External Analysis
It is the assessment and analysis of the world in which the organization operates
What Is External Analysis?
An external analysis, also known as environmental analysis, is the assessment and analysis of the world in which the organization operates.
An environmental analysis is a comprehensive study of all the external factors affecting the organization and its businesses. The environmental analysis enables the company to prepare a caution signal against the external elements the organization should be ready for.
This analysis is generally conducted to understand the extrinsic environment and how it affects the operations and execution. This is done since all businesses are in dynamic and ever-changing environments and are subjected to forces beyond the firm's control.
As the rain when you ride a bike. You can only accustom yourself and caution your riding of the bike according to the water-soaked road, and cannot change the rain. Similarly, an organization can only change and accustom itself according to the changing environment.
An organization's strategy should be well-equipped to answer such external forces.
When to execute an External Analysis?
External analysis should be executed before the strategic planning process. All the external factors affecting the business should be evaluated before the planning process because this will help the organization clear its vision and help understand its limitations.
Its industry and broader environment determine the specific external factors affecting the firm's strategy and business operations. Many external factors make up most of the firm's external business environment.
Some of the examples of the critical external business environment factors are:
- Legal and regulatory factors.
- Market forces.
- Industry trends.
- Competition.
- Technological changes.
- Stakeholder groups and their social concerns.
- Globalization trends, emerging markets, and non-government organizations.
Identify all the opportunities and threats from the external environment, along with understanding the intrinsic strengths and weaknesses of the organization. Also known as SWOT Analysis.
How is an External Analysis useful?
The external analysis aids the organization in improving the products and services along with strengthening the strategy to meet the needs of customers and stakeholders, both internal and external.
The environmental analysis helps to grow and proliferate business since it provides an analysis of the factors affecting business.
Management with these insights will take steps to mitigate the risk arising from the environment, accept the risk as it is, take precautionary steps necessary, or may accept the opportunity to generate profits.
External analysis is when you analyze the industry, market, or external environment changes that would impact the company's operations. Businesses and companies conduct an environmental analysis to keep up with the changes in the industry.
External analysis means examining the industry environment of a company, factors such as:
- Competitive structure
- Competitive position
- Dynamics
- History
On a macro scale, the external analysis includes
- Macroeconomic
- Global
- Political
- Social
- Demographic
- Technological analysis
Components of external analysis
External analysis is the detailed assessment of the factors and components that affect the business's performance and operation.
Some important external environment components are industries, supply chains, competitors, economic trends, and PEST analysis.
These components are the most crucial elements in environmental analysis.
The industrial analysis will help the organization understand the industrial trends and practices, whereas competitive analysis will aid in understanding the competition and their practices.
So on, economic trends identify the latest trends in the external environment. And each of these elements is to be analyzed individually.
Here is a detailed explanation of each element of external analysis.
1. Supply Chain
The supply chain collects people, organizations, information, resources, and activities involved in providing products and services to the ultimate consumer.
It's the most important external factor for analysis for manufacturing units because the supply chain starts right from the warehouses, where the raw materials are stored to deliver the finished products to the consumers.
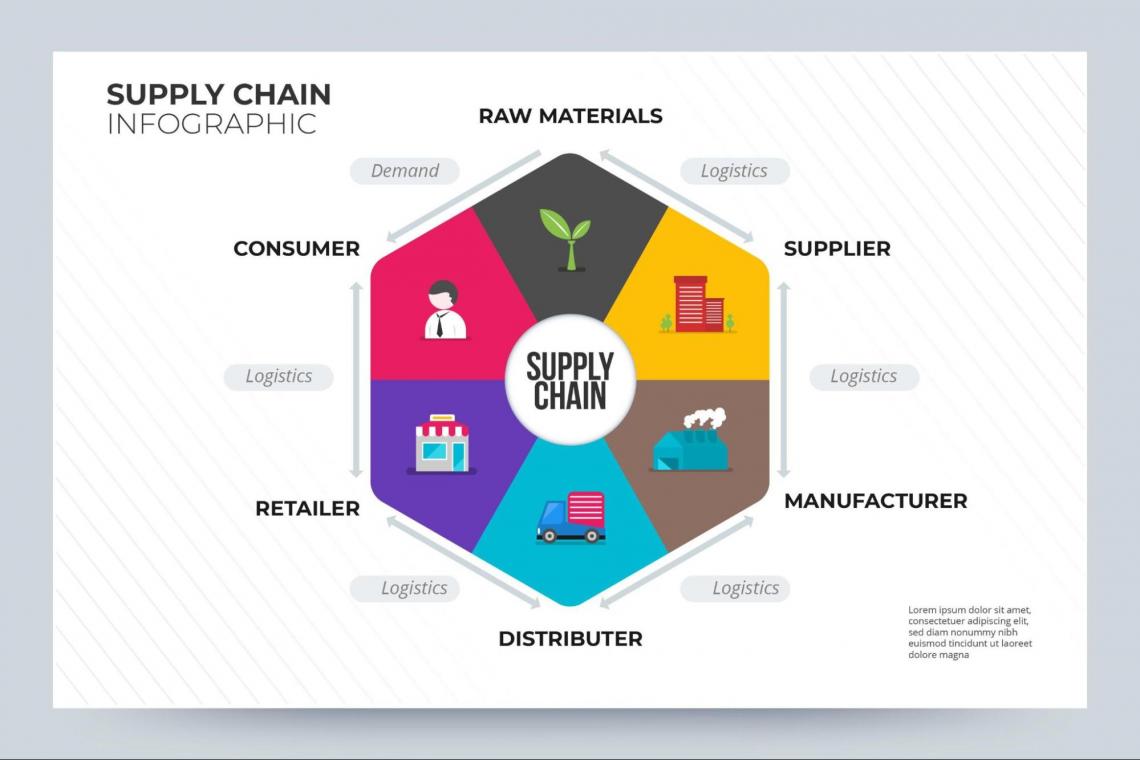
The organization must gain perfect knowledge about the cost of sourcing and procuring raw materials, the expenses involved in converting them into finished products, and the cost of delivering them.
With a strong understanding of the supply chain and the environment surrounding it, the organization can choose the right management techniques to help the firm integrate its activities, reduce costs, maximize profits, and ultimately satisfy customers.
JIT, lean manufacturing, MRP, and ERP are some supply chain and production methodologies.
2. Industry
Analysis of the industry facilitates understanding the company's position relative to other companies that produce similar products or services.
Understanding the forces in the industry is an important component of effective strategic planning.
Industry analysis enables business owners to identify the threats and opportunities facing their businesses and to focus their resources on developing unique capabilities that could lead to a competitive advantage.
An organization well-informed about the compliances in the industry can save itself from transgressing against the regulations for the industry's benefit.
Some industrial compliances include the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
An industrial analysis consists of three major elements:
- The underlying forces at work in the industry.
- The attractiveness of the industry.
- The critical factors that determine a company's success within the industry.
3. Economic Trends
Assessing and analyzing potential changes in economic trends such as interest rates, inflation, trading laws, and recession levels helps businesses adapt.
It helps business owners determine how these elements could affect how much they profit during a given period.
Recession, trading laws, inflation, interest rates, and regulations constitute the most critically affecting components in the external environment.
When you study economic trends, it helps you to find out how such factors would impact the profitability of the company.
4. Competitors/Competitive Analysis
Another component in the external environment is the competitor of the firm that poses a threat to the business. The competitors aren't just for healthy competition. They are the driving force and source of motivation for the organization.
The constant urge to do better than the competitors will help the organization improve its operations, management, and internal and external activities will help the company do better.
The competition is always a threat to the existing business in a healthy way, always up to launching new products, improving their operations, reducing costs and expenses, and maximizing their profits, finally capturing the market.
Focus on areas such as:
- Number of current industry competitors with similar products, prices, target audience, and overall company size
- Potential barriers to entering a new industry such as government laws, product saturation, or brand loyalty
- Acceptable pricing businesses can assign to goods that encourage sales while maintaining profit and staying on the same level as competitors.
- Effects that competitors' goods will have on another business's sale of the same type of goods.
- Results of complementary products or services on the business's success
Reviewing these factors on a business's industry competitors helps that business determine the best price points, alternative industries to pursue, measures to improve product quality & profitability, and marketing tactics to maintain a successful business.
From the strategic planning viewpoint, to gain a better and more informed understanding of the industry and competition, a thorough assessment of the competitive environment should be conducted, including the competitors the firm must face and the structure and/or boundaries of the environment.
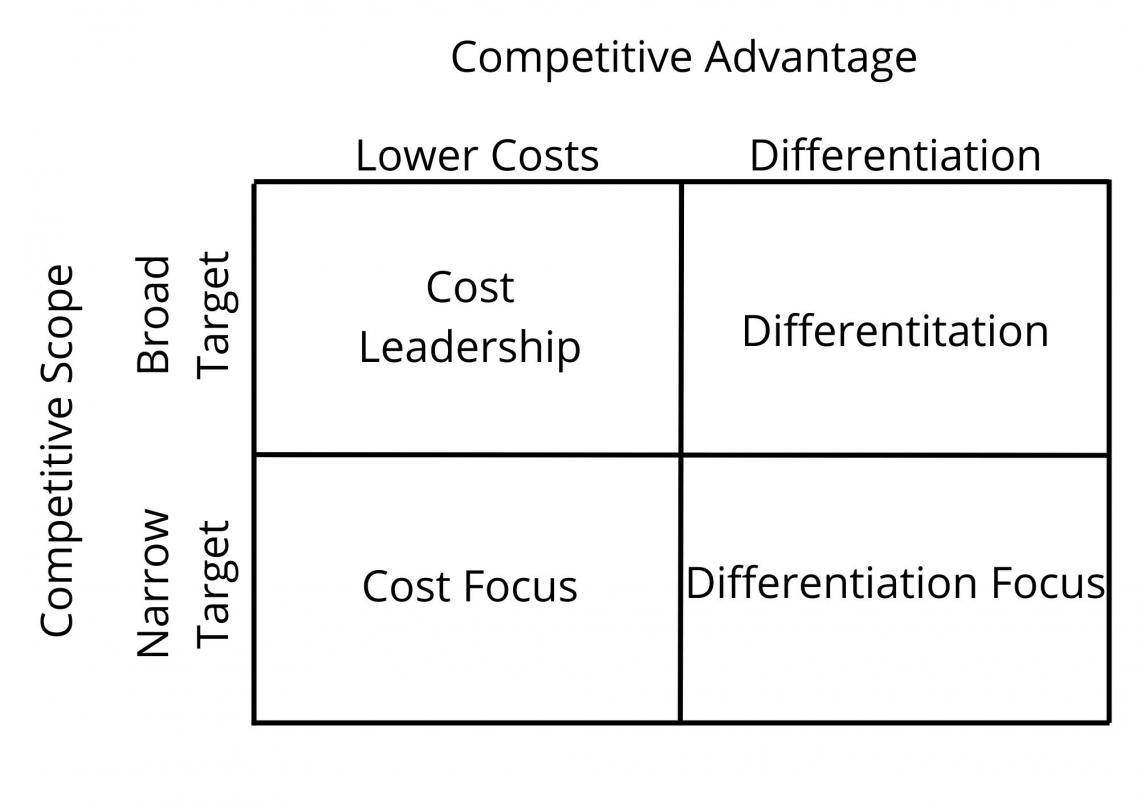
These are called Generic Competitive Strategies, formulated by Micheal Porter to gain a competitive advantage. These strategies are cost leadership strategy, differentiation strategy, and focus strategy.
Such extensive analysis will put the firm in a more advantageous position and gear it to take on several competitors that may merge and acquire the weak ones.
5. PEST Analysis
PEST stands for political, environmental, social, and technological. It's also known as STEP analysis. All the factors in the external environment are studied.
- Political factors: Laws, regulations, and trade barriers.
- Economic factors: Inflation, interest rates, and exchange rates.
- Social factors: Age, population, and income levels.
- Technological factors: R&D, new technologies, and tools.
An expanded version of the
exists named PESTEL analysis. Where "E" stands for environmental factors(environmental laws and environmental regulations) and "L" stands for legal factors limiting the business.6. ICEDRIPS Analysis
Another creative method to analyze the external components is the ICEDRIPS checklist. It's generally used to analyze the opportunities and threats in this fast-changing world.
Where:
- I = Innovations
- C = Competitors
- E = Economic factors
- D = Demographics
- R = Regulatory environment
- I = Infrastructure
- P = Partners
- S = Social trends
7. Porter's Five Competitive Forces
Business theorist Michael E. Porter has developed a model of the structure of industries, competition, and the external economic environment.
An analysis of the five competitive forces is conducted to determine long-term profitability, measured by long-term return on investment. This analysis includes an evaluation of the following:
- Basic economic characteristics of the industry
- Technical characteristics of the industry requirements
- The attractiveness of the industry
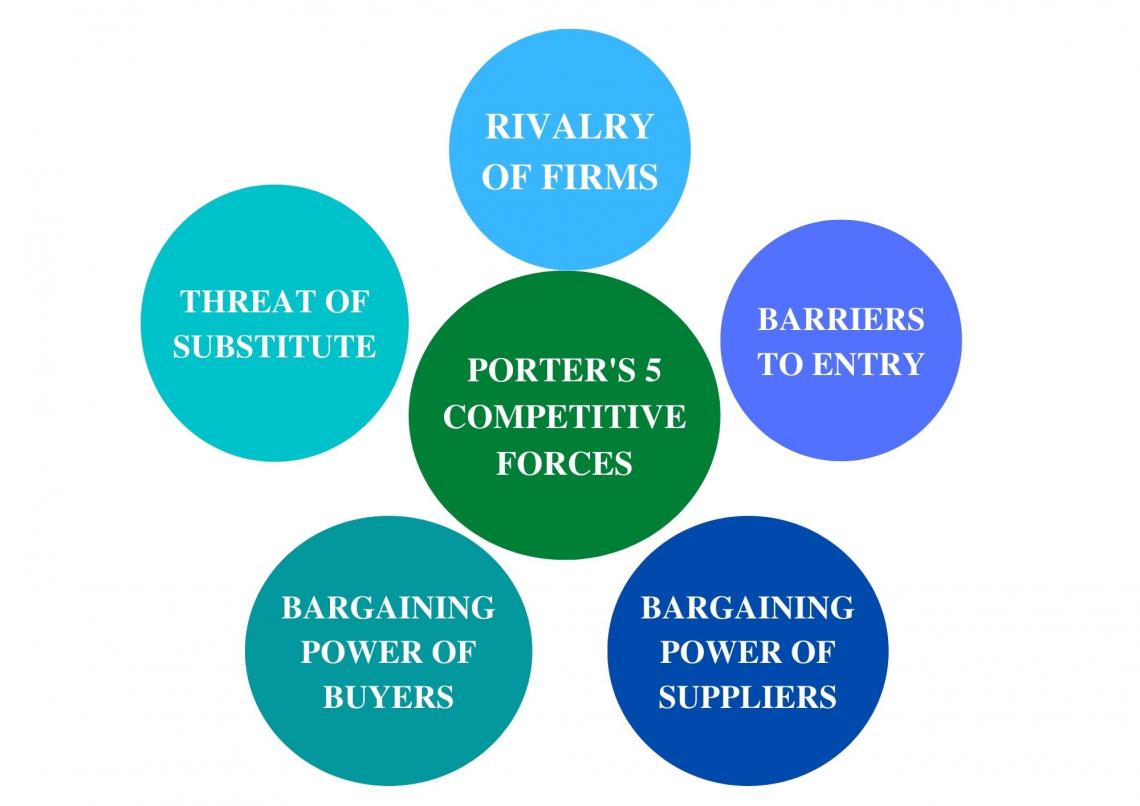
a. Rivalry among the existing firms
The intense rivalry between the firms exists, pointing toward strong competition. Price cutting, large advertising budgets, and constant introduction of new products are common.
The stage of the industry life cycle starts with rapid growth, growth, and maturity, ending with a decline or rapid decline.
It's characterized by less differentiation between products, high costs of switching, high amounts of fixed costs concerning variable costs, and economies of scale due to large-scale expansion.
The long-term profitability depends upon the barriers to entry in the industry.
Factors such as
- Economies of scale aren't significant
- Weak brand identity
- Low costs of switching to other suppliers
- Lower product differentiation
- Low capital requirements
- Low exit barriers
- Government subsidies
- No cost advantages of vertical integration
c. Threat of substitutes
The Threat of substitutes limits the price increases and the profit margins. The greater the Threat, the greater the chance of new entry and substitute, and the less attractive the industry is to potential entrants.
Considerations affecting the Threat of substitutes are relative prices, costs of switching to a substitute, and customer inclination to use a substitute.
d. Threat to buyers' bargaining power
As this threat increases, the industry's appeal to potential entrants decreases.
Buyers' bargaining power varies with the following factors:
- When purchasing power is in the hands of few buyers.
- High switching costs decrease buyers' bargaining power and vice versa.
- Threat to backward(upstream) vertical integration.
- Buyers are most likely to bargain aggressively when the profit margins are low.
- Buyers are in a stronger position with the supplier's product being differentiated.
- The most important material is to lower the bargaining power of the buyer.
e. Threat of suppliers' bargaining power
As the Threat of suppliers' bargaining power increases, the industry's appeal to potential entrants decreases. It affects the competition through pricing and the manipulation of the quantity supplied.
- Suppliers' bargaining power is greater when:
- Switching costs are substantial.
- Prices of substitutes are high.
- Threat forward (downstream) vertical integration
- When the input is value-adding by the buyer
- The industry is concentrated or organized
Buyers' best responses are to develop favorable and mutually beneficial relationships with suppliers or diversify their supply sources.
Benefits of the external analysis
The benefits of this analysis are numerous, offering insights that can guide the future direction and overall success of a company. Some of the benefits are:
1. The first benefit of external analysis is identifying the opportunities and threats from the external environment. Timely and adequate measures to answer the situation will help the firm optimize its income/financial statements, solvency, liquidity, and cash flow positions.
2. The management can prepare strategic plans that are well-informed, and the budgets are prepared after that. It is important to identify new opportunities and address the threats that have emerged or are likely to emerge soon.
3. Ensures the company remains cautious about the external environment and focuses on customers, potential customers, and competitors, as well as on the economic and political circumstances in which the business must operate.
4. external analysis makes companies more active in their operations. Aware of the competition and the industry trends, the firm can have the upper hand to be active and evolving in business operations. This helps the organization to grow its businesses and reap the benefits.
5. When a company conducts external analysis, it allows management to recognize potential opportunities that would help the company differentiate its offers from the competitors.









or Want to Sign up with your social account?