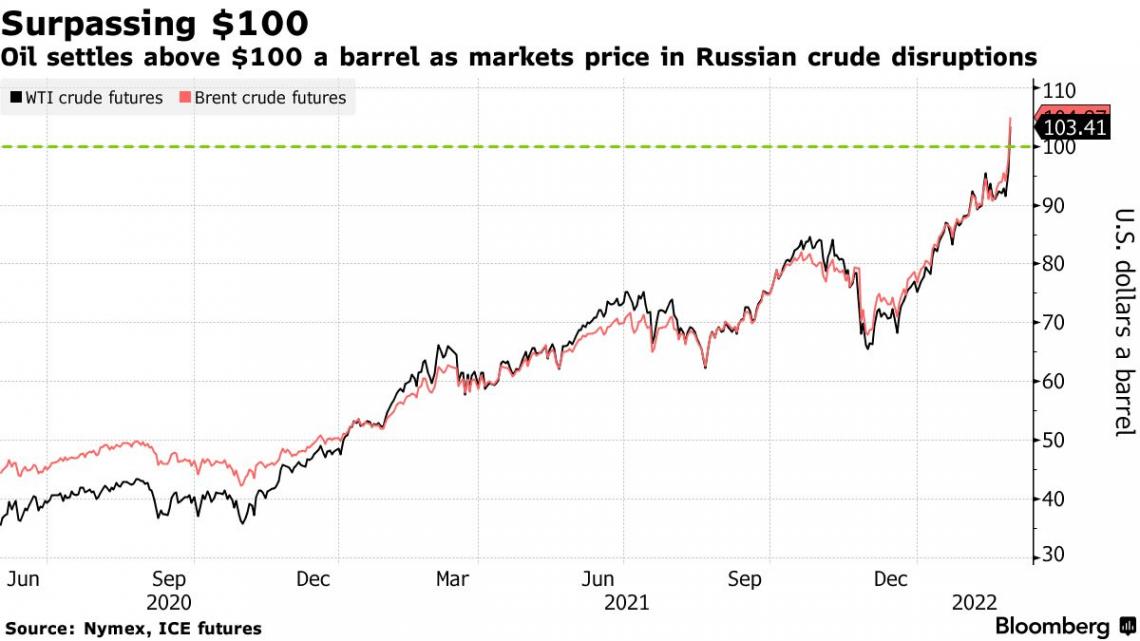
This image shows how oil prices rose in 2022. The main factors were production cuts by OPEC+ and the Ukraine war. These factors lead to a rise in inflation, causing panic in many countries, especially in the Eurozone.
Hedging Against Inflation
Implementing tactics and making investments that can help shield your wealth from the depleting impacts of rising costs is hedging against inflation. Here are a few practical strategies for protecting against inflation:
- Invest in Inflation-Protected Securities: Government bonds with an inflation protection feature are known as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS). Investors receive a real rate of return from these investments since their primary value varies along with changes in the Consumer Price Index.
- Portfolio Diversification: Spreading your investments over various asset classes helps lower risk. Consider including investments like stocks, real estate, and commodities that have historically served as inflation hedges in your portfolio.
- Investing in Real Assets: Actual assets, like commodities, frequently increase in value with high inflation. Purchasing real estate assets, such as rental properties or real estate investment trusts, can serve as hedges against price increases.
- Precious Metals: Silver and other precious metals have long been used as inflation hedges. When currencies are devalued, they often hold their worth. Consider setting up a portion of your portfolio for physical holdings in precious metals or metal ETFs.
- Stocks with Pricing Power: Increased production costs can be passed on to customers by businesses with strong pricing power. Such businesses, frequently found in industries including healthcare, utilities, and consumer goods, might act as a hedge against inflation.
- Inflation-Linked Bonds: Other than TIPS, some nations also issue inflation-linked bonds. These bonds offer interest payments that increase in line with inflation, protecting bondholders' purchasing power.
- Commodities: A hedge against inflation can be obtained through investing in actual commodities like oil, agriculture products, or precious metals and through commodity exchange-traded funds (ETFs). As the price of products and services rises, commodities frequently experience price increases.
- Foreign Currencies: A defense against home inflation can be obtained by investing in foreign currencies, particularly those of nations with lower inflation rates. However, fluctuating currency exchange rates are possible.
Which is a Better Hedge, Gold or TIPS?
Although gold and TIPS are both regarded as traditional inflation hedges, they couldn't be more dissimilar. Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, or TIPS, are inflation-protected bonds that are issued by the U.S. Treasury. Their face value is linked to the CPI and modified in accordance with shifts in the inflation rate.
Since TIPS (Treasury Inflation Protected Securities) also operate as a hedge against deflation and an economic slowdown or recession, they are currently far more appealing than gold.
Over extended periods, gold is said to maintain pace with inflation, but there is no assurance that this will be the case, particularly for shorter time frames. TIPS are based on fluctuations in the CPI, which overstates inflation over time.
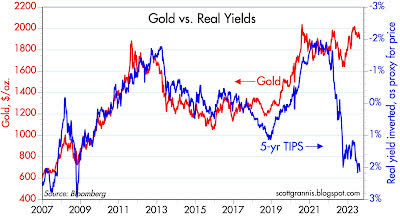
Gold and TIPS tend to correlate, but not all the time.
The recent spike in inflation has increased demand for gold to previously unheard-of heights. Real rates have risen dramatically in response to Fed tightening, but TIPS prices have fallen.
In a scenario of low and stable inflation (which is presumably what we are entering), gold is significantly more risky on the downside than TIPS.
If the Fed eases, TIPS' price potential could increase, and the amount that the Fed can tighten controls their downside risk.
High real rates represent a risk to the price of gold, and it seems likely that inflation will soon reach the Fed's goal level, if not lower.
TIPS are a hedge against deflation and recession since both will induce the Fed to ease, cutting real rates and driving up TIPS prices.
Since TIPS offers a real yield that is guaranteed by the government and has its principal regularly adjusted for inflation, they are a desirable and safe inflation hedge.
Inflation Hedge Benefits And Drawbacks
Investing in an inflation hedge to safeguard your assets and ensure returns on the hedge has several benefits. There are a few potential drawbacks to consider, though.
Since numerous factors besides inflation have an impact on any investment, there is no ideal inflation hedge. The returns on your inflation-hedging asset will not always rise with an increase in inflation, guaranteeing protection from inflation.
Every investment has its risk, which could lead to losses. Whether it's investing in commodities, gold, or any inflation hedge, the financial markets can change their course and move against you.
Cash, if kept on hand, will inevitably lose value over time. That is one of the factors that draws anyone with extra cash to stock market investment.
Some hedges include additional expenses, such as storage and maintenance, and they might not be liquid. Additionally, some hedges don't provide any income, which may make it harder for investors to cover continuing expenses.
Overall, when including inflation hedges in an investment strategy, careful thought and diversification are necessary.
Conclusion
Your money may be lost to inflation. Therefore, it's advisable to avoid retaining too much cash even though having a little on hand is helpful for financial security. If you do, you might discover that it simply doesn't purchase as much as it formerly did.
Hedging against inflation helps assess your finances as inflation rates rise and determine if there are any changes that can be made to better preserve your money. You can fight rising inflation by making investments in stocks, bonds, and other conventional investment vehicles.
Numerous choices are accessible if you want to research alternative investing. Whatever path you take, diversifying your portfolio can help you reduce the chance of losing money if one investment doesn't work out.
Investors constantly balance risk and reward in an effort to optimize growth while staying within certain risk parameters.
Along with all the other risk-reward components of investing, it is crucial to understand the consequences of inflation and the types of assets to consider or avoid.



or Want to Sign up with your social account?